Endocrinology Flashcards
Prehormone syntheiss occurs in the __________ and is directed by a specific mRNA
endoplasmic reticulum
__________ are cleaved from prehormone. producing prohormone, which is transported to the Golgi apparatus
Signal peptides
Addtional peptide sequences are cleaved in the golgo apparatus to form the _________, which is packaged in secretory granules for later release
Hormone
Steroid hormones are derivatives of _____________
Cholesterol
Amine hormones (Thyroid hormones, epinephrine, norepinephrine) are derivatives of ___________
tyrosine
Most commonly applied principle for regulating hormone secretion
self limiting
Negative feedback
Explosive and self reinforcing regulating principle of hormone secretion
Positive feedback
Stimulates secretion of TSH and prolactin
Thytotropin releasing hormone (TRH)
hypothalamus
Stimulates secretion of ACTH
CRH
hypothalamus
Stimulates secretion of LH and FSH
GnRH
Stimulates secretion of growth hormone
GHRH
Hypothalamus
Inhibits secretion of growth hormone
Somatotropin release-inhibiting hormone (Somatostain)
Hypothalamus
Inhibits secretion of prolactin
Prolactin-inhibiting hormone (dopamine)
hypothalamus
Stimulates synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones
TSH
anterior pituitary
Stimualtes growth of ovarian follicles and estrogen secretion.
Promotoes sperm maturation (testes)
FSH
anterior pituitary
Stimulates ovulation, formation of corpus luteum, and synthesis of estrogen and progesterone (Ovary)
Stimualtes synthesis and secretion of testosterone (testes)
LH
Anterior pituitary
Stimualtes protein synthesis and overall growth
GH
anterior pituitary
Stimulates milk production and breast development
Prolactin
anterior pituitary
Stimulates synthesis and secretion of adrenal cortical hormones
ACTH
anterior pituitary
stimulates the synthesis and secretion of adrenal cortical hormones
ACTH
Anterior pituitary
Stimulates melanin synthesis
MSH
Anterior pituitary
Milk ejection, uterine contraction
OXytocin
posterior pituitary
Stimulates water reabsorption by renal collecting ducts and contraction of arterioles
ADH
Posterior pituitary
Skeletal growth; increase oxygen comsumption, heat production, increase protein, fat and CHO use; maturation of nervous system (perinatal)
L-Thyroxine
Triiodothyronine
Thyroid gland
Stimualtes gluconeogenesis; antiinflammatory; immunosuppression
Glucocorticoids
adrenal cortex
Growth and development of female reproductive organs; follicular phase of menstrual cycle
Estradiol
Ovary
Luteal phase of menstrual cycle
Progesterone
Ovary
Spermatogenesis; male secondary sex characteristics
testosterone
Testes
Increase serum calcium, decrease serum phosphate
PTH
parathyroid gland
Decrease serum calcium
Calcitonin
Thyroid gland (parafollicular cells)
Increase renal sodium reabsorption, increase renal K secretion, Increase renal H secretion
Aldosterone
adrenal cortex
Increase intestinal sodium reabsotpion, increase bone mineralization
1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol
Kidney (activation)
Decrease blood glucose, decrease blood amino acid, decrease blood fatty acid
Insulin
Pancrea (Beta cells)
Increase blood glucose, increase blood fatty acids
Glucagon
Pancrea (alpha cells)
increase estrogen and progesterone synthesis in copus luteum of pregnancy
HCG
Placenta
Same actions as growth hormone and prolactin during pregnancy
Human placental lactogen
Placenta
Hormones determine the sensitivity of target tissue by regulating the __________________
number or sensitivity of receptors
- Down-regulation
- Up-regulation
- in the ovary ,estrogen upregulates its own receptor for LH
______are GTP proteins that couple hormone receptors to adjacent effector molecules
G proteins
G proteins are used in the ___________ and __________ second messenger systems
Adenylate cyclase
IP3
G proteins have 3 subunits ____________
alpha
beta
gamma
the _______ subunit can bind either GDP or GTP.
