Exam 4 Oral Cavity Flashcards
1
Q
External features of mouth
A
- Philtrum: Indentation stretching from nasal septum to middle upper lip
- Labial commisure: Point where upper and lower lips meet
- Angle: Angle between upper and lower lip; medial to labial commisure
- Vermilion border: Border between lip epithelium and skin of face
- Oral fissure (rima oris): Line between upper and lower lips

2
Q
Two parts of oral cavity
- What are they?
- Where is each located?
- What are their features?
A
- Oral vestibule
- Located between cheek/lip and alveolar ridges and teeth.
- Features:
- Oral mucosal lining converges midline and forms superior (maxillary) and inferior (madibular) labial frenulum
- Lateral cheek formed by buccinator muscle
- Parotid duct opens in parotid papilla adjacent to second maxillary molar.
- Oral cavity proper
- Bounded anteriorly and laterally by alveolar ridges and teeth (dental arch); open posteriorly to oropharynx
- Roof is hard/soft palate
- Floor is tongue

3
Q
Teeth
- How are they anchored to mandible/maxilla?
- What are the different kinds? (Anteromedial to posterolateral)
- Innervation
A
- Anchored to mandible/maxilla in alveolar processes of maxilla/mandible by periodontal ligaments
- Kinds from anteromedial to posterolateral:
- Incisor (2)
- Canine (1)
- Premolar (2)
- Molar (3)
- Innervation:
- Maxilla by V2
- Incisors and canine: Anterior superior alveolar
- Premolars and half of first molar: Middle superior alveolar
- Middle first molar and 2nd and 3rd molars: Posterior superior alveolar
- Mandible by V3
- All teeth by inferior alveolar nerve
- Maxilla by V2

4
Q
Palate
- How much of palate is formed by hard palate? Soft palate?
- What forms the hard palate?
- What are the features of the hard palate?
- What is the function of the soft palate?
- What forms the soft palate?
A
- Anterior 2/3 of palate from hard palate; posterior 1/3 from soft palate
- Hard palate formed by maxillary and palatine bones
- Hard palate features:
- Palatine foramina: Located on posterior part of palatine bone near pyramidal process
- Incisive fossa: Located anteriorly; Opening of incisive canal.
- Nasopalatine and septal branch of sphenopalatine nn pass through incisive canal
- Soft palate is highly movable and separates oropharynx from nasopharynx
- Soft palat formed by tensor and levator veli palatini muscles.

5
Q
Palatine gland
- What is it?
- What is its innervation?
A
- Mucous gland of both palates
- Innervated by postganglionic parasympathetics fibers from pterygopalatine ganglion via greater palatine nerve.
6
Q
Neurovasculature of palates
- What is their innervation?
- What kind of fibers do these nerves carry?
- What is their blood supply?
A
- Hard palate innervated by greater palatine nerve (branch of V2)
- Carries general sensory, postganglionic parasympathetic fibers from pterygopalatine ganglion, postganglionic sympathetic fibers from deep petrosal nerve
- Soft palate innervated by lesser palatine nerve (branch of V2)
- Carries general sensory, postganglionic parasympathetic fibers from pterygopalatine ganglion, postganglionic sympathetic fibers from deep petrosal nerve
- Hard palate blood supply from greater palatine artery
- Soft palate blood supply from lesser palatine artery
- Branches off descending palatine artery
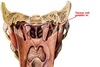
7
Q
Tensor veli palatini muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Scaphoid fossa of medial pterygoid plate, spine of sphenoid, auditory tube
- Distal Attachment: Palatine aponeurosis
- Tendon of tensor veli palitini wrapped around hamulus of medial pterygoid plate (inferior end of posterior border of medial pterygoid plate)
- Action: Tenses palatine aponeurosis to extend hard palate and open auditory tube during swallowing
- Innervation: Mandibular nerve (CN V3)
8
Q
Levator veli palitini muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Temporal bone (petrous part)
- Distal Attachment: Palatine aponeurosis
- Action: Elevates soft palate during swallowing
- Innervation: Pharyngeal branch of vagus (CN X)

