Cataract Flashcards
1
Q
What is a cataract?
A
- Cloudy lesion (opacity) in the lens that can reduce the transparency of the lens
- Can affect different parts of the lens primarily
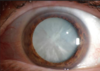
2
Q
Why does the lense appear cloudy in a cataract?
A
Chemical modification of the lens proteins –> change in lens colour

3
Q
What is the epidemiology of Cataracts?
A
Common
- increases with age (56% of >60 YO)
- More likely in females
4
Q
What is the aetiology of the development of cataract?
A
Age
- Or other reasons e.g. Trauma
- Chronic eye condition e.g. anterior uveitis, congestive angle-closure glaucoma and others
- Chronic systemic disease e.g. DMT2, , myotonic dystrophy, neurofibromatosis type 2, and severe atopic dermatitis
- Congenital abnormality in children
5
Q
What are risk factors for the development of a cataract?
A
- FH of age-related cataracts
- corticosteroid treatment
- Smoking
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet B light
- Female gender
6
Q
What are the symptoms of a patient with cataract?
A
Painless, Progressive reduction in visual acuity and sharpness
- Blurred vision
- Worse seeing at night
- Difficulty reading text.
- Sensitivity to light and glare.
- ‘Halos’ around lights and double vision in a single eye.
- Polyopia (multiple images).
- Frequent changes of spectacle prescription as a result of cataracts developing.
- Difficulty recognizing faces.
- Problems watching television.
- Gradual reduction in perception of colour intensity (especially blues)

7
Q
Which investigations would you do in a patient with suspected cataract?
A
- Visual Acuity (Snellen chart)
- Ocular alignment and motility.
- Ophthalmoscopy:
- Defect in red reflex
- Normal Optic nerve and fundus
- Slit-lamp examination to physically examine the lens
- an opacity can be seen in the lens if cataract is present
- Cataract visible
- Intraocular pressure measurement
- To rule out glaucoma, standard measurement
- A glare vision test
- Reduced visual accurate (though maximal spectacle correction)
8
Q
Why does the vision become blury in a patient with cataracts?
A
Protein depositions in lense cause change in refractive pover of lense –> blurred due to no focal point