alpha
- when GDP is bound = INACTIVE
- when GTP is bound = ACTIVE
hormones that uses cAMP mechanism
- ACTH
- LH and FSH
- TSH
- ADH (v2 receptor)
- HCG
- MSH
- CRH
- B1 and B2 receptors
- Calcitonin
- PTH
- Glucagon
Hormones that uses IP3 mechanism
GnRH
TRH
GHRH
ATII
ADH (V1 receptor)
Oxytocin
Alpha 1 receptors
Hormones that uses Steroid hormone mechanism
Glucocorticoids
Estrogen
Testosterone
Progesterone
Aldosterone
Vit. D
Thyroid hormone
Hormones that uses tyrosine kinase
Insulin
IGF-1
Growth hormone
Prolactin
Hormones that use cGMP mechanism
ANP
Nitric oxide
Adenylate cyclase mechanism
- Hormone binds to a receptor
- GDP is released from the G protein and relpaced by GTP
- Activated adenylate cyclase catalyzes ATP to cAMP
- cAMP activates protein kinase A
- cAMP is degraded to 5’ AMP by phosphodiesterase
- inhibited by caffeine

IP3 mechanism
- Hormone bind to receptor activates phopholipase C
- via cell membrane
- via a G protein
- Phospholipase C liberates diacylclycerol and IP3
- IP3 mobilizes calcium from ER. Activates protein kinase C

Guanylyl cyclase
- ANP
- Acts through a receptor gyanylyl cyclase. where the extracellular side of the receptors binds ANP and the intracellular side has guanylyl cyclase activity
- NO
- acts through cytosolic guanylyl cyclase
- converts GTP to cyclic GMP, which is the second messenger
Receptor tyrosine kinase
- bind to extracellular side of the receptor
- Intracellular side has intrinsic tyrosine kinase actovoty
- monomer
- dimer
- insulin
- insulin growth factor
mechanism of action of growth hormone
tyrosine kinase-associated receptor
- GH binds to the extracellular side of the receptor
- The intracellular side of the receptor does not have tyrosine activity but is non covalently associated with tyrosine kinase (JAK)
Steroid hormone and thyroid hormone mechanism
- Steroid hormone diffuses across the cell membrane and binds to its receptor
- Hormone-receptor complex enters the nucleus and dimerize
- The hormone-receptor dimers are transcription factors that bind to steroid responsive elements (SREs) and initiate DNA transcription
- New mRNA is produced
- the new protein hace specific physiologic functions

The __________lobe of the pituitary gland is linked to the hypothalamus by the hypothalamic-hypophysial portal system
Anterior
The ________ lobe of the pituitary gland is derived from neural tissues. The cell bodies are located in the hypothalamic nuclei
Posterior
TSH, LH, and FSH belong to the same glycoprotein family. The _________ subunit are identical
Alpha
ACTH, MSH, B-lipotropin and B-endorphin are derived from a single precursor, __________________
Proopiomelanocortin
______ and ______ are produced in the intermediary lobe, which is rudimentary in adult human
Alpha and BEta MSH
Most important hormone for normal growth to adult size.
Growth hormone
Growth hormone is a single chain polypeptode that is homologous with _______ and _______
Prolactin
human placental lactogen
Growth hormone is relased in a __________ manner
pulsatile
Growth hormone secretion is increased by _______________
Sleep, stress, hormones related to puberty, starvation, exercise and hypoglycemia
Growth hormone secretion is decreased by ____________
Somatostatin, somatomedins, obesity, hyperglycemia and pregnancy
__________ ar eproduced when growth hormone acts on target tissues. They inhibit secretion of GH by acting directly on the anterior pituitary and by stimulating secretion of somatostain from the hypothalamus
Somatomedins
Negative feedback control by GHRH and GH
- GHRH inhibits its own secretion from the hypothalamus
- GH also inhibits its own secretion by stimulating the secretion fo somatostatin from the hypothalamus
in the liver, GH generates the production of ________________, which serves as the intermediaries of several physiologic actions
Somatomedins (insulin-like growth factor)
- the IGF receptor has tyrosine kinase activity
Growth hormone deficiency
- Lack of anterior pituitary GH
- hypothalamic dysfunction
- Failure to generate IGF in the liver
- Growth hormone receptor deficiency
Growth hormone excess can be treated with ____________
Somatostatin analogs (octreotide) which inhibit growth hormone secretion
Hypersecretion of growth hormone causes __________
Acromegaly
- Before puberty = increased linear growth (gigantism)
- After puberty = causes increased periosteal bone growth, increased organ size, and glucose intolerance
Major hormone responsible for lactogenesis
Prolactin
