Chapter 4: Identical Particles Flashcards
(20 cards)
Identical Particles
Identical particles are always indistinguishale, because one cannot measure position and momentum simultaneously
- identical ≡ no quantum number or observable to distinguish
- Consider n particles, each with Hilbery Space H1, basis | α >, and dimension d
- Total Hilbert Space Hn
- Basis | α1 . . . αn >
- Dimension dn
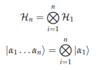
Many-Body Operators
If A is single-particle operator acting on H1, generalization for n-particles
- Ai acts only on particle i
- All many-body operators are symmetric
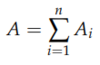
Many-Body Operators
(Momentum)
Many-Body Operators
(Density)
Permutations
- No unique labeling scheme → permutations important
- Permutation are new symmetry, which cannot be broken
- Permutation operator UΠ
- unitary
- operator square-root one → eigenvalues ±1
- Expectation values invariant under permutations → [UΠ, A] = 0
- “identical” ⇐⇒ [UΠ, A] = 0 ∀A which can be measured
- The signum tells you whether you pickup a minus sign when swapping two particles
- Group of all permutations Sn
- Two relevant representations: symmetry and anti-symmetric

Symmetric Representation
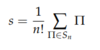
Anti-Symmetric Representation
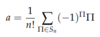
Permutation Hilbert Spaces
- bosons ≡ all symmetric wavefunctions
- fermions ≡ all anti-symmetric wavefunctions
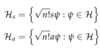
Spin-Statistics Theorem
All (fermions) bosons have (half-)integer spin.

Combined Particles
(Two Fermions: Overview)
- Hilbert Space
- Wavefunction →decompose into orbital φ and spin χ part
- NOTE: Either φ or χ can be anti-symmetric, but not both
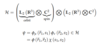
Combined Particles
(Two Fermions: Orbital [Symmetric] Wavefunction)

Combined Particles
(Two Fermions: Orbital [Anti-Symmetric] Wavefunction)
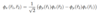
Combined Particles
(Two Fermions: Spin [Symmetric] Wavefunction)
total angular momentum tum s = 1 ≡ triplet state
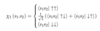
Combined Particles
(Two Fermions: Spin [Anti-Symmetric] Wavefunction)
total angular momentum s = 0 ≡ singlet state

Combined Particles
(Two Fermions: Total Wavefunction)
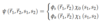
Combined Particles
(Two Bosons)
- Here, no spin
- Higher probability of two bosons being in the same place

Combined Particles
(Bose-Einstein Condensate)

Ground State of Non-Interacting Fermions
- Eigenstates φα(x) with energy Eα
- Project our anti-symmetric part using a
- Resuls in anti-symmetrized Slater determinant

Electrons in Free Space
- Electrons form Fermi sea
- NOTE: Place waves cannot be normalized. so introduce elemental volume with PBC
- Density, Fermi energy, and groundstate energy

Atoms in Periodic Table
Can undersand via Hydrogen atom up to Argon


