Exam 4 Infratemporal Fossa Flashcards
1
Q
Temporal Fossa
- Where is it?
- What separates it from infratemporal fossa?
- What does it contain?
A
- Shallow depression surrounded by superior and inferior temporal lines that funnels inferiorly to pass below zygomatic arch and ends at base of skull.
- Infratemporal crest separates it from infratemporal fossa
- Contains temporalis muscle

2
Q
Boundaries of Infratemporal Fossa
- Features in each boundary
A
- Superior: Greater wing of sphenoid & squamous temporal bones
- Features: Foramen ovale & foramen spinosum
- Inferior: Open, filled by medial pterygoid muscle
- Medial: Lateral pterygoid plate
- Features: Pterygomaxillary fissure (b/w medial and anterior walls)
- Lateral: Ramus and condyle of mandible
- Features: Lingula, mandibular foramen & canal
- Anterior: Posterior maxilla
- Features: Alveolar foramina
- Posterior: not bony
3
Q
Conents of infratemporal fossa
A
- Inferior portion of temporalis muscle
- Lateral and medial pterygoid muscles
- Maxillary arteries and its branches
- Pterygoid venous plexus
- Branches of CN V3
- Chorda tympani (off CN VII)
- Otic ganglion
4
Q
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
- What are its articular surfaces?
- What are its ligaments and what are their functions?
- What are the movements of its joint cavities?
- What is its innervation?
- What is its blood supply?
A
- Articular surfaces: Mandibular condyle/head (inferior) (Light blue), Articular tubercle of temporal bone (superior) (Lime green), Mandibular fossa of temporal bone (superior) (Purple)
- Ligaments:
- Lateral ligament of TMJ (Orange): Prevents posterior & inferior dislocation of joint
- Articular disc (White): Between condyle and mandibular fossa
- Stylomandibular ligament (Sky blue): Does not significantly contribute to joint strength
- Sphenomandibular ligament (Pink): Primary passive support of mandible; Checks movement of mandible at TMJ
- Joint cavities:
- Upper: Translatory (gliding) movements
- Lower: Hinge movement
- Innervation: Auriculotemporal nerve (primarily); Anterior portion by nerve to masseter
- Blood supply: Superficial temporal artery (primarily); Anterior portion by branches from muscular branches of maxillary artery

5
Q
Temporalis Muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Floor of temporal fossa and deep surface of temporal fascia
- Distal Attachment: Medial aspect of coronoid process and anteromedial ramus of mandible
- Action: Bilaterally, anterior fibers maintain resting tonus in upright position and elevation of mandible
- Bilateral posterior fibers are primary retractors of mandible
- Innervation: CN V3

6
Q
Clicking of TMJ
- What causes it?
A
- Minor disc displacement
- Osteoarthritis
7
Q
Masseter Muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Inferior border of zygomatic arch and zygomatic process of maxilla
- Distal Attachment: Angle of mandible and lateral surface of ramus of mandible
- Action: Bilateral movements produce elevation of mandible and protrusion
- Innervation: CN V3

8
Q
Lateral Pterygoid Muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Superior head from inferior surface of greater wing of sphenoid; Inferior head arises from lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate
- Distal Attachment: Superior head inserts on articular capsule, articular disc, and pterygoid fovea; Inferior head inserts onto pterygoid fovea on anterior aspect of condylar neck
- Action: Bilaterally, results in protrusion of mandible and depression of mandible
- Unilaterally, moves mandible to opposite side (contralateral excursion)
- Innervation: CN V3

9
Q
Medial Pterygoid Muscle
- Proximal Attachment
- Distal Attachment
- Action
- Innervation
A
- Proximal Attachment: Deep head from medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate; Superficial head arises form tuberosity of maxilla
- Distal Attachment: Medial surface of mandible
- Action: Bilaterally, elevation of mandible & contributes to protrusion
- Unilaterally, moves mandible to opposite side (contralateral excursion)
- Innervation: CN V3

10
Q
Which muscles cause the following movements:
- Elevation
- Depression
- Protrusion
- Retrusion
- Right lateral movements
- Left lateral movements
A
- Elevation: Temporalis, masseter, medial pterygoid
- Depression: Gravity, lateral pterygoid, suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles, platysma
- Protrusion: Masseter, lateral pterygoid, medial pterygoid
- Retrusion: Temporalis, geniohyoid, digastrics
- Right lateral movements: Left medial pterygoid, left lateral pterygoid
- Left lateral movements: Right medial pterygoid, right lateral pterygoid
11
Q
First Part of Maxillary Artery
- Where is it?
- Branches and what they supply
A
- Arises posterior to neck of mandible
- Branches:
- Deep auricular artery: Supplies external acoustic meatus and lateral tympanic membrane
- Anterior tympanic artery: Supplies middle ear cavity
- Middle meningeal artery: Supplies dura mater & calvaria (via forament spinosum)
- Accessory middle meningeal artery: Supplies dura mater & calvaria (via foramen spinosum)
- Inferior alveolar artery: Supplies mandible & teeth (via mandibular foramen & canal) and gives off mental artery

