Derm Portion Flashcards
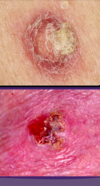
cellulitis

where does this infection occur? what are the 3 organisms most likely to cause this in adults? what are the 3 organisms likely in kids? what are the 5 symptoms the patient will experience? what is the strange animal you can get this from? what do you do to DX this?
acute, spreading inflammation of the dermis and subcuteous tissues, occurs from breaks in the skin
adults: s. aureus, group A strep can get it from cat bite pasturella mulicida
children: hae. influenzae (periorbital), strep pneumoniae, s. aureus
expanding, red, swollen and tender, FEVER!! HEAD!! LYMPAHDENOPHATHY!! EDEMA!! NOT sharply demarkated…pt feels ILL
DX: culturing and drainage of discharge by needle aspiration
cellulitis

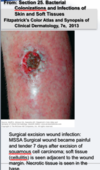
what are the four treatment options? and what is really important to do when treating a cellulitis patient?
- rest/heat
- begin treatment ASAP with abx that cover haemophilis influenzae, strep and staph!
- dicloxacillin or cephalosporin, if allergic to penicillin use erythromycin
- if severe give first generation cephalo IV!!
really important to mark the boarders so you can tell if it is improving or not!! may need surgery if necrotizing infection develops

actinic kerratosis
“solar keratosis”
what does this have the potential to develop into? what type of condition is this? what causes this? who is it more common in? what does it feel like and what cells are increasing? what are the 3 treatment options?

potential to develop ino squamous cell carinoma

thickening of the horny layer of the epidermis, premelignant condition caused by sun exposure
-more common in fair skinned individiuals. can also develop into cutaneous horn!!!
rough dry “sandpaper” appearence from hyperkeratinization** and **plaques
TX: topical 5-fluorouricil, cryrosurgery, laser
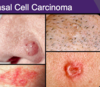
basal cell carcinoma
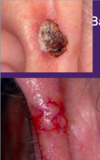
how does this cancer most commonly present? fast or slow? why does the pt ususally seek help? where is it most common? what is the treatment?
MOST COMMON SKIN CANCER
pearly boarder (most common presentation), smooth nodule with telangectasis!!! KNOW THIS
spreads SLOW, easily treated they can itch or bleed and this is why pt seeks help because it won’t heal!!
ear, face, neck most common!!!
Can come in these 3 other presentations, but not as important:
Flat scaly lesions
Flesh colored or Brown
Morpheaform-scar like
Tx: complete eradication
- excise
- curettage
- cryrotherapy
- surgery
- mohs
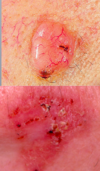
more pics of basal cell carcinoma
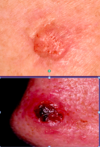
Melanoma

how aggressive? what is it most commonly associated with? metastasis? what colors can it be? what abou borders? how does the pigment spread? what about lesion type? what is the treatment?
VERRYYYYY AGRESSIVE!!!!
80% ASSOCIATED WITH UV RADIATION!!!! (can be in eye and anus)
HIGH METASTASIZEEEEEEE RATE!!!!!
BLACK OR DARK BROWN, SOMETIMES BLUE WITH MULTIPLE COLORS
IRREGULAR BORDERS
OUTWARD SPREADING PIGMENT
CAN BE MACULAR TO NODULAR OR FLAT
Tx:
*****MUST EXCISE ALLL OF IT THROUGH MOHS OR FULL THICKNESS EXCISIONAL BIOPSY!!!*****

what are the four types of melanoma and who/where would you find them?

1. Superficial spreading malignant melanoma
****MOST COMMON***
single melanoma
upper back and legs
mostly adults
plaque irregular
GREAT IRREGULARITY
always growing
2. lentigo maligna melanoma
in eldery
3. nodular malignant melanoma
4. acral lentiginous melanomas
***In palms, soles, nail beds***

what determines the prognostic factor for melanoma mets? what are four regional places with worse prognosis?
the depth of the cancer=breslow’s depth
**deeper=worse prognosis**
worse prognosis if on upper back, upper arm, neck, or scalp
what is the most common melanoma type?
superficial spreading melanoma
where are the 5 places melanoma likes to metastasize?
- lymph nodes
- skin
- liver
- lungs
- brain
what is key in melanoma?
early detection!!!
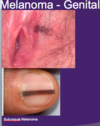
NAIL AND GENITAL MELNOMA

LENTIGO MALIGNA
squamous cell carcinoma
what happens in this? why do patients often seek help? metastasis? what are two things that commonly preced it? what are the treatments?
2nd most common type of skin cancer

originates in the keratinocytes of the mucosa and skin KERATINIZATION
patients often seek help because they bleed or itch and they don’t seem to heel (same as basal)
red firm nodules, scaly with crust, sometimes bleed METASTASIZES
often preceeded by actinic keratosis or HPV
Tx:
excision, curettage, cyrotherapy, radiation, mohs,
squamous cell carcinoma account for what percent of skin cancers?
20 %