- Participates with estrogen, in breast development
- structurally homologous to growth hormone
Prolactin secretion is tonically inhibited by _____________
Dopamine
- TRH increases proalctin secretion
Regulation of prolactin secretion

Actions of prolactin
- Stimulates milk production
- Stimulates breast development
- Inhibits ovulation (decreasing synthesis and relase of GnRH)
- inhibits spermatogenesis
Prolactin excess
- hypothalamic destruction (loss of inhibitory control)
- prolactinomas
- galactorrhea
- Failure to ovulate and amenorrhea
Prolactin excess can be treated with _________
bromocriptine
Hormones of the posterior lobe of the pituitary
ADH and Oxytocin
- synthesized in the hypothalamic nuclei
- package in secretory granuleswith their respective neurophysins
- travel down the nerve axons by secretion by the posterior pituitary
ADH originates primarily in the ___________ ofthe hypothalamus
supraoptic nuclei
- Regulates serum osmolarity by increasing water permeability of the late distal tubules and collecting duct
Factors that increase ADH secretion
- Serum osmolarity
- volume contraction
- Pain
- Nasuea (powerful stimulant)
- Hypoglycemia
- Nicotine , opiates, antineoplastic drugs
Factors that decrease ADH secretion
- Decrease serum osmolarity
- ethanol
- alpha agonists
- ANP
Actions of ADH
- Increase water permeability (aquaporin 2) of the principal cells of the late distal and collecting ducts (via V2 receptor and adenylate cyclase- cAMP mechanism)
- Constriction of vascular smooth muscle (via V1 receptor and an IP3/calcium mechanism)
Oxytocin origanates primaruly in the ____________ of the hypothalamus
paraventricualr nuclei
- causes ejection of milk from the breast when stimualted by suckling.
Major stimulus for oxytocin secretion
Suckling
- Afferent fibers carry impulses from the nipple to the spinal cord. Relays in the hypothalamus trigger the release of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary
Actions of oxytocin
- contraction of myoepithelial cells in the breast
- Contraction of the uterus
- reduce post partum bleeding
_______is synthesized from tyrosine in the thyroid follicular cells, packaged in secretory vesicles, and extruded into the follicular lumen
Thyroglobulin
___________ present in the thyroid follicular epithelial cells
Actively transports I into the thyroid follicular cells for subsequent incoporation into thyroid hormones
The iodide (I) pump or Na-I cotransport
- Inhibited by thiocyanate and perchlorate anions
Oxidation of I to I2 is catalyzed by ___________ in the follicular cell membrane
Peroxidase
- I2 is the reactive form, which will be “organified” by combination with tyrosine on thyroglubulin
The peroxidase enzyme is inhibited by _________, which is used therapeutically to reduce thyroid hormone syntheis for the treament of hyperthyroidism
Propylthiouracil
Organification of I2 involves tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin react with I2 to form _________ and ____________
Monoidotyrosine and Diiodotyrosine
High levels of Iodide inhibit organification and therefore inhibit synthesis of thyroid hormone
Wolff-Chaikoff effect
Coupling reactions of MIT and DIT
- When 2 molecules of DIT combine, T4 is formed
- when 1 DIT combines with 1 MIT, T3 is formed
Leftover MIT and DIT are deiodinated by ___________. The I2 that is released is reutilized to synthesize more thyroid hormones
Thyroid deiodinase
In the circulation, most of the T3 and T4 is bound to __________
thyroxine-binding globulin
- In hepatic failure, TBG levels decreases, leading to decrease in total thyroid hormone levels, but normal levels of free hormone
- In pregnancy, TBG levels increase leading to an increase in total thyroid hormone levels, but notmal levels of free hormone
In the peripheral tissues T4 is converted to T3 by ____________
5’-iodinase
- T3 is more biologically active than T4
Synthesis of thyroid hormones
- Thyroglobulin is synthesized
- Iodide pump or Na-I cotransport
- Oxidation of I to I2
- Organification of I2
- Coupling of MIT and DIT
- Stimulation of thyroid cells by STG
- Binding of T3 and T4
- Conversion of T4 to T3
TSH increases both the synthesis and the secretion of thyroidhormones by the follicular cells via an ______________ mechanism
adenylate cyclase - cAMP
_____ down regulates TRH receptors in the anterior pituitary and thereby inhibits TSH secretion
T3
____ are components of the immunoglobulin G fraction of plasma proteins and are antibodies to TSH receptors on the thyroid gland.
Thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins
Thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins bind to TSH and like TSH, ____________________
Stimualte the thyroid gland to secrete T3 and T4
Thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins circulate in high concentrations in patients with _________, which is characterized by high circulating thyroid hormones and accordingly, low concentrations of TSH
Grave’s disease
Actions of thyroid hormones
-
Growth
- bone formation
- bone maturation
-
CNS
- Perinatal period
- requires thyroid hormone in perinatal period
- Adulthood
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Perinatal period
-
Autonomic Nervous system
- Upregualtes B1-adrenergic receptors in the heart
-
Basal metabolic rate
- Increased oxygen consumption and BMR
- Increases the syntheis of Na, K ATPase
-
Cardiovascular and Respiratory systems
- Increased CO
-
Metabolic effects
- glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, and glucose oxidation
The overall effect of thyroid hormone is ___________
catabolic
The ________ produces aldosterone
zona glomerulosa
The _______ produces glucocorticoids(cortisol) and androgens (dehydroepiandrosterone and androstenedione)
Zona fasciculata and reticularis
21 carbon steroid include _________, _____________ ,______________ and _______
Progesterone, deoxycortisone, aldosterone, and cortisol
_______ is the precursor for the others in the 21 carbon series
Progesterone
_________ leads to the production of deoxycortisone, which has mineralcorticoid (but not glucocorticoid) activity
Hydroxylation at C-21
________ leads to the production of glucocorticoids (cortisol)
hydroxylation at C-17
______have androgenic acrtivity and are precursors to the estrogens
Androdenic activity
If the steroid has been previously hydroxylated at C17, the C20,21 side chain can be cleaved to yield the 19-carbon steroids ____________ or __________ in the adrenal cortex
Dehydroepiandrosterone
androstenedione
adrenal androgens have a ketone group at C-17 and are exrreted as __________ in the urine
17-ketosteroids
in the testes, androstenedione is converted to ___________
testosterone
______ have estrogenic activity
18 carbon steroids
- Oxidation of the A ring (aromatization) to produce estrogens occurs in the ovaries and placenta, but not in the adrenal cortex or testes
Secretory products of the adrenal cortex and medulla
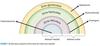
Synthetic pathways for glucocorticoids, androgens, and mineralocorticoids in the adrenal cortex

glucocorticoid secretion oscillates with a 24 hour periodicity or ________
circadian rhythm
- For those who sleep at night, cortisol levels are highest just before walking and lowest evening
CRH-containing neurons are located in the _________ of the hypothalamus
Paraventricular nuclei
CRH binds to receptors on corticotrophs of the anterior pituitary and directs them to synthesize __________ and secretes ACTH
POMC
the second messenger for CRH is _____________
cAMP
ACTH increases steroid hormone synthesis in all zones of the adrenal cortex by stimulating ________ and increasing the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone
cholesterol desmolase
Chronically increased levels of ACTH cause ___________ of the adrenal cortex
Hypertrophy
The second messenger for ACTH is __________
cAMP
________inhibits the secretion of CRH from the hypothalamus and the secretion of ACTH from the anterior pituitary
Cortisol
the _________ is based on the ability to inhibit of dexamethasone to inhibit ACTH secretion.
Dexamethasone suppression test
- In normal persons, low dose dexamethasone inhibits ACTH secretion and, consequently, cortisol secretion
- In persons with ACTH-secreting tumors, low dose dexamethasone does not inhibit cortisol secretion but high dose does.
- In persons with adrenal cortical tumors, neither low nor high dose dexamathasone inhibits cortisol secretion
an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I.
renin
Angiotensin II acts on the ______________ to increase the conversion of corticosterone to adoseterone
Zona glomerulosa
Hyper or Hypo [K] increases aldosterone secretion.
