Congenital Defects Flashcards
What is a congenital defect?
Defect present at birth
What is a genetic defect?
Hereditary gene defect
Are all congenital defects genetic?
No
Are all genetic defects congenital?
No
What does it mean when we say that not all genetic defects are congenital?
Expression/manifestation of defect may not occur at birth; EX: late juvenile and adult onset diseases
What are some examples of late juvenile and adult onset diseases that are genetic but not congenital?
Huntington’s Disease, various Lysosomal Storage Diseases
What can altered cell side, altered structure, and altered function lead to?
Can have effects on organ size and shape its function
What is the outcome of normal lysosomal degradation on a complex substrate?
Small diffusible end products
What is the outcome of lysosomal enxyme deficiency on a complex substrate?
Some small diffusible end products and mostly stored nonmetabolized products
When can you predict the route of cell death in congenital/genetic defects?
If the organelle function is known
When can you predict the timeline, route of organ failure, and systemic effects in congenital/genetic defects?
If the role of the cell is known
What is the primary cause of a lysosomal storage disease?
Genetic defect that leads to an altered protein activity and the accumulation of metabolites in lysosomes.
What are 2 secondary causes of lysosomal storage diseases?
Changes in cellular processes Secondary biochemical pathways
What are 3 downstream pathways that are affected by either the primary or secondary causes of lysosomal storage diseases?
Tissue pathology, altered gene expression, and tertiary biochemical pathways
What is the end result of lysosomal storage disease?
cell/tissue damage and death
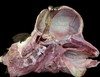
What is this?

Schistosomus reflexus - rare and fatal congenital disorder
What is teratology?
Study of malformations
What are teratogens?
Any substance that causes malformations (viruses, chemicals, radiation that can cause mutations)
What is a malformation?
Morphologically abnormal intrinsic development
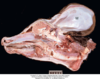
What is a deformation?
Abnormal form due to extrinsic causes (can be biomechanical)
What is an example of a deformation?
Animal with malformed skull due to impingement during pregnancy
What is agenesis?
Total absence of a structure
What is aplasia?
Small remnant of a structure
What is hypoplasia?
Structure never reached apprpriate size (usually will call it hypoplasia if all layers of an organ are present and it is just small)
What is anaplasia?
Loss of cellular differentiation (often indicates irreversible progression to neoplasia)
Neoplasia –> pleomorphism, malignancy
What is dysplasia and what can it be?
Abnormal formation of a structure; can be preneoplastic (EX: hip dysplasia)
What is the difference in frequency of occurrence of congenital defects in humans vs. animals?
Humans = well-documented and reported, studied whenever possible
Animals = frequency not known with certainty, not always possible to observe/document/study
Why are congenital defects in animals not frequently identified?
No necropsy
Why are congenital defects in animals not frequently reported?
May decrease value of breeding line; owners may not know where to report to
Why are fetal death frequencies in animals not known with certainty?
They are not always recognized
Why is frequency of congenital defects in animals not known with certainty and what variables can affect the frequency?
Not identified, not reported, fetal deaths; frequency can be affected by breed or line, presence of toxic plants, etc.
What are two importances about congenital defects?
economic and sentinel