Conflict Flashcards
The Conflict Process
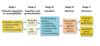
The Dual Concerns Model

Managed Conflict
•Researchers have started to focus more on managing the whole context in which conflicts occur, both before and after the behavioural stage of conflict.
Parties in conflict use one of three frames:
•Interests: people talk about their “positions” but often what is at stake is their underlying interests
•
•Rights: people may be concerned about who is “right” – that is, who has legitimacy, who is correct, and what is fair
•
•Power: people may wish to resolve a conflict on the basis of who is stronger
Characteristics of a Distributive Bargaining Situation
- Starting points (initial offer should allow for concession making)
- Target points
- Resistance point (reservation point/walkaway point)
- Alternative options (BATNA)
Positive bargaining range
Negative bargaining range:
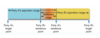
The Role of Alternatives to a Negotiated Agreement
Alternatives give the negotiator power to walk away from the negotiation
- If alternatives are attractive, negotiators can:
- Set their goals higher
- Make fewer concessions
•
- If there are no attractive alternatives:
- Negotiators have much less bargaining power
Effective Negotiation Tactics
Forbearance (waiting is haste
•Requires a lot of patience
Effective Negotiation Tactics
Silence:
Surprise
Demonstrates self-control, confidence, discipline, and calm. Must know when to talk and when to stop.
A sudden shift in the course you have taken
Effective Negotiation Tactics
Fait accompli:
•Involves taking a chance (e.g., violate a patent and then work on a settlement, start a lawsuit, then talk).
Effective Negotiation Tactics
Apparent withdrawal
Reversal
Probing
- Apparent withdrawal: Requires, forbearance, self-discipline and deception.
- Reversal: Act in opposition to what may be considered to be the popular trend or goal.
- Probing/Testing: Helps you identify the other party’s BATNA, target, resistance point, etc.
Effective Negotiation Tactics
Setting limits
Conditions under which one is willing to negotiate.

