FDN2_SM_WK3_Histology Flashcards
Epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
What kind of tissue is this?

Stratified squamous epithelium

Match the arrows with the following:
Elastic fiber
Collagen fiber
Macrophage
Fibroblast


What kind of cell junctions attatch epithelial cells to each other in the middle of an epithelial layer?
Macula adherens junctions (aka desmosomes)
These are focal “spot welds”
What kind of tissue is D?

Smooth Muscle

What kind of tissue is this?

Skeletal Muscle

Suppose you know that a tissue’s main function is secretory… What kind of tissue is it likely to be?
Epithelial
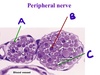
What do Schwann cells look like in a cross-section of a nerve?
They have thin, wavy, purple nuclei on H&E stain
They are abundant
They will be arranged in rings around neurons
Where might non-keratinized epithelium be found?
Esophagus, oral cavity, vagina, anal canal
What is the most common type of collagen in the body?
Type I: It is found in skin, tendons, vasculature, organs, bone
Where in the muscle cell is troponin found?
Thin filaments of skeletal and cardiac muscle
What are the arrows pointing to?

Fibroblast nuclei

What kind of tissue is this?

Cardiac Muscle

What are satellite cells?
Glial cells in the PNS that surround ganglia (cell bodies)
What kind of tissue is this?

Cardiac Muscle

What are microglia?
Macrophages of the CNS; they ingest foreign material, debris, and organisms
What is a defining feature of epitheilum?
Cells are closely attached to one another
What is loose connectie tissue made from?
Many cell types; Lots of ground substance in between fibrils. High fat content
What are the 3 possible triggers for smooth muscle contraction?
- Sympathetic neurons innervate muscle, voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open -> causes release of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Stretch causes mechanosensitive Ca2+ channels to open -> causes relsease of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Surface hormone receptors respond to a chemical signal -> Second messenger opens channel in ER -> Ca2+ released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum binds to calmodulin, activates enzyme that phosphorylates myosin light chain kinase, myosin can now interact with actin
Which muscle types contain tropmyosin?
Skeletal, Cardiac
What is dense, regular connective tissue made from?
Parallel bundles of collagen
Where is reticular connective tissue found?
Kidney, spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow
How is collagen synthesized?
Procollagen is made in fibroblasts and released
3 procollagen fibers are assembled into a collagen fiber in the extracellular matrix
What does myelin look like under a microscope?
White space surrounding a neuronal axon (not visible on H&E stain)
May be able to see the nucleus of a Schwann cell
Appears black on an osmium stain

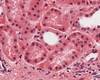
What type of epithelial cells are in this picture?

Simple cuboidal