Hyperkalemia
Actions of glucocorticoids (Cortisol)
- Stimulation of gluconeogensis
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Suppression of the immune response
- Maintenance of vascular responsiveness to catecholamines
Stimulation of gluconeogenesis by cortisols
- Increase protein catabolis,
- Decrease glucose utilization and insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue
- Increase lipolysis, which provides more glycerol for the liver
Anti-inflammatory effects of cortisol
- induce syntheis of lipocortin
- inhibitor of phospholipase A2
- Inhibits production of IL-2 and inhbits proliferation of T lymphocytes
- Inhibit the release of histamine and serotonin from mast cells and platelets
Suppression of the immune response by cortisol
- inhibit production of IL-2 and T lymphocytes, both of ehich are critical for cellular immunity
- Used to prevent rejection of transplanted organs
Maintenance of vascular responsiveness to catecholamines by the cortisol
Up regulates alpa 1 receptors on arterioles, increasing their sensitivity to the vasoconstrictor effects of Norepinephrine
Actions of Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
Increase Na reabsorption (action on the principal cells of the late distal and collecting duct)
Increase renal K secretion(action of the principal cells of the distal tubule and collecting duct)
Increase renal H secretion (action on the alpha intercalated cells of the late distal tubule and collecting duct
Addison disease
Primary adrenocortical insufficiency
- most commonly caused by autoimmune destruction of the adrenal cortex and causes acute adrenal crisis
Adrenocortical insufficiency is characterized by ____________
- Decrease adrenal glucocorticoid, androgen, and mineralocorticoid
- Increase ACTH (low cortisol levels, stimulate ACTH secretion by negative feedback)
- Hypoglycemia (caused by cortisol deficiency)
- Hyperpigmentation
- Weight loss, weakness, nausea, and vomiting
- Decrease pubic and axillary hair in women
- ECF volume contraction, hypotension, hyperkalemia, and metabolic acidosis
most commonly caused by autoimmune destruction of the adrenal cortex and causes acute adrenal crisis
Addison disease
caused nu primary deficiency of ACTH
does not exhibit hyperpigmentation
does not exhibit volume contraction, hyperkalemia, or metabolic acidosis
Secondary adrenocortical insifficiency
Adrenocortical excess
most commonly caused by the administration of pharmacologic doses of glucocorticoids
also caused by primaty hyperplasia of the adrenal glands
Cushing syndrome
- Cushing disease when it is caused by overproduction of ACTH
Cushing disease is characterized by ______
- Increased cortisol and androgren levels
- decrease ACTH (if caused by priamry adrenal hyperplasia or pharmacologic doses of glucocorticosteroids) increase ACTH if caused by overproduction of ACTH
- hyperglycemia
- Increase protein catabolism amd muscle wasting
- Central obesity (round face, supraclavicular fat, buffalo hump)
- Poor wound healing
- Virilization of women (caused by elevate levels of adrenal androgens)
- Hypertension (caused by elevated levels of cortisol and aldoseterone)
- Osteoporosis (elevated cortisol levels cause increased bone reorption)
- striae
inhibitor of steroid hormone synthesis, can be used to treat cushing disease
Ketoconazole
Hyperaldosteronism
Caused by aldosterone secreting tumor
Conn syndrome
Conn syndrome is characterized by __________
- Hypertension (increase sodium reabsorption)
- Hypokalemia (increase K secretion)
- Metabolic alkalosis (aldosterone increases H+ secretion)
- Decrease renin secretion (increase ECF volume and BP inhibit renin secretion)
Most common biochemical abnormality of the steroidogenic pathway
belongs to a group of dosorders characterized by adrenogenital syndrome
21B- Hydroxylase deficiency
21B-hydroxylase deficiency is characterized by _________
- Decrease cortisol and aldosterone levels
- Increase 17-hyrdoxyprogesterone and progesterone levels
- Increase ACTH
- Hyperplasia of zona fasciculata and zona reticularis
- Increase adrenal androgens and increase urinary 17-ketosteroids
- Virilization in women
- Early acceleration of linear growth and early appearance of pubic and axillary hair
- Suppresion of gonadal function in both men and women
17a hydroxylase deficiency is characterized by
- Decrease androgen and glucocorticoid levels
- Increase mineralocorticoid levels
- lack of pubic and axillary hair
- hypoglycemia
- metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia, and hypertension
- Increaase ACTH
_______link beta cells to each other, aplha cells to each other, and beta cells to alpha cells for rapid communication
gap junctions
The major factor that regulates glucagon secretion is the ________________
