Chapter 11 Flashcards
(83 cards)
What are the three fundamental steps completed by everything in the nervous system?
- A sensory function detects internal and external stimuli. (receptors) PNS
- An interpretation is made (analysis). CNS PNS
- A motor response occurs (effectors).
What are the functions of the nervous system?
-The nervous system detects environmental changes -responds to such events along with endocrine system -responsible for all our behaviors, memories, and movement *It is able to do this because of the excitable characteristic of nervous tissue -Its ability to generate nerve impulses (action potentials)
What are the two parts of your nervous system?
Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
What does the CNS (central nervous system) consist of?
brain and spinal cord
What does the PNS (peripheral nervous system) consist of?
consists of all nervous tissue outside the CNS -Nerves -Ganglia -sensory receptors
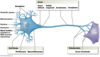
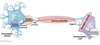
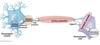
what is a synaptic cleft?
gap between the pre and post synaptic cells
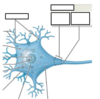
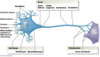
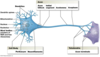
what are dendrites?
-(little trees) are the receiving end of the neuron -short, highly branched structures that conduct impulses toward the cell body
what are the functions of neurons?
-gather information at dendrites -process it in the dendritic tree and cell body -transmit the information down their axon to the axon terminals
what are synaptic vesicles?
membrane sacs that store packets of neurotransmitter chemicals
many neurons contain ____ or ____ types of neurotransmitters?
two or three
each neuron has different effects on the ___________ cell
postsynaptic
a neuron usually has one neurotransmitter, but can have more than one? T/F?
true
what are the four components of most neurons?
-Dendrites -A cell body -An axon -Axon terminals
what are the function of astrocytes?
-provide physical support to neurons -maintain the blood-brain barrier -make scar tissue after CNS injury
what is the function of Oligodendrocytes?
produce myelin in CNS
what is the function of Microglia?
phagocytosis of debris and pathogens
what is the function of Ependymal cells?
form and circulate CSF
what are neuroglia?
-(glial cells) play a major role in support and nutrition of neurons -they do not generate or conduct nerve impulses
what are glial cells?
-(neuroglia) play a major role in support and nutrition of neurons -they do not generate or conduct nerve impulses
do glial cells generate nerve impulses?
no
what is a synapse?
site of communication between two neurons or between a neuron and another effector cell
what does the axon divide into?
-The axon divides into many fine processes called telodendria. -may be highly branched as they interact with the dendrites of “downstream” neurons -the tips swell into bulb-shaped synaptic/axon terminals.
what is telodendria?
-The axon divides into many fine processes called telodendria. -may be highly branched as they interact with the dendrites of “downstream” neurons -the tips swell into bulb-shaped synaptic/axon terminals.
what is an axon?
conduct impulses away from the cell body toward another neuron or effector cell