FDN2_SM_WK3_Histology Flashcards
Epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
What kind of tissue is this?

Stratified squamous epithelium

Match the arrows with the following:
Elastic fiber
Collagen fiber
Macrophage
Fibroblast


What kind of cell junctions attatch epithelial cells to each other in the middle of an epithelial layer?
Macula adherens junctions (aka desmosomes)
These are focal “spot welds”
What kind of tissue is D?

Smooth Muscle

What kind of tissue is this?

Skeletal Muscle

Suppose you know that a tissue’s main function is secretory… What kind of tissue is it likely to be?
Epithelial
What do Schwann cells look like in a cross-section of a nerve?
They have thin, wavy, purple nuclei on H&E stain
They are abundant
They will be arranged in rings around neurons
Where might non-keratinized epithelium be found?
Esophagus, oral cavity, vagina, anal canal
What is the most common type of collagen in the body?
Type I: It is found in skin, tendons, vasculature, organs, bone
Where in the muscle cell is troponin found?
Thin filaments of skeletal and cardiac muscle
What are the arrows pointing to?

Fibroblast nuclei

What kind of tissue is this?

Cardiac Muscle

What are satellite cells?
Glial cells in the PNS that surround ganglia (cell bodies)
What kind of tissue is this?

Cardiac Muscle

What are microglia?
Macrophages of the CNS; they ingest foreign material, debris, and organisms
What is a defining feature of epitheilum?
Cells are closely attached to one another
What is loose connectie tissue made from?
Many cell types; Lots of ground substance in between fibrils. High fat content
What are the 3 possible triggers for smooth muscle contraction?
- Sympathetic neurons innervate muscle, voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open -> causes release of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Stretch causes mechanosensitive Ca2+ channels to open -> causes relsease of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Surface hormone receptors respond to a chemical signal -> Second messenger opens channel in ER -> Ca2+ released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum binds to calmodulin, activates enzyme that phosphorylates myosin light chain kinase, myosin can now interact with actin
Which muscle types contain tropmyosin?
Skeletal, Cardiac
What is dense, regular connective tissue made from?
Parallel bundles of collagen
Where is reticular connective tissue found?
Kidney, spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow
How is collagen synthesized?
Procollagen is made in fibroblasts and released
3 procollagen fibers are assembled into a collagen fiber in the extracellular matrix
What does myelin look like under a microscope?
White space surrounding a neuronal axon (not visible on H&E stain)
May be able to see the nucleus of a Schwann cell
Appears black on an osmium stain

What type of epithelial cells are in this picture?

Simple cuboidal

Supppose this is a tissue sample from the colonic submucosa
What kind of tissue does each arrow point to?

1 - epithelial
2 - loose connective
3 - smooth muscle (surrounds the GI tract)

What kind of connective tissue is resistant to multidirectional forces?
Dense, irregular connective tissue?
What is an ependymal cell?
A type of glial cell in the CNS that produces cerebrospinal fluid.
They form the choroid plexus and line ventricles of the brain and spinal canal
What are glial cells?
Supporting cells in the nervous system
What is a node of ranvier?
A gap in the myeling sheath; An action potential can “jump” between nodes of ranvier
Where is keratinized epithelim found?
Skin
What is dense, irregular connective tissue made from?
Woven collagen fibers with some elastin
What is a dendrite?
Where the cell body receives information
What are the 4 main types of tissue?
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
Adipose
What kind of cells produce myelin?
Oligodendrocytes in the CNS
Schwann cells in the PNS
What kind of tissue is A?

Cardiac Muscle

What kind of tissue is this?

Smooth muscle (uterus)

Which thin filaments are present in all three muscle types?
Actin, Tropomyosin
What is the arrow pointing to?

A reticular fiber

Nuclei from which cells make up the majority of visible nuclei in a cross-section of a neuron?
Schwann cells;
What are some characteristic features of dense, regular connective tissue?
Resistant to lengthening
Dark pink on H&E stain
Wavier than smooth muscle
What kind of tissue is this?