blood glucose concentration
- Increased blood amino acids stimulate glucagon secretion, which prevents hypoglycemia caused by unopposed insulin in response to a high potential meal
The second messenger for glucagon is
cAMP
Glucose increases the blood glucose concentration
- Increase glycogenolysis
- increase gluconeogenesis
Glucagon increases blood fatty acid and ketoacid concentration
- Glucagon increases lipolysis. The inhibition of fatty acid synthesis in effect “shunts” substrates toward gluconeogenesis
Ketoacids (B-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate) are produced from ___________
acetyl CoA
Glucagon increases urea production
Amino acids are used for gluconeogenesis (stimulated by glucagon), and the resulting amino group are incorporated into urea
Comparison of Insulin and Glucagon

Secrete insulin
Beta cells
Central islet
Secrete glucagon
alpha cells
outer rim of islet
Secretes somatostanin and gastrin
Delta cells
Intermixed
the _______ is packaged and secreted along with insulin, and its concentration is used to monitor beta cell function in diabetic patients who are receiving exogenous insulin
C-peptide
major factor that regulates insulin secretion
Blood glucose concentration
- increased blood glucose stimulates insulin secretion
Mechanism of insulin secretion
- Glucose, the stimulant for insulin secretion, binds to the glut2 receptor on the beta cells
- Glucose is oxidized to ATP, which closes K channels in the cell membrane and leads to depolarization of the beta cells.
- Depolarization opens Calcium channels, which leads to increase in tracellular calcium and then to secretion of insulin
The ____ subunits of insulin receptor span the cell memnrane and have intrinsic tyosine kinase activity.
Beta
Actions of Insulin
-
decreases blood glucose concentration
- Increases uptake of glucose
- Promotes formation of glycogen
- decrease gluconeogenesis (increases the production of 2,6 biphosphate)
-
Decreases blood fatty acid and ketoacid concentraions
- stimualtes fat deposition and inhibits lipolysis
- inhibits ketoacid formation in the liver
-
Decreases blood amino acid concentration
- insulin is anabolic
-
Decreases Blood K concentration
- increases K uptake into the cells
Secreted by the delta cells of the pancrease
Inhibits the secretion of insulin, glucagon, and gastrin
Somatostatin
40% of the total Ca in blood is __________
bound to plasma proteins
- 60% of the total Ca in blood is not bout nad is ultrafilterable
- calcium complexed to anions
- free ionized Ca
_____ calcium is biologically active
Free, ionized
Is seen in growing children
Intenstinal ca absorption exceeds urinary excretion, and the excess is deposited in the growing bones
Positive Calcium Balance
Seen in women during pregnancy or lactation
intestinal calcium absorption is less than calcium excretion, and the deficit comes from the maternal bones
Negative Calcium Balance
Major hormone for the regulation of serum calcium
synthesized and secrered by chief cells
Parathyroid hormones
Secretion of PTH is controlled by serum calcium binding to _____________ in the parathyroid cell membrane
Ca-sensing receptors
- Decreased serum calcium increases PTH secretion
- decreased binding to the calcium sensing receptor
- Mild decreases in serum [Mg] stimulte PTH secretion
- Severe decreases in serm [Mg] inhibit PTH secretion and produce symptoms of hypoparathyroidism (hypocalcemia)
second messenger for PTH secretion by theparathyroid gland is ____________
cAMP
Actions of PTH
- increase in serum calcium and a decrease in serum phosphate
The second messgener for PTH actions on its target tissues is ________
cAMP
PTH _________ bone resorption, which brings both calcium and phosphate from bone mineral into the ECF
increases
Resorption of the organic matrix of bone is reflected in increased_____________excretion
hydroxyproline
PTH inhibits renal phosphate _________ in the proximal tubule and therefore, increases phosphate excretion (phosphaturic effect).
Reabsorption
cAMP generated as a result of the action of PTH on the proximal tubule excreted in the ________
urine (urinaru cAMP)
PTH increases renal calcium reabsorption in the __________.
Distal tubule
PTH increases intestinal Calcium absorption indirectly by stimulating the production of ______________
1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol in the kidney
Primary hyperparathyroidism is most commonly caused by _________
parathyroid adenoma
- Characterized by
- increase serum calcium
- decrease serum phosphate
- increase urinary phosphate excretion (phosphaturic effect of PTH)
- Increase urinary calcium excretion (increased filtered load of calcium)
- Increase urinary cAMP
- increase bone resortption
caused by PTH-related peptide (PTH-rp) secreted by some malignant.
Humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy
- PTHrp has all the physiologic actions of PTH
- Increase serim calcium
- Decrease serum phosphate
- increase urinary phosphate excretion (phosphaturic)
- decrease serum PTh levels
Hypoparathyroidism is most commonly a result of __________ or ______________
thyroid surgery or congenital
- characterized by
- Decrease serum calcium and tetany
- increase serum phosphate (hyperphosphatemia)
- decrease urinary phosphate excretion
______is the result of defective Gs protein in the kidney and bone, which causes end-organ resistance to PTH
Psudohypoparathyroidism type 1a - ALBRIGHT HEREDITARY OSTEODYSTROPHY
- Hypocalcemia
- hyperphosphatemia
- circulating PTH levels are elevated
Effects of Chronic renal failure
- Increased serum phosphate
- decreased ionized calcium
- Decreased production of 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol
- Decreased causes secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Renal osteodystrophy
autosomal dominat disorder with decreased urinary calcium excretion and increased serum calcium
caused by inactivating mutations of the calcium sensing receptors that regulate PTH secretion
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH)
Provides calcium and phosphate to ECF for bone mineralization
Vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency in children
Rickets
In adults, vitamin D causes
Osteomalacia
Vitamin D metabolism
- Cholecalciferol, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, and 24,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol are inactive
-
1,25 dihydroxy cholecalciferol is the active form
- catalyzed by the enzyme 1a-hydroxylase
1a-hydroxylase activity is increased in _______
- Decrease serum calcium
- Increase PTH levels
- Decrease serum phosphate
Actions of 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol
coordinated to increase both calcium and phosphate in ECF to mineralize new bone
- Increases intestinal calcium absorption. Vitamin D-Dependent Ca-binding protein (calbindin D-28K) is induced by 1,25 dihyroxycholecalciferol
- Increase intestinal phosphate absorption
- Increases renal reabsorption of calcium and phosphate
- Increases bone resorption
Calcitonin is synthesized and secreted by the __________ of the thyroid
Parafollicular cells
Calcitonin secretion is stimulated by __________
increase in serum calcium
Calcitonin acts primarily to ________
inhibit bone resorption
_____ is defined by sex chromosone XY in males, and XX in females
Genetic sex
Defined by the presence of tests in males and ovaries in females
Gonadal sex
defined by the characteristics of the internal genital tract and the external genitalia
Phenotypic sex
The testes of gonadal males secretes ____________ and ________
anti-mullerian hormone and testoterone
____ stimulates the growth and differentiation of the wolffian ducts, which develop into male internal genital tract
Testosterone
_____ causes atrophy of the mullerian ducts (which would have become the female internal genital tract
Anti-mullerian hormone
Sexual differentiation in males and Female

The ovaries of gonadal female secretes ______, but not anti -mullerian hormone or testosterone
Estrogen
Testosterone is the major androgen synthesized and secreted by the _______
Leydig cells
Leydig cells do not contain __________ or ________ and therefore do not synthesize glucocorticoids or mineralocorticoids
21B-hydroxylase
11B- hydroxylase
____increases testosterone synthesis by stimulating cholesterol desmolase, the first step in the pathway
LH
Accessory sex organs contain _____, which converts testosterone to its active form, dihydrotestosterone
5a reductase
Finasteride is __________ and may be used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia. because they block the activation of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone in prostate
5 alpha reductase
________ of the hypothalamus secrete GnRH into the hypothalamic -hypophysial portal blood.
Arcuate nuclei
- GnRH stimualtes the anterior pituitary to secrete FSH and LH
FSH acts on the _____ to maintain spermatogenesis.
Sertoli cells
- The sertoli cells also secretes inhibin which is involved in negative feedback of FSH secretion
LH acts to the ____ to promote testosterone synthesis.
