deck 8 Flashcards
(25 cards)
What’s the diagnosis?

blocked APC
blocked APC may manifest as:
- delayed R-R interval
- tall T wave in between
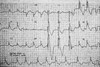
History of chronic Afib with the following rhythm strip.
think of dig toxicity
- rhythm strip shows junctional tachycardia
- in the setting of digoxin usage, this may be CHB w/ junctional escape (“regularized Afib”)
Pt with chief complaint of worsening DOE has below EKG. Most striking feature of this EKG?

electrical alternans
45M p/w worsening chest pain and recent viral illness. EKG shown below. Likely diagnosis?

pericarditis, stage 1 (early)
pertinent EKG findings:
- diffuse concave-up STEs
- PR depression inferiorally
- PR elevation aVR
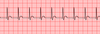
What stage pericarditis is shown below?
pericarditis, stage 3
characterized by:
- isoelectric ST and PR segments
- diffuse T wave inversions
EKG stage of pericarditis?

pericarditis, stage 2 (days later)
characterized by:
- diffuse T-wave flattening
- isoelectric ST segment
Most likely cause of LAD in EKG shown below?

probably LAFB
- LAD + POSITVE QRS amplitude in aVR → axis is between -60 and -90 -> usually happens with left anterior hemiblock
- *note: by definition LAFB has profound left axis deviation (-45 to -60)
48M who doesn’t take any medications has EKG shown below. What EP intervention will he likely need if you restore sinus rhythm?

dual chamber PPM
- EKG shows Aflutter with 6:1 AVB
- > 4:1 AV conduction ⇒ AVN pathology
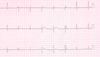
Most likely rhythm in strip shown below?

ectopic low-atrial rhythm
- pertinent EKG findings: regular AV conduction w/ negative P-wave in II
- since PR interval = ~0.12, rhythm is likely low atrial (PR > 0.11 goes w/ atrial source)
35M with syncope while playing tennis has this EKG.

think of HOCM
EKG shows:
- large-amplitude QRS
- pseudoinfarct pattern in precordium
- hypertrophy-related ST changes (HSTs)
Young pt with pleuritic chest pain after being punched in chest has EKG shown below. Biomarkers are negative. Most likely diagnosis?

early repolarization
to better characterize etiology of concave-up STEs, look at V6 ST segment:
- STE:TWH > 25% → goes w/ pericarditis
- STE:TWH
EKG shows
- concave-up STEs in precordial leads
- STE:TWH (v6) ≈ 10% ⇒ early repol more likely
Female with EKG shown below has syncopal episode.

think of apical HCM
- typical apical HCM findings: deep asymmetric TWIs in V3-V6
Brugada criteria for Vtach? (4)
VT diagnosed when ANY of the following present:
- Absence of RS in all precordial leads
- RS interval is > 100 ms in 1+ precordial leads
- AV dissociation
- morphologic criteria in both V1/V2 AND V6
Definition of “RS interval” used in the Brugada criteria for VT?
RS interval = start of R wave to nadir of S wave
Definition of precordial transition lead (PTL)?
PTL = precordial lead where R/S amplitude is 1
Pt with Stage 4 CKD is found with K of 7.2. EKG does not display any ST changes. Why no hyperacute ST changes?
- Peaked T waves usually only occur in ACUTE hyperkalemia
- This pt likely has chronic hyperkalemia from CKD
Differential diagnosis of group beating on EKG? (4)
- sinoatrial dz: 2nd degree SAE block, Blocked APCs
- AVN dz: 2nd degree AVB
- HPS dz: Concealed His-bundle depolarizations
Criteria for pathologic Q wave in Rt precordial leads?
essentially, q of any type in V1-V3
technical definition for Q in Rt precordial leads→ either of the following in V1-V3:
- qR w/ q > 20 ms
- QS
How can you distinguish between the two types of 2nd degree sinus exit block (SEB)?
- 2nd degree SEB, type 1: PP’ is LESS THAN TWICE the normal PP interval
- 2nd degree SEB, type 2: PP’ is a multiple of normal PP interval

*where PP’ = p to p interval that contains pause
What is the diagnosis indicated by the arrows?

aberrantly-conducted APCs
EKG shows:
- APCs
- extra-systolic QRSs that conduct with RBBB pattern
Name 3 features of Ashman’s phenomenon that help distinguish it from PVCs.
- initial QRS forces are same direction as normal sinus beat (and terminal forces are RBBB pattern)
- presence of other normally-conducted APCs
- SAN is reset (should see non-compensatory pause)
What should you think of when pt in question stem has “heart failure” or “Afib?”
digoxin-related EKG findings
EKG presentation of hypothermia? (8)
- atrial arrhythmias: : sinus brady, Afib
- PAN-prolongation of conduction: prolonged PR, widened QRS
- repolarization anomalies: prolonged QTc, Osbourne waves
- pause-dependent escape rhythms: AV junctional escape, VT/VF
What percentage of patients with low body temperature will have hypothermia-induced AFib?
incidence of hypothermia-induced Afib = 50-60%