Bowel Elimination Flashcards
?
Normal process in which our body eliminates (defecation) waste products in the form of feces
Bowel elimination
Motility —> movement
That allows chyme to travel through the small and large intestine through contraction and dilation of smooth muscles (peristalsis)
Normal Defecation
What’s Normal?
Frequency - several times/day to once/week
Minimal effort - NO straining
NO blood; no use of laxatives
If one passes stools
- without excessive urgency (running to bathroom)
- with minimal effort and no straining
- without blood loss
- without the use of laxatives
Normal Stool
- Soft, formed, semisolid, approx 75% water and 25% solid
- If passage through colon is slower more water is absorbed from the feces, making it dry and hard, more difficult to pass
- If passage through colon faster than normal, less water is absorbed from feces and stools are watery
Factors Affecting Bowel Elimination
* Developmental Stage
Adults
- Patterns set in childhood continue through to adulthood
- Dependent on diet (fiber intake), fluid intake, and activity level
- Peristalsis, intestinal smooth muscle tone, perineal muscle tone, and sphincter control decrease with age
Infant
? - green, black, tarry, sticky, odorless stools
? - golden yellow stools
? - tan stools
Stools tend to be watery d/t immature large intestine… as normal flora (bacteria) develops stools become firmer
Meconium
Breastfeed
Formula-fed
Children
2-3 years age develops ability to control defecation
Requires neural and muscular control as well as conscious effort
Factors Affecting Bowel Elimination cont’d
* Personal & sociocultural factors
Privacy
- Time to have a bowel movement
- New parents
- Fast-paced jobs
- Embarrassment/public bathrooms
Stress
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Primary risk factor for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
* Nutrition, hydration, & activity level
Diet
- Food promotes peristalsis (green leafy vegetables)
- High-fiber food increases peristalsis
- Yogurt
Supplements
- Calcium (can cause constipation), magnesium, Vitamin C (these 2 loosen stool)
Hydration
- 6-8 eight ounce glasses of fluid/day (1500-2000 mL)
Activity
- Physical activity promotes peristalsis
- Sedentary living leads to weak abdominal muscles
Factors Affecting Bowel Elimination cont’d
* Medications
Antacids
- Neutralize stomach acid; used for heartburn; SLOW peristalsis
- Milk of magnesia, Maalox, Mylanta, Alka Seltzer
Aspirin & other NSAIDs
- Naproxen, Ibuprofen, celecoxib (Celebrex)
- Irritate stomach; over usage may lead to ulcerations of the stomach or duodenum
Antibiotics
- Destroy bacteria but also destroy bacteria normally found in the intestinal flora - this leads to diarrhea
- To maintain colon bacteria client may use supplemental probiotics (Acidophilus) or yogurt
Iron
- Clients who take supplemental iron to treat anemia for example may have constipation; iron also changes stool color to black
- If taken on an empty stomach may cause nausea
Pain Medications
- Opioids (narcotics) slow peristaltic movement and leads to constipation
Factors Affecting Bowel Elimination cont’d
Antimotility Drugs
- Used to treat diarrhea; they slow peristalsis by direct action on the lining of the GI tract by either inhibiting local reflexes (Bismuth), direct action on the muscles of the GI tract to slow activity (loperamide), or action on CNS that causes GI tract to spasm and slow motility (diphenoxylate)
- Diphenoxylate (Lomotil), loperamide (Imodium), Bismuth subsalicylate
- Adverse effects: GI discomfort, distention, dry mouth, nausea, constipation, dizziness, drowsiness, tiredness
Laxatives or cathartic
- Short-term treatment of constipation
- Stimulates peristalsis
* Prevent straining (MI patients)
* Help evacuate bowel for certain diagnostic procedures
> Chemical stimulant
> Bulking agents
> Osmotic laxatives
> Stool softeners
> Lubricant laxatives
Chemical Stimulants
- Irritate plexus nerve leading to increased peristalsis
- Senna (Senokot), Bisacodyl (Dulcolax), castor oil (blocks absorption of fats)
Chemical Stimulants cont’d
- Adverse effect…diarrhea, abdominal cramping, nausea, and cathartic dependence
- Because they interfere with timing and process of absorption, should be taken 30 minutes apart from other medications
Bulking Agents
- Non-foods high in FIBER - increase motility by increasing fluid into the intestine - this enlarges bulk & stimulates stretch receptors
Bulking Agents cont’d
- MUST be taken with plenty fluid
* Fiber attracts fluid into colon and increased bulk stimulates urge to defecate
