Chapter 2: Structural Analysis Flashcards
(19 cards)
Bragg Condition
(3 points)
- Simple explanation for discrete spots in diffraction patterns
- Constructive interference occurs only when Bragg condition is met
- 2d sin θ = nλ
Wave Diffraction of Periodic Solids
(Assumptions: 2 points)
- Wavelength of incident radiation on the order of lattice constant
- λ ≈ A
- Elastic scattering
Bragg Condition Take-Away
(2 points)
- Bragg peaks occur where scattering angle meets condition
- Allows for determination of interplanar spacing d
Fourier Analysis
(2 points)
- Fourier series of function with periodicity or Bravais lattice can only contain wave vectors which belong to reciprocal lattice
- Allows translation between reciprocal and real space
Lattice Planes and Miller Indices
(2 points)
- For every set of parallel planes, there exists lattice vector G that are perpendicular to the planes.
- For shortest one Gmin
- |Gmin| = 2π/d
Bragg Condition Restriction
- λ < 2d
Laue Condition Take-Away
(2 points)
- Allows for discovery of reciprocal lattice basis
- Real lattice can be found from reciprocal lattice
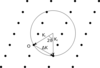
Ewald Construction
(3 points)
- Origin of crystal at center
- Create circle with radius r = 2π/λ = |k|
- Lattice points on perimeter indicate constructive interference
General Refraction Theory
Allows resolution of crystal structure from diffraction patterns
Reciprocal Lattice
(3 points)
- Sell of all vectors k which lead to plane waves with the periodicity of the Bravais lattice
- All k = G such that exp(iGR) = 1, where R is a real space lattice vector
- G is wave vector of reciprocal space
Reciprocal Lattice Vectors
(3 points)
- G = hb1 + k b2 + lb3
- Requirement: G·R = 2πn
- Reciprocal lattice of reciprocal lattice is original lattice
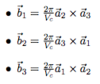
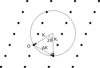
Ewald Construction Purpose
(3 points)
Used to determine:
- Wave vector of incident and refracted beams
- Diffraction angle
- Reciprocal lattice of crystal
Debye-Waller Factor
Used to describe the attenuation of scattering peaks due to thermal motion
Bragg Condition Assumptions
(2 points)
- Crystal consists of parallel planes with separation distance d
- Incident wave partially reflected at each plane
Bragg-Laue Equivalence
(2 points)
- Bragg condition is special case of Laue condition
- For minimum reciprocal lattice vector Gmin
Brillouin Zone
- Wigner-Seitz cell of the reciprocal lattice
Laue Condition
- Constructive interference occurs when the different in incident and refracted wavefectors equals a reciprocal lattice vector
- k’ − k = ∆k = G
Laue Condition Assumptions
(4 points)
- 3D Lattice
- Incoming wave is a plane wave
- Each lattice points re-emits as spherical wave
- Elastic scattering
Structure Factor
Mathematical description of how matter scatters incident radiation