12
Q
Second Part of Maxillary Artery
- Where is it located?
- What are its branches and what do they supply?
A
- Passes anteriorly either superficial or deep to lateral pterygoid muscle
- Branches:
- Deep temporal arteries (ant. & post.): Supply temporalis muscle
- Pterygoid arteries: Supply lateral & medial pterygoid muslces
- Artery to masseter: Supplies masseter muscle (deep surface)
- Buccal artery: Supplies buccinator muscle

13
Q
Third Part of Maxillary Artery
- Where is it located?
- What are its branches and what do they supply?
A
- Courses through pterygomaxillary fissure to enter pterygopalatine fossa
- Branches:
- Posterior superior alveolar artery: Supplies maxillary molar & premolar teeth, maxillary sinus & posterior superior gingivae
- Infra-orbital artery: Supplies inferior eyelid, lacrimal sac, side of nose, & upper lip
- Descending palatine artery: Supplies maxillary gingivae, palatine glands, palate of mouth
- Artery of pterygoid canal: Supplies superior part of pharynx
- Pharyngeal artery: Supplies roof of pharynx, sphenoidal sinus
- Sphenopalatine artery: Terminal branch of maxillary artery, supplies lateral nasal wall & nasal septum

14
Q
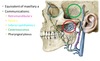
Pterygoid Venous Plexus
- Where is it?
- What does it communicate with?
A
- Located between temporal and pterygoid muscles
- Communicates with facial vein, cavernous sinus, pharyngeal plexus, retromandibular vein, and inferior ophthalmic vein
15
Q
Somatic motor branches of mandibular division of trigeminal (CN V3)
- What do they supply?
A
- Deep temporal nerves (anterior, middle, & posterior): Supply temporalis muscle
- Masseteric nerve: Passes through mandibular notch to supply masseter muscle
- Nerve to lateral pterygoid: Supplies lateral pterygoid
- Nerve to medial pterygoid: Supplies medial pterygoid
- Nerve to tensor tympani: Supplies tensor tympani muscle
- Nerve to tensor veli palatine: Supplies tensor veli palatini muscle
- Nerve to mylohyoid: Supplie mylohyoid & anterior belly of digastric muscles (branch off inferior alveolar nerve)

16
Q
Somatic sensory branches of mandibular division of trigeminal (CN V3)
- What do they supply?
A
- Auriculotemporal nerve: Supplies sensory fibers to TMJ, anterior ear (auricle & external meatus), anterior surface of tympanic membrane, & temporal region
- Inferior alveolar nerve: Supplies sensory fibers to mandibular teeth
- Gives off mental nerve to supply skin & mucous membranes of lower lip, skin of cheek, & vestibular gingiva of mandibular incisors
- Lingual nerve: Supplies sensory innervation to anterior 2/3 of tongue, mucosa of floor of mouth, & mandibular lingual gingivae
- Also have taste fibers from chordae tympani
- Long buccal nerve: Sensory innervation to skin over cheek, mucous membrane lining cheek, & buccal surface of mandibular buccal gingiva of molar region

17
Q
Parasympathetics of mandibular branch of trigeminal (CN V3)
- Where do they arise?
- What do they supply?
A
- Auriculotemporal: Parasympathetics from lesser petrosal nerve hitch a ride on this nerve
- Supply parotid gland
- Lingual: Parasympathetics from chorda tympani nerve hitch a ride and synapse in submandibular ganglion
- Supply submandibular and sublingual glands

18
Q
Otic Ganglion
- Where is it located?
- What synapses here?
A
- Located inferior to foramen ovale, medial to root of CN V3, posterior to medial pterygoid muscle
- Preganglionic parasympathetics from lesser petrosal nerve off CN IX synapse here
- Hitch a ride on auriculotemporal nerve to reach parotid gland

19
Q
Chorda tympani nerve
- Where does it arise?
- What fibers does it carry?
- What do they supply?
- What does it hitch a ride on?
A
- Branch off facial nerve (CN VII)
- Contains:
- Afferent taste fibers from anterior 2/3 of tongue
- Preganglionic parasympathetics supply submandibular ganglion.
- Postganglionic parasympathetics supply submandibular gland and sublingual glands
- Hitches a ride on lingual nerve

20
Q
Posterior Superior Alveolar Nerves
- Where are they located?
- Where do they arise from?
- What do they supply?
A
- From pterygopalatine fossa, enters infratemporal fossa via pterygomaxillary fissure, descends on posteriolateral surface of maxilla, pass through lateral wall of maxillary sinus
- Branch from maxillary nerve (CN V2)
- Supply sensory to posterior molars