9
Q
Palatoglossus muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
- What does it form?
A
- Proximal Attachment: Palatine aponeurosis
- Distal Attachment: Lateral aspect of tongue
- Action: Elevates posterior tongue, depresses palate to close oropharyngeal isthmus during mastication
- Innervation: Pharyngeal branch of vagus (CN X)
- Forms palatoglossal fold

10
Q
Palatopharyngeus muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
- What does it form?
A
- Proximal Attachment: Hard palate, superior palatine aponeurosis
- Distal Attachment: Lateral pharyngeal wall
- Action: Narrows oropharyngeal isthmus and elevates during swallowing
- Innervation: Vagus nerve (CN X) from pharyngeal plexus

11
Q
Tongue
- What forms the posterior 1/3?
- What forms the anterior 2/3?
- What is the tip called?
- Features of the dorsum of tongue?
A
- Root forms posterior 1/3
- Body forms anterior 2/3
- Tip is called apex
- Features:
- Median sulcus: Groove running down midline of tongue
- Sulcus terminalis: V-shaped sulcus marking separation between anterior 2/3 (oral) and posterior 1/3 (pharyngeal) parts
- Forament cecum: Median pit in apex of tongue; site of origin of thyroid gland in embryo
- Vallecula: Continuation of tongue posteriorly with anterior epiglottis

12
Q
What provides sensory innervation to the tongue?
A
- Lingual nerve (off V3): Provides general senses to anterior 2/3
- Chorda tympani (joins lingual nerve): Provides taste to anterior 2/3
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX): Provides both general sense and tase to posterior 1/3 of tongue
- Internal laryngeal nerve (off CN X): Provides general sense and taste to anterior surface of epiglottis

13
Q
Genioglossus muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Mental spine of mandible
- Distal Attachment: Dorsum of tongue, hyoid bone
- Action: Depresses and protrudes tongue
- Innervation: Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)

14
Q
Hypoglossus muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Body and greater horn of hyoid bone
- Distal Attachment: Lateral and inferior aspect of tongue
- Action: Depresses and retracts tongue
- Innervation: Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)

15
Q
Styloglossus muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Styloid process and stylohyoid ligament
- Distal Attachment: Lateral and inferior aspect of tongue
- Action: Retracts tongue and draws it up for swallowing
- Innervation: Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)

16
Q
Intrinsic muscles of tongue
- What are they?
- What are their functions?
- What is their innervation?
A
- Longitudinal muscles: Shorten (thicken/heighten) tongue
- Transverse muscle: Narrows tongue
- Verticle muscle: Flattens and broadens tongue
- Innervation: Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
17
Q
Glands of sublingual space
- What are they?
- Where are they located?
- Where do they drain?
A
- Submandibular gland: Located on superior surface of mylohyoid muslce near its posteiror margin
- Duct emerges from superior part of gland and passes anteriorly;
- Empties into sublingual caruncle immediately lateral to frenulum of tongue.
- Lingual nerve crosses under this duct.
- Duct emerges from superior part of gland and passes anteriorly;
- Sublingual gland: Lies against sublingual fossa in medial surface of mandible
- Empties into oral cavity with its 15-20 short ducts along its entire length

18
Q
Branches off lingual artery (passes medial to hypoglossus muscle)
- What are they?
- Where do they run?
A
- Dorsal lingual artery: Comes off lingual artery immediately before it passes deep to hypglossus muscle
- Deep lingual artery: One of two terminal branches; Passes superiorly on lateral surface of tongue
- Sublingual artery: Other terminal branch; Supplies the lower part of tongue and sublingual gland

19
Q
Lymphatic drainage of tongue
- Where does each part drain?
A
- Posterior 1/3: Drained by superior deep cervical nodes
- Middle Part: Drained contralaterally by inferior cervical nodes
- Drained ipsilaterally by submandibular nodes
- Tip of Tongue: Drained by submental nodes, which empty into deep cervical nodes



