Drug Receptors & Pharmacodynamics Flashcards
What determines drug dose?
affinity to receptor
- many drugs given in mg amounts and measure in ng/dL concentrations
- mus thave high affinity
Drug size, shape, charge are impt for what characteristic of receptors?
selectivity
what mediates pharmacologic action of drugs?
receptors
-implies “signal transduction”
Dose Response curves

Dose-response curve as semi-log plots
y-axis= agonist effect
x-axis= log (drug concentration)
-yields sigmoidal curve

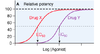
Comparing dose-response curve. Which drug is more portent?
Drug X is more potent than Drug Y
- lower drug concentration for EC50
- but equally efficious (max. effect same)
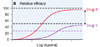
Compare dose-response curves. Which is more efficacious?
Drug X is more efficacious than Drug Y
- ..and more potent too; EC50 is lower
What does competitive antagonist do to the dose response curve?
Competitive antagonist shift curve right
- EC50 also increases
- maximal effect remains the same
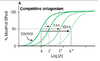
How does competitive antagonism do to the max effect (at high dose)? EC50?
- The max effect (at high does) remains unchanged
- Increased EC50

How does a NON-competitive antagonist do to max effect? EC50?
- Max effect is lower
- EC50 is unchanged
What does a non competitivea antogonist do to the hight of sigmoidal curve on semi-log and non-log
lower maximal height

Chemical antagosnism
Binds to agonist preventing action at receptor
e.g. Protamine vs Heparin
Physiologic antogonism
activate a different pathway with essentially opposite effects
e.g. isulin vs glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia
Potency of dose response curves
- x-axis issue
- what concentration of drug yields 50% maximal effect? EC50

Efficacy Dose-response curve
- y axis issue
- What is the maximal response?

When is Quantal Dose-effect curves used?
when the effect is either/or?
- provide infor about the variation in sensitivity to the drug in a given population.
- response to at progressively increasing doses
- small variation=steep curve
e. g. seizure, relief of headache, death

Media Effective dose/ Media toxic (lethal dose)/ therapeutic index
used in quantal dose effective curves
- ED50
- TD50, LD50
- ratio btw LD50 to ED50: lower index can overdose more easily
Variations in drug response: Idiosyncratic
usually due to genetic diff
Variations in drug response: respose
degree of response varies with therapy
- tolerance
- tachyphylaxis (repsonse dimishes rapidly after administrations, may be related to depletion of neurotransmitters)


