Eye Infections 2 Flashcards
Discrete foci of retinitis w/white retinal or choroidal lesions can be seen in _________ (disease).
cat scratch
(microbe: bartinella hensalae)

Parinaud’s Oculoglandular syndrome is caused by _________. Presents with _______.
- Caused by cat scratch disease (Bartonella henselae)
- Conjunctivitis and neuroretinitis

Moraxella catarrhalis characteristics (3)
- Gram negative diplococci
- Oxidase positive
- Antibiotic resistant to penicillin, ampicillin, amoxicillin

Which microbe causes a positive hockey puck test?

Moraxella catarrhalis

HSV characteristics (3)
- Linear
- dsDNA
- Enveloped
Incubation for HSV
2-11 days

Herpes simplex virus is spread via _____
Contaminated secretions on mucous membranes
(incubation is 2-11 days. Most infectious during early days of primary infection)
Ocular herpes definition
HSV infection of the conjunctiva w/swollen eyelids
(If the cornea is involved it is herpes simplex keratitis)
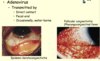
Herpes simplex keratitis (aka Dendritic Keratitis) deadens _______ and forms a _____ pattern
- nerves
- Virus branches out in the dendritic pattern


Dendritic keratitis AKA herpes simplex keratitis

Adenovirus characteristics
- Non-enveloped
- Icosahedral
- Double-stranded DNA

Cytomegalovirus characteristics (2)
- Double-stranded DNA
- Membrane enveloped
(Latency and reactivation; related to HSV)

Adenovirus transmitted by _____ (2).
- Direct contact
- Fecal-oral
(occoasionally water-borne)
CMV retinitis: symptoms (3)
- floaters
- flashes
- blind spots
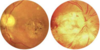
Define Pizza Pie retinopathy is caused by ______(virus) and presents with _______(3).
- caused by CMV
- Wool spots
- Infiltrate
- Hemorrhaging

Retinopathies caused by CMV are prevelent in which patient population?
- Immuno-compromised
- Neonates of mothers who are infected

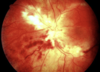
pizza pie retinopathy
(CMV virus)

Wart like lesions of the eyelides can form from the _____.
pox virus (VZV)
Sabouraud dextrose agar is used almost exclusively for ______.
fungal species

Most commonly seen fungi in the lab?

Aspergillus

What are the top 2 most commonly recovered fungi in opportunistic mycoses?
- Candida
- Aspergillus
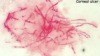
Aspergillus, but you can’t determine the exact fungi. still gives you a direction for trmt

Acremonium: 3 species that cause infection
- •Acremonium falciforme
- •Acremonium kiliense
- •Acremonium recifei
Acremonium morphology
Conidia usually appears in clusters or balls

Penicillium can cause which 2 ocular disease?
- keratitis
- endophthalmitis

Penicillium is a filamentous fungi that is found in _____ (3).
- Air
- Decaying vegetation
- Soil
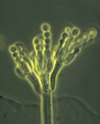
Rhizopus Causative agent for group of fungal infections classified as _____
Zygomycosis

Predisposing factors to zygomycosis?
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Immunosuppression

Zygomycosis nosocomial infections are due to ____(2)
- Contaminated adhesive tape
- Wooden tongue depressors
(usually fatal)

Mucormycosis is an infection due to _______ species, which are _______ (route of transmission) and deadly.
- rhizopus
- inhaled or ingested

Rhizopus (aka black bread mold) morphology (3).

- aseptate
- pigmented rhizoids (root-like hyphae)
- forms sporangiophores

What are the main differences between exogenous and endogenous endophthalmitis?
Exogenous follows surgery or trauma & is usually bacterial

Whitish chorioretinal spots with filamentous borders → causes vitreal haze and Roth’s spots are clinical manifestations of _______ infection.
Candida

Roth’s spots are associated with _______.
retinal hemorrhages (white centered hemorrhages)

Contact lens cases are contaminated with ____ (3).
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Protozoa
(All with catalase activity)

Pseudomonas characteristics (3)
- Gram-negative
- Motile
- Grape like odor

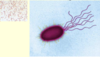
Pseudomonas

Bacillus cereus characteristics (5)
- Enterotoxin
- Heat resistant spores
- Hemolysin
- Phospholipase
- Protease