Skeletal muscle
(a cross-section)

What kind of tissue is this?

Simple columnar epithelium

What are the defining characteristics of muscle tissue?
- Can contract
- Responsible for movement
What kind of tissue is this?

Skeletal Muscle

What is the smooth-muscle equivalent of troponin?
Calmodulin
Ca2+ binds to it, allows contraction to continue
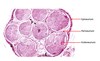
What are the 3 layers of connective tissue supporting the peripheral nervous system?
Endoneurium, Perineurium, Epineurium
Describe the shape of smooth muscle cells
Short, spindle shaped with a central cigar-shaped nuleus
What kind of tissue is this?

Dense, irregular connective tissue
Few nuclei = connective tissue
Bright pink = dense
Wavy-ness = irregular

Where is dense, regular connective tissue found?
Tendons
What kind of cell junctions prevent materials from passing in between epithelial cells?
Zona occludens (aka tight junctions)
What is a myofibroblast?
Dual threat!
The secretory function of a fibroblast and the contractile properties of a smooth muscle cell
What are the defining features of connective tissue?
Cells that are separated from each other and surrouned by extracellular matrix
What kind of cells make up the perineurium?
Fibroblasts: they produce the connective tissue that surrounds each fascicle
Where do we find epithelial tissue?
Exterior of the body
Covering the outer surface of internal organs
Lining body cavities, tubes, and ducts
In glands
What are the characteristics that define epithelial tissues?
Shape (Squamous, cubiodal, columnar)
Number of cells (simple or stratified)
Keratinized or non-keratinized
Where is loose connective tissue found?
Superficial fascia (under the skin)
Which component of connective tissue exracellular matrix is responsible for hydration?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Which vitamin is important in collagen assembly?
Vitamin C
What is the ? pointing to?

Nissl bodies

What is the perineurium?
Specialized connective tissue surrounding each nerve fascile
- Made out of fibroblasts
- Contriubutes to the Blood-Brain Barrier
- Has tight junctions
Where in the body would you find tissues with a high elastic fiber content?
Lungs, aorta, skin, elastic cartilege, fetal tissue
What is the name for the dense, irregular connective tissue surrounding the entire nerve?
Epineruium
Which muscle types are striated?
Skeletal, Cardiac
Why do dendrites contain microtublules and neurofilaments?
So materials can be transported intracellularly in both directions
Fibroblasts in the PNS are like ________ in the CNS
Astrocytes
What kind of tissue is this?
(This is a clinical correlation but I already made the slide before I realized and I don’t want to delete it sorry!)

Atrophied skeletal muscle
- More space in between myocytes
- Myocyte gets thinner, darker pink, wavier
- Nuclei centralize

What is reticular connective tissue made out of?
Reticulin, which is made from collagen
What are the 4 main types of connective tissue?
Loose
Dense
Reticular
Adipose
What kind of cells produce cerebrospinal fluid?
Ependymal cells
What kind of tissue is this?

Adipose Tissue

What kind of epithelium is found at absorptive surfaces
Simple columnar
Examples: Small intestine, bronchioles
What is the defining characteristic of nervous tissue?
Controls and integrates functional activities of organs and organ systems
Enables teh body to respond to continuous change in the environment
What is C pointing to?
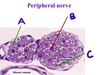
A myelin sheath

What is a ganglion?
A cell body in the peripheral nervous system
What type of muscle cell has a sigle, cigar-shaped nucleus?
Smooth
What is the function of zona occludens?
Zona occludens are tight junctions
They connect adjacent cells closely together to nothing can seep though
Example: the blood-brain barrier
What is the primary component of ground substance?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Where is dense, irregular connective tissue found?
Joint capsules, under skin, in fascia
What kind of tissue is the arrow pointing to?

