Chapter 8 Failure Flashcards
(34 cards)
What is a simple fracture
The separation of a body into two or more pieces
Ductile fracture
- slow crack
- fails with warning
- significant plastic deformation
Brittle fracture
- Rapid crack
- little or no plastic deformation
- fails without warning
cup and cone fracture vs brittle fracture

examples of ductile and brittle fractures

5 stages of a moderately ductile failure
necking, void nucleation, void growth, crack propagation, fracture

principles of fracture mechanics

fracture mechanics formula
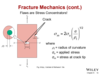
fracture mechanics, stress concentration formula

what is crack propagation
a stepwise discontinuous process, which agrees with propagation observed in the field

crack propagation and its criteria

what is fracture toughness
the measure of a material’s resistance to brittle fracture when a crack is present
fracture toughness formula

plane fracture toughness

What is the difference between fracture toughness and plane strain fracture toughness?
What is the difference between fracture toughness and plane strain fracture toughness?
They are different terms. Toughness is the ability of a material (assumed to be perfect, meaning no cracks) to absorb energy to fracture. It is measured by the area under the stress-strain curve to the point of fracture. Fracture Toughness is the ability of material with pre-cracks to resist fracture by absorbing energy
fracture toughness ranges between
metal alloys
ceramics
polymers
composite fibers

design against fracture formula and scenarios

design example aircraft wing


* quick reference *
Example of brittle fracture of ductile materials

What is an impact test on ductile materials
the amount of energy absorbed by a material during fracture.

what influence does T (temp) have on impact energy

what is fatigue failure
is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface.
*quick reference *
Fatigue Failure

two types of fatigue behavior
two types of fatigue behavior
Fatigue limit - the highest stress that a material can withstand for an infinite number of cycles without breaking —called also endurance
Fatigue life is defined as the number of cycles that lead to the failure of a structural system