Acanthamoeba are free living amoebas that require _________.
NO vector or human carrier state
Keratitis associated with acanthamoeba is contracted from ____(3)
- Wearing non-disposable lenses
- Homemade sodium chloride Solutions
- Wearing of contacts while swimming
(have been found in swimming pools)
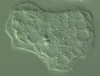
Acanthamoeba
Staphylococcus epidermidis characteristics (5)
- Biofilms
- Catalase positive
- Coagulase-negative
- Facultative anaerobe
- Gram positive cocci

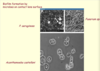
Toxoplasma Gondii is contracted by_____ (4).
- Congenital transmission
- Contaminated water containing tissue cysts
- Eating contaminated meat
- Oocytes shed by infected cats

Toxoplasma Gondii can cause which key feature of infection?
necrotic foci

Congential toxoplasma gondii affects (2 structures)
- Chorioretinitis
- Brain

3 morphological forms of Toxoplasma Gondii
- cysts
- oocysts
- tachyzoite

Toxoplasma Gondii tachyzoite is a _____form.
vegitative
Toxoplasma Gondii sporozoites are found in ______.
feces
Toxoplasma Gondii labs?
IFA (immunoflourescent assay) with FITC albeled antihuman IgG
(indirect: uses a direct Ab direct to the organism and another Ab with a flourescent tag)

Loa Loa is a _____( microbe type).
filiarial nematode

Loa Loa transmission & geography
- Chrysops fly
- West Africa

Chrysops fly bite humans and deposit ______
3rd stage larvae into the human

After the chysops fly bites the human and deposits 3rd stage larvae, the larvae develop into adults and produce ________ which migrates to the ______.
- microfilaria
- blood
Loa Loa worms typically end up in the _____.
eye

Onchocerca volvulus is spread by ______ (vector). Causes ____ (disease).
- Simulium (the black fly)
- River Blindness

Onchocerca volvulus life cycle
introduction of larvae from the bite of an infected black fly → migrate to subcutaneous tissues where they form nodules and mature into adults→ mating→female sheds microfilaria → migrate from the nodules

Onchocerca volvulus microfilaria travel along blood vessels and nerves to the eyes infecting the ____ (3).
- Choroid
- Cornea
- Optic nerve

Dead microfilaria induce which inflammatory responses in the eyes (2)?
- Secondary cataracts
- Ocular lesions
Define Myiasis
Infection of tissues or organs of animals or man by fly larvae

Myasis can cause infection of ______ (7 structures).
- Conjunctivitis: Oestrus ovis (sheep botfly)
- Eyes (opthalmomyiasis)
- Nose
- Paranasal sinuses
- Skin wounds
- Throat
- Urogenital tract


Moraxella catarrhalis may cause infection in which 5 organs?
- Respiratory
- Middle ear
- Eye
- CNS
- Joints

Fusarium fungal species are known to cause which 2 ocular diseases?
- Endophthalmitis
- Keratitis
(also causes Otitis media)

Cat scratch disease can cause which ocular syndromes (3)?
- Parinaud’s Oculoglandular Syndrome
- Vitritis (infection of the eye jelly)
- Posterior uveitis
(microbe: Bartonella hensalae)

Adenovirus can cause which 3 ophthalmic diseases?
- Conjunctivitis
- Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis
- Pharyngoconjunctival fever
(also causes: common cold, Tonsillitis, Ear infection)

Aspergillosis may cause which 4 conditions?
- Opportunistic infections
- Allergic States
- Endophthalmitis
- Toxicosis

Acanthamoeba causes two distinct clinical symptoms
- Granulomatous amebic encephalitis (AIDs pts)
- Keratitis (contact lens wearers)
Varicella-zoster virus can cause which ophthalmic diseases (5)?
- Endophthalmitis
- Keratitis
- Lacrimal apparatus infection
- Scleritis
- Viral blepharitis
Herpes simplex virus can cause which ocular diseases (4)?
(other than ocular herpes)
- Endophthalmitis
- Lacrimal apparatus infection
- Scleritis
- Viral blepharitis
Candida can cause which ophthalmic conditions (5)?
- Conjunctivitis
- Episcleritis
- Exogenous and endogenous endophthalmitis
- Iritis
- Iritis abscess
(seeding into the retina)