Smooth muscle
(surrouding an artery)

What kind of tissue is the arrow pointing to?

Loose connective tissue
Lots of open space, light pink

Describe the shape of cardiac muscle cells
Shorter than skeletal muscle
Branching
Each cell has one central nucleus
Where would you find an intercalated disk?
Cardiac muscle cell
The cells attach to each other at intercalated disks
Suppose you see many random elastic fiber coils in a tissue sample. What does this mean?
The tissue is stretchy! It can accomodate expansion
Which cells make up the majority of cells in the CNS?
Glial cells
Where is stratified columnar epithelium found?
Conjunctiva of the eye, parts of the pharynx, anus, uterus, and male urethra and vas deferens
What are the main types of fibers found in connective tissue?
Collagen and elastin
Collagen is much more common!
What cell types make up connective tissue?
Fibroblasts/myofibroblasts
Macrophages
Adipocytes
Pericytes
Mast cells
Other white blood cells
What triggers skeletal muscle to contract?
Neuron innervates muscle (releases ACh, it binds to nicotinic ACh receptor)
Membrane depolarizes
Voltage-sensitive calcium channels on T-tublule cause SR to release Ca2+
Troponin binds to Ca2+
Tropomysoin is freed, and can interact with actin
What are the arrows pointing to?

Elastin fibers

This is a picture of grey matter in the brain:
What is E pointing to?

Dendrites

What kind of epithelim lines the lumen of ducts and tubules?
Simple cuboidal
Knowing that this is a sample from a peripheral nerve, what kinds of nuclei are most abundant?

Schwann cell nuclei

What is the purpose of a hemidesmosome?
Anchors the cell to the basement membrane
Where is pseudostratified epithelium likely to be found?
Large airways of the respitory system (trachea)
Epididymis
What is the purpose of the basement membrane?
Attaches and anchors epithelial cells to underlying tissues
Separates epithelial cells and connective tissue
Separates layers of cells
Can act as a filter (kidney)
Role in cell-cell communication
What are the pink things in the tissue that the arrow is pointing to?

Collagen fibers
This is loose connective tissue; the collagen fibers are loosely packed

Where is smooth muscle found?
The walls of blood vessels and organs
What is B pointing to?
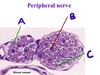
A Schwann cell nucleus

What kind of connective tissue is resistant to lengthening?
Dense, regular connective tissue
What kind of tissue is this?

Dense, regular connective tissue

Describe the appearance of a skeletal muscle cell
Striated
Multinucleated
Nuclei on the edge of the cell
Long
Give some examples of glial cells in the CNS and PNS
CNS: Astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, ependymal
PNS: Schwann, Satellite
Match each muscle type with a picture


Where is transitional epithelum likely to be found?
Bladder
A mutation in the fibrilin gene will result in defective ________
Elastic fibers
What does a smooth muscle cell look like under a microscope?
Bright pink (eosinophilic cytoplasm)
Elongated, blunt-ended nuclei (cigar shaped)
Which muscle type is innervated by somatomotor neurons?
Skeletal
What kind of epithelium lines blood vessles and body cavities?
Simple squamous epithelium
What is the function of a fibroblast?
Make fibers and extracellular matrix components
(The workhorse of connective tissue)
What is a Nissl Body?
A stack of rough ER in the cytoplasm of a neuron cell body
They make protein
What are some characteristic features of loose connective tissue?
Few fibers, lots of ground substance*
High fat content
Light pink under H&E stain
*Ground substance looks like empty space under a microscope
What is the name for the specialized connective tissue that surrounds each nerve fascicle?
Perineurium
What is the function of macula adherens?
Desmosomes
They are specific welding points that help cells stick together
Name 4 types of supporting cells (glial cells) in the CNS
- Oligodendrocytes
- Microglia
- Astrocytes
- Ependymal cells
What are neurilemma?
Layers of schwann cells surrounding a neuron
What kind of tissue is this?

