Exam 4 Larynx Flashcards
1
Q
Larynx
- Where is it located?
- Function?
- Structure
A
- Extends from lower part of pharynx to trachea; suspended by hyoid bone
- Acts as a compound sphincter to prevent passage of food or drink into airway during swallowing
- Regulates flow of air to and from lungs during phonation
- Cartilage skeleton made up of 9 cartilages:
- 3 paired: Arytenoid, Corniculate, Cuneiform
- 3 unpaired: Thyroid, Cricoid, Epiglottis

2
Q
Thyroid cartilage
- Where is it located?
- Structure?
- What muscles are attached to it?
A
- Below hyoid, joined by broad, thin thyrohyoid membrane
- Structure:
- Two flat laminae join anteriorly to form laryngeal prominence (Adam’s apple)
- Incomplete posteriorly
- Superior and inferior horns off posterior margin; inferior horns articulate with cricoid cartilage
- Oblique line attachment pt for: Sternothyroid, Thyrohyoid, and Inferior constrictor muscles

3
Q
Cricoid cartilage
- Where is it located?
- Structure
- What is it the border between?
A
- Anchored to thyroid cartilage at cricothyroid joints by thick cricothyroid ligament
- Structure:
- Narrow anterior arch
- High posterior lamina
- Superior articular facets for arytenoid cartilages
- Inferior margin of larynx and superior margin of trachea
ONLY COMPLETE RING IN AIRWAY

4
Q
Epiglottis
- Where is it located?
- Structure
- Function
A
- Located behind root of tongue; lower end is attached to back of thyroid cartilage
- Spoon-shaped plate made of elastic cartilage
- During swallowing, closes over larynx to prevent food and drink from entering airway

5
Q
Arytenoid cartilage
- Where is it located?
- Structure (What muscles attach here?)
- Function?
A
- Located above cricoid cartilage
- Structure:
- Pyramid shaped
- Anterior vocal processes: Attachment for vocal ligament and vocalis muscle
- Muscular processes: Attachment for thyroarytenoid, lateral and posterior cricoarytenoid muscles
- Function: Swivels when muscles contract to modify size/shape of airway opening to control phonation

6
Q
Corniculate cartilages
- Where are they located?
A
- Positioned on top of arytenoid cartilages
- Enclosed within aryepiglottic folds

7
Q
Cuneiform cartilages
- Where are they located?
A
- Enclosed in aryepiglottic folds anterior to corniculate cartilages
- DO NOT articulate with other laryngeal cartilages

8
Q
Ligaments of larynx
- What are they?
- What do they connect?
- Parts (if applicable)
A
- Thyrohyoid membrane
- Extends from thyroid cartilage to medial surface of hyoid bone
- Thick middle portion = middle thyrohyoid ligament
- Cricothyroid ligament
- Extends from arch of cricoid cartilage to thyroid cartilage, as well as vocal process of arytenoid cartilages
- Vocal ligament
- Extends from posterior surface of thyroid cartilage to vocal process of arytenoid cartilage
- Upper border of conus elasticus
- Vestibular (ventricular) ligament
- Extends from thyroid cartilage to anterior lateral surface of arytenoid cartilage
- Conus elasticus (cricovocal ligament)
- Extends upward from entire arch of cricoid cartilage to vocal ligaments
- Formed by cricothyroid, median cricothyroid, and vocal ligaments

9
Q
Cavities and folds of larynx
- What are they?
- Where are they located?
A
- Vestibule of larynx
- Extends from laryngeal inlet to vestibular folds
- Ventricles of larynx
- Extend between ventricular fold and vocal fold
- Rima glottidis
- Space between vocal folds and arytenoid cartilages
- Narrowest portion of laryngeal cavity
- Infraglottic cavity
- Extends from rima glottidis to lower body of cricoid cartilge
- Vestibular folds (false vocal cords)
- Extend from thyroid cartilage to vocal ligament of arytenoid cartilage
- Vocal folds (true vocal cords)
- Extend from angle of thyroid cartilage to vocal processes of arytenoid cartilages
- Contain vocal ligament and vocalis muscle
- Alter shape of rima glottidis by movement of arytenoids to facilitate phonation and respiration (the rima glottidis is wide during inspiration and narrow during expiration and sound production)

