Body Parts Flashcards
IT band
Leg

Piriformis
Front hip
- associated with sciatica, cause leg pain
Sciatica refers to back pain caused by a problem with the sciatic nerve. This is a large nerve that runs from the lower back down the back of each leg. When something injures or puts pressure on the sciaticnerve, it can cause pain in the lower back that spreads to the hip, buttocks, and leg.

Gluteus medius and maximus
gluteus medius and gluteus maximus are primary abductors of the hip and as such they can prevent hip adduction (knees inward).

serratus anterior
front under shoulder
weak serratus anterior can result in an inability of these scapular muscles to hold the medial border of the scapula in place against the ribs. This is known as scapular “winging” and results in instability in the scapulothoracic joint that can lead to instability and injury in the shoulder girdle and/or shoulder joint.

infraspinatus
near lat - tight muscle may cause internal shoulder rotation
The infraspinatus and teres minor are primary external shoulder rotators; if they are tight, they will limit internal shoulder rotation. ACE Personal Trainer Manual (5th ed.), page 184

teres minor
near shoulder
The infraspinatus and teres minor are primary external shoulder rotators; if they are tight, they will limit internal shoulder rotation. ACE Personal Trainer Manual (5th ed.), page 184

lateral epicondyle
elbow
“Tennis elbow” is a common name for lateral epicondylitis, or inflammation of the wrist extensor tendons at their origin on the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. ACE Personal Trainer Manual (5th ed.), pages 581-582

pectorals
shoulders
a standing posture with shoulders that are rounded forward and hands that face backward instead of toward each other is indicative of shortened pectorals and latissimus dorsi, as well as overstretched and potentially weakened scapular retractors and shoulder external rotators that passively allow the shoulders to fall forward into internal rotation.

latissimus dorsi
latissimus dorsi

a standing posture with shoulders that are rounded forward and hands that face backward instead of toward each other is indicative of shortened pectorals and latissimus dorsi, as well as overstretched and potentially weakened scapular retractors and shoulder external rotators that passively allow the shoulders to fall forward into internal rotation.
suprailium
tummy fat for skin fold test
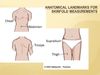
tensor fascia latae
hip

plantarflexors
calf - point foot down

rectus fermoris
one of the quad

iliopsoas
hip

carpal tunnels
wrist

infraspinatus
shoulder

Muscle spindle (nerve)
senses stretch and speed
The muscle spindle is a proprioceptor. a sense organ that receives information from muscle, that senses STRETCH and the SPEED of the stretch. When you stretch and feel the message that you are at the ENDPOINT of your stretch the spindle is sending a reflex arc signal to your spinal column telling you not to stretch any further. This sense organ protects you from overstretching or stretching too fast and hurting yourself.
https://www.unm.edu/~lkravitz/Exercise%20Phys/spindleGTO.html
Golgi Tendon Organ
senses tension of stretch.
The golgi tendon organ is a proprioceptor, sense organ that receives information from the tendon, that senses TENSION. When you lift weights, the golgi tendon organ is the sense organ that tells you how much tension the muscle is exerting. If there is too much muscle tension the golgi tendon organ will inhibit the muscle from creating any force (via a reflex arc), thus protecting the you from injuring itself.
https://www.unm.edu/~lkravitz/Exercise%20Phys/spindleGTO.html
cervical spine extensors
back of the neck
hip abductors
hip abdutors
if weak, together with weak gluteus medius and maximus, the other side of the pelvis will drop more than 5 degress

hip adductors
hip adductors

external hip rotators
external hip rotators

hip flexors
hip flexors

hip extensors
hip extensors

















