Development of Peripheral Nervous System Flashcards
(22 cards)
The Peripheral Nervous System consist of what?
12 Cranial Nerves
Spinal Nerves
Ganglia
Enteric plexus - inervates gut
Sensory Receptors
Discribe the order of Grey Matter
Dorsal or posterior horn is Sensory
The lateral horn is autonomics
The anterior or ventral horn is motor
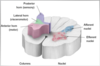
Describe the formation of the spinal cord
Where does it form?
What is the difference between Alar and Baslar plates?
Alar plate is for sensory neurons
Baslar plate is for motor neurons + presynaptic neurons for autonomics
They are seperated by the Sulcus limitans

1st order sensory neurons come from where?
2nd and 3rd?
Embryonic Crest
Alar Plate
Stem cells in the Neural Canal produce what cells in the Ventricular Zone?
Ependmyoblasts
Ependymal cells - Line the ventricals and Central Canal
Choroid plexus cells - Makes CSF
Stem cells in the Neural Canal produce what cells in the Intermediate Zone?
Neurons
Astrocytes - Structural cells that regulate environment
Stem cells in the Neural Canal produce what cells in the Marginal cells?
Mylenated axons (Oligodentrocytes)
Where do Microglial cells come from in the CNS?
What do they do?
Monocytes
Phagocytose debris and dead cells
Where is the end of the spinal cord found in adults vs infants?
L1 or L2 for adults
L2 or L3 for new borns
What cells do neuro crest cells give rise to?
Spinal Ganglion and Sensory Neurons in the periphery
Schwann Cells
How is the alar and basal plate signaled to form the spinal cord
By a gradient
High BMP from Roof plate on alar side activate PAX3 and PAX7 to generate its differentiation
High Shh from floor plate and notocord levels on basal side activate NXK2.2 and NKX6.1 to promote
(just dorsal there are slightly lower Shh and higher BMP, this allows for ventral motor neurons)
Where does the development of the PNS come from
The neuro crest cells and the ectodermal placodes (from ectoderm)?
Specific cells that develop from the neural tube (neuro ectoderm).
motor neurons - located in ventral horn
pre-ganglionic autonomic neurons - located in lateral horn
Specific cells from neurocrest.
Neurons of dorsal root ganglia
Sensory ganglia of cranial nerves
Schwann Cells
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic neurons
Decribe the classifications of motor neurons derived from the neuroectoderm.
GSE (general somatic efferent) - Somatic muscle - somite derived
GVE (general visceral efferent) - autonomics to smooth and cardiac muscles and glands
SVE (Brachial or Special visceral efferent) - muscles derived from pharyngeal arches
Describe the classifications of motor neurons derived from the neurocrest.
- *GVA (General visceral afferent)**: sensory of visceral structures – Ectoderm
- *SSA (Special somatic afferent):** hearing, balance and sight – Endoderm
SVA (Special visceral afferent): taste and smell: chemical
senses
GSA (General somatic afferent): sensory in the skin, joint
capsule, tendon, muscle
The parasympathetic or sympathetic nervous sytem are involved in a two cell link system. Describe this.
What is the difference?
Short peganglionic nerves from spinal cord which are myelinated send signals to long postganglionic nerves which are not
Sympathetic = short to long
Parasympathetic = long to short
Sympathetics come from where?
The lateral horns of the spinal cord. Are found in the T1 to L2.
Parasympathetics come from where?
Cranial Nerves III, XII, IX, X
Sacral 2nd to 4th (GVE)
Ganglia usually found in viscera or in the 4 cranial ganglia
Describe whether the dorsal and ventral root are efferent or afferent
Dorsal = efferent
Ventral = afferent
Motor neurons are derived from what?
The neural ectoderm
(often long axons)
Sensory Neurons are derived from what?
The neura crest