* DRUG OF CHOICE FOR TREATMENT OF CONSTIPATION
* Metamucil, Citrucel, FiberCon, psyllium
* Adverse effects: diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, dizziness, weakness may be r/t loss of fluid and electrolyte imbalance
Osmotic laxatives
- Add water to bowel thus distending bowel
- Polyethylene glycol (MiraLax), lactulose, magnesium citrate, magnesium hydroxide (MOM)
Pregnancy
- Morning sickness leads to loss of fluid leading to less fluid in the bowel - constipation
- As uterus gets bigger intestines get displaced - constipation
- Progesterone also decreases motility
Stool softeners
- Allow moisture and fat to penetrate stool
- Docusate sodium
Lubricant laxatives
- Coat stool & GI tract with thin waterproof layer, interfering with absorption (also impedes absorption of nutrients)
- Mineral oil
- Used with clients with hemorrhoids, or recent rectal surgery; also used with clients who shouldn’t strain d/t diseases like MI
- Adverse effects: diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, dizziness, headache, weakness may be r/t loss of fluid and electrolyte imbalance
Surgery & Procedures
Anesthesia
- General anesthesia as well as pain medications administered pre & post-op slow motility - constipation
Stress
- Stress caused by the operative process leads to activation of general adaptation syndrome (GAS), autonomic nervous system, and endocrine responses which all lead to slowing down of the peristaltic movements
Surgery & Procedures cont’d
Bowel manipulation during surgery
- Abdominal surgery or pelvic surgeries where bowel is manipulated may lead to paralytic ileus - cessation of peristalsis movement; bowel continues to produce secretions - secretions remain stagnant, cause distention and discomfort, usually these patients end up with an NGT to low-constant or intermittent suction to remove secretions until bowel movements resume
Surgery & Procedures cont’d
Decreased mobility
- r/t pain
Perineal surgery
- Episiotomy… fear of pain or tearing sutures when moving bowels
Surgery & Procedures cont’d
Anal sphincter surgery
- Uncontrolled rectal drainage after surgery
Pathological Conditions
?
- “an adverse health effect arising from an immune response that occurs reproducibly on exposure to a certain food”
- Common allergens: dairy, egg whites, shellfish, gluten, peanuts, citrus fruits, & soy
- Immune response trigger reactions mild rash to anaphylactic shock
- Common GI symptoms: constipation, diarrhea, red blister rash to anus, abdominal discomfort, bloating, excessive gas and intestinal bleeding
food allergies
Pathological Conditions cont’d
Food intolerances
- Difference between food allergy and food intolerance is that food intolerance is ?
- Discomfort, pain, gas, bloating, diarrhea, constipation…AFTER consuming certain foods
specifically linked to the GI system
?
Enzyme lactase deficiency…needed for the breakdown of milk sugar (lactose)
Can mimic a food allergy but it’s not immune-related…sometimes r/t lack of something (enzyme) in our body
Lactose Intolerance
Pathological Conditions cont’d
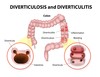
?
- Areas of the colon that balloon out from increased force on mucosal tissues…happens when colon must repeatedly push highly compacted fecal matter making the muscles work harder thus enlarging the muscles
- Sometimes the sac-like pouches become infected and ___ (inflammation) occurs
- Risk factors include low fiber diet, high intake of red meats, and obesity
Diverticulosis
Diverticulitis
Assessment of Bowel Elimination
Focused nursing history
- What’s normal?
- Look at client reactions
> Embarrassment
> Appropriate language that makes patient comfortable
> Ask about any medications, including over-the-counter - especially calcium or iron supplements associated with constipation
Medications that are associated with constipation
- Antacids containing aluminum hydroxide (Mylanta or Gaviscon) or calcium carbonate (Caltrate or Tums)
- Anticholinergic drugs (belladonna, ipratropium (Atrovent), tiotropium (Sipriva), tolterodine (Detrol)
- Anticonvulsants (phenytoin)
- Antidiarrheals (loperamide)
- Antihistamines (diphenhydramine)
- Antiparkinsons (amantadine hydrochloride)
Medications that are associated with constipation cont’d
- Antipsychotic (chlorpromazine)
- Calcium channel blockers (verapamil); calcium supplements
- Diuretics (furosemide)
- Iron supplements; lithium
- NSAIDs (ibuprofen); opioids (morphine)
- Sympathomimetics (ephedrine); tricyclic antidepressants (nortriptyline)