10
Q
Muscles of Larynx
What is the general function of the muscles?
- Extrinsic
- Intrinsic
A
- Extrinsic: Suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles
- Act to elevate or depress larynx during swallowing
- Intrinsic: Act within larynx to manipulate ariway and vocal ligaments by moving arytenoid cartilages or cricothyroid joints
- All are innervated by branches of CN X, mainly recurrent laryngeal nerve
11
Q
Cricothyroid muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Arch of cricoid cartilage
- Distal Attachment: Inferior horn and lower lamina of thryoid cartilage
- Action: Tenses vocal cords
- Innervation: CN X (via external laryngeal branch of superior laryngeal nerve)

12
Q
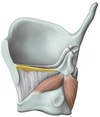
Vocalis muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Angle between two laminae of thyroid cartilage
- Distal Attachment: Vocal processes of arytenoid cartilages
- Action: Relaxes and adducts vocal cords
- Innervation: CN X (via recurrent laryngeal nerve)
13
Q
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Posterior surface of lamina of cricoid cartilage
- Distal Attachment: Muscular process of arytenoid cartilage
- Action: Abducts vocal cords
- Innervation: CN X (via recurrent laryngeal nerve)

14
Q
Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Arch of cricoid cartilage
- Distal Attachment: Muscular process of arytenoid cartilages
- Action: Adducts vocal cords
- Innervation: CN X (via recurrent laryngeal nerve)

15
Q
Transverse arytenoid muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Posterior surface of arytenoid cartilage
- Distal Attachment: Opposite arytenoid cartilage
- Action: Adducts vocal cords (closes laryngeal inlet)
- Innervation: CN X (via recurrent laryngeal nerve)

16
Q
Oblique arytenoid muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Muscular process of arytenoid cartilage
- Distal Attachment: Apex of opposite arytenoid cartilage
- Action: Adducts vocal cords (closes laryngeal inlet)
- Innervation: CN X (via recurrent laryngeal nerve)

17
Q
Aryepiglottic muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Apex of arytenoid cartilage
- Distal Attachment: Side of epiglottic cartilage
- Action: Adducts vocal cords (weak), pulls epiglottis down to close laryngeal inlet during swallowing
- Innervation: CN X (via recurrent laryngeal nerve)

18
Q
Thyroarytenoid muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Inner surface of thyroid lamina
- Distal Attachment: Anterolateral surface of arytenoid cartilage
- Action: Adducts and relaxes vocal cords
- Innervation: CN X (via recurrent laryngeal nerve)

19
Q
Thyroepiglottic muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Anteromedial surface of lamina of thyroid cartilage
- Distal Attachment: Lateral margin of epiglottic cartilage
- Action: Adducts vocal cords
- Innervation: CN X (via recurrent laryngeal nerve)

20
Q
Blood supply of larynx
- Arterial supply
- Venous drainage
A
- Most blood comes from Superior laryngeal artery (External carotid -> Superior thyroid a -> Superior laryngeal a)
- Accompanies superior laryngeal n and enters larynx through thyrohyoid membrane
- Blood also received from Inferior laryngeal artery (Subclavian artery -> Thyrocervical trunk -> Inferior thyroid artery -> Inferior laryngeal artery)
- Accompanies recurrent laryngeal nerve into larynx
- Venous drainage: Superior and inferior laryngeal veins
- Run with arteries of same name

21
Q
Innervation of Larynx
- What are the nerves?
- What is their function?
A
- Recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Innervates all intrinsic muscles of larynx EXCEPT cricothyroid
- Sensory innervation below vocal cord
- Internal laryngeal nerve
- Supplies sensory innervation to mucous membrane above vocal cord
- Runs with superior laryngeal artery
- External laryngeal nerve
- Innervates cricothyroid and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles
- Accompanied by superior thyroid artery

22
Q
Laryngeal obstruction (choking)
- What causes it?
- How is it resolved?
A
- Caused by aspirated foods becoming lodged at rima glottidis
- Heimlich maneuver resolves it by causing rapid burst of air through larynx to dislodge obstruction
23
Q
Laryngitis
- What is it?
- Symptoms?
A
- Inflammation of mucous membrane of larynx
- Symptoms:
- Dryness/soreness of throat
- Hoarseness
- Cough
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
24
Q
Lesion of recurrent laryngeal nerve
- What causes it?
- Symptoms
A
- Can be caused by thyroidectomy or cricothyrotomy or rarely by aortic aneurysm
- Symptoms
- Unilateral: Hoarseness, loss of cough, dysphagia
- Bilateral: Breathlessness, loss of voice