Reticular connective tissue
The sample is from a lymph node

What kind of tissue is C?

Cross-section of peripheral nerve without cell bodies
(Thank you @Nathan Schlobin!)

Ground substance contains which 3 major groups of molecules?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) = most common
Proteoglycans
Multiadhesive glycoproteins
What kind of tissue is the liver made out of?
Epithelial
What kind of tissue is B?

Skeletal Muscle Cross Section
What are some charactaristics of reticular connective tissue?
Reticular fibers are thin and stain black on an elastic (EVG) stain
Between the fibers there may be open spaces or lots of cell
Reticular connective tissue creates a supportive meshwork for hematopoietic tissues to allow cells to pass through
What are the 3 types of muscle?
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
What are some characteristic features of dense, irregular connective tissue
Fibers going muliple directions
Dark pink on H&E stain
Resistant to mulit-directional forces
What is the purpose of an intercalated disk?
It propagates depolarizations from cell to cell
What triggers cardiac muscle to contract?
Sympathetic nervous system innervation initiates contraction
Voltage-gated extracellular Ca2+ open
Increased Ca2+ triggers the release of intracellular Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ binds to troponin
Tropomyosin is freed, myosin can interact with actin
What kind of tissue is this?

Dense, regular connective tissue
Wavy appearance, parallel lines, few nuclei

What kind of tissue is the endometrium?
Loose connective tissue
What are some characteristics of adipose tissue?
White on H&E stain (fat doesn’t stain)
Nucleus on the edge
Looks like marshmallows surrounded by cell membrane and a nucleus
What is the name for the loose connective tissue that surrounds each neuron?
Endoneurium
Where does connective tissue arise from?
Mesoderm
This is a picture of grey matter in the brain:
What is A pointing to?

Supportive glial cells

What is the basement membrane made from?
Extracellular matrix
What kind of cell junctions attach cells to each other near their apical membrane?
Zona Adherens (aka Adherens Junctions)
What kind of tissue is this?

Sympathetic ganglion
(Look for large cell bodies)
The dark dots are nuclei of satellite cells

What is fibrilin?
A component of microfibrils necessary for assembling elastic fibers
Where might you find a dense body?
Smooth muscle cell
A dense body is the contractile unit
What is adipose tissue made from?
Adipocytes
Which types of collagen form networks in the basement membrane?
Type V, Type VI
What are some possible funcitonal roles of epithelial cells?
Secretory
Protective
Absorptive
Moving things along
What is the function of zona adherens?
Adherens Junctions; they are a continuous band around the cell
They help cells stick together
What is the epineurium?
Dense, irregular connective tissue that surrounds groups of fascicles to enclose the whole nerve
- Fills the space between fascicles
What kind of tissue is this?

Smooth muscle

What is the purpose of reticular connective tissue?
Foms the meshwork of lymph nodes and other hematopoetic tissues to allow cells to pass through
What is the function of ground substance?
Mechanical support, hydration, regulation of cell migration
Where are perineural cells located?
Within nerve fibers of the CNS; they surround each individual nerve facicle
What is the endoneurium?
Loose connective tissue surrounding each neuron
What tissue type is this?

Epithelial

This is a picture of grey matter in the brain:
What is C pointing to?

An axon

What is the function of gap junctions?
Coordinate the function of the epithelium
Gap junctions create a direct pore between two cells. It allows small molecules to pass through for cell-cell communication and metaboilism
What are elastic fibers made from?
Elastin and microfibrils
What tissue type is this?

Epithelial

Match each letter (A-C) with the correct layer of connective tissue
What is D?

D is a fascicle
This is a picture of grey matter in the brain:
What is D pointing to?

Neuron Cell Body

Which type of muscle contains T-tubules organized into a triad?
Skeletal
What causes striated muscle to appear striated under a microscope?
Presence of sarcomeres
What is A pointing to?

An axon



