(cardioresp) electrocardiography & rhythm disorders Flashcards
what is the clinical relevance of the ECG?
helps to identify conduction abnormalities, structural abnormalities and perfusion abnormalities

what are the advantages of ECGs?
relatively cheap and easy to undertake
reproducible between people and centres and over time
quick turnaround on results and reports

what are the components to an ECG?
electrodes (stick onto skin directly)
cables/wires (connect to electrodes)
leads (results - representation of electrical activity from a specific perspective)

what are the electrodes in an ECG?
small, conductive patches that stick to the skin and are placed at certain spots on the limbs to record electrical activity
what are the leads in an ECG?
an ECG lead is a graphical representation of the heart’s electrical activity which is calculated by analysing data from several ECG electrodes.
what are the cables/wires in an ECG?
cables/wires connect the electrodes on the skin surface to the ECG machine
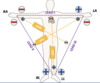
how many electrodes, cables and leads are present in an ECG?
10 electrodes
10 cables/wires
12 leads
why is an ECG important?
used to record the electrical activity of the heart from different angles to both identify and locate pathology
what is a vector?
a quantity that has both magnitude and direction
typically represented by an arrow in the net direction of movement, whose size reflected the magnitude of the vector

how is a vector respresented?
typically represented by an arrow in the net direction of movement, whose size reflected the magnitude of the vector

which electrode are upward deflections towards?
positive electrode
which electrode are downward deflections towards?
negative electrode
what does the steepness of the vector line denote?
the velocity of the action potential
what does the width of the vector line denote?
the duration of the event
what does an isoelectric line represent?
no net change in voltage = no depolarisation occuring
what does an isoelectric line look like?
vectors are perpendicular to the lead
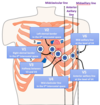
describe the electrical conduction pathway within the heart
sinoatrial node
(via internodal tracts)
atrioventricular node
(via bundle of His)
branched bundles (i.e left and right bundle branches)
Purkinje fibres

when does the line deflect downwards on an ECG?
wave of depolarisation moving towards –ve from +ve
when does the line deflect upwards on an ECG?
wave of depolarisation moving towards +ve from -ve
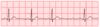
what are the letter components of an ECG?
P, Q, R, S and T
what is a P wave?
the electrical signal that stimulates atrial depolarisation, preceding contraction of the atria (atrial systole) = a few milliseconds apart

what is the QRS complex?
the electrical signal that stimulates ventricular depolarisation, preceding contraction of the ventricles (ventricular systole) = a few milliseconds apart
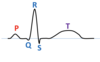
what is a T wave?
the electrical signal that stimulates ventricular repolarisation, preceding relaxation of the ventricles (ventricular diastole) = a few milliseconds apart

what does the QRS complex precede?
ventricular contraction = occurs a few milliseconds after