Leydig cells
- Testosterone acts via an intratesticular paracrine mechanism to reinforce the spermatogenic effects of FSH in the Sertoli cells
______inhibits the secretion of LH by inhibiting the release of GnRH from the hypothalamus and by directly inhibiting the release if LH from the anterior pituitary
Testosterone
______produced by the sertoli cells, inhibits the secretion of FSH from the anterior pituitary
Inhibin
Actions of testosterone
- Differentiation of epididymis, vas deference and seminal vessels
- Pubertal growth spurt
- Cessation of pubertal growth spurt (epiphyseal closure)
- Libido
- Spermatogenesis in sertoli cells (paracrine effect)
- Deepening of voice
- Increased muscle mass
- Growth of penis and semonal vesicles
- Negative feedback on anterior pituitary
Actions of dihydrosterone
- Differentiation of penis, scrotum, and prostate
- Male hair pattern
- Male Pattern baldness
- Sebaceous gland activity
- Growth of prostate
caused by deficiency of andrigen receptors in target tissues of males
Testosterone and dihydrotestosterone actions in target tissues are absent
Androgen insensitivity disorder (testicular feminizing syndrome)
- Female external genitalia but there is no genital tract.
- Testosterone levels are elevated due to lack of testosterone receptors in the anterior pituitary (lack of feedback inhibition)
In childhood, hormone levels are lowest and FSH____LH
greater than
At puberty and during the reproductive years, hormone levels increase and LH _____ FSH
greater than
In senesence, homone levels are highest and FSH ____ LH
Greater than
Theca cells produce ______ (stimulated at the first step by LH). Andorstenedione diffuses to nearby granulosa cells, which contain 17B-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, which converts androstenedione to testosterone and aromatase which converts testosterone to 17B estradiol (stimulated by FSH)
testosterone
FSH and LH stimulate the following in the ovaries
- Steroidogenesis in the ovarian follicle and corpus luteum
- Follicular development beyond the antral stage
- Ovulation
- Luteinization
Actions of estrogen
- Has both negative and positive feedback effects on FSH and LH secretion
- causes maturation and maintenance of the fallopian tube, uterus, cervix, and vagina
- Causes development of female secondary sex characteristics at puberty
- Causes the development of the breasts
- Upregulates estrogen, LH, and progesterone receptors
- Causes proliferation and development of ovarian granulosa cells
- Maintains pregnancy
- lowers the uterine threshold to contractile stimuli during pregnancy
- Stimulates prolactin secretion (but then blocks its action on the breast)
Actions of progesterone
- Has negative feedbacks effects on FSH and LH secretion during luteal phase
- Maintains secretory activity of the uterus during the luteal phase
- Maintains pregnancy
- Raises the uterine threshold to contractile stimuli during pregnancy
- Participates in development of the breasts
Follicular Phase
- days 0 to 14
- A primordial follicle develops to the graafian stage, with atresia of neighboring follicles
- :LH and FSH are upregulated in theca and granulosa cells
- Estradiol levels increase and cause proliferation of the uterus
- FSH and LH levels are suppressed by the negative feedback effect of estradiol on the anterior pituitary
- Progesterone levels are low
Ovulation
- day 14
- 14 days before menses, regardless of cycle length
-
LH surge (positive feedback)
- burst of estradiol
- Ovulation occurs as a result of the estrogen-induced LH surge
- Estrogen decrease just after ovulation
- Cervical mucus increases in quantity
Luteal phase
- day 14 to 28
- the corpus luteum begins to develop, and it synthesizes estrogen and progesterone
- Vascularity and secretory activity of the endometrium increase to prepare for receipt of a fertilized egg
- Basal body temperature increases because the effect of the progesterone
- If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum regresses at the end of the luteal phase. As a result, estradiol and progesterone levels decrease abruptylu
Menses
- Days 0 to 4
- The endometrium is sloughed because of the abrupt withdrawal of estradiol and progesterone
Menstrual cycle

If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum is rescued from regression by ___________ which is produced by the placenta
human chorionic gonadotropin
The major placental estrogen is __________
Estriol
Prolactin levels ______ steadily during pregnancy
increase
Lactation does not occur during pregnancy because ______ and _____ block the action of prolactin on the breast
Estrogen and progesterone
Ovulation is suppressed as long as ________ continues
lactation
- Inhibits hypothalamic GnRH secretion
- Inhibits the action of GnRH on the anterior pituitary and consequently inhibits LH and FSH secretion
- Antagonizes the actions of LH and FSH on the ovaries


