5.1.5 Plant and Animal Responses (not complete!!) Flashcards
What is the central nervous system (CNS)?
- made up of the brain and the spinal cord
What is the peripheral nervous system?
- made up of the neurones that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
- has two different functional systems
What are the two different functional systems of the peripheral nervous system?
- somatic nervous system: controls conscious activities
- autonomic nervous system: controls unconscious activities
- this has two divisions which have opposite effects on the body
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
- part of the peripheral nervous system and the autonomic nervous system
- the flight or fight system
- releases the neurotransmitter nooradrenaline
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
- rest and digest
- calms the body down
- neurones release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
What does the hypothalamus found and what does it control?
- found just above the pituitary gland
- maintains body temperature
- hypothalamus produces hormones and controls the pituitary gland
Where is the pituitary gland and what does it do?
- found beneath hypothalamus
- controlled by the hypothalamus
- releases hormones and stimulates other glands e.g. adrenal glands to release their hormones
Where is the medulla oblongata and what is its function?
- at the base of the brain, top of the spinal cord
- automatically controls breathing rate and heart rate
Where is the cerebellum and what does it control?
- underneath the cerebrum, at the back
- has a folded cortex
- controls muscle coordination, posture and coordination of balance
Where is the cerebrum and what does it control?
- largest part of the brain
- divided into the two cerebral hemispheres
- has a thin outer layer called cerebral cortex, which is highly folded
- involved in vision, hearing, thinking, learning
Describe the blinking reflex
- sensory nerve endings in the cornea are stimulated by touch
- a nerve impulse is sent along the sensory neurone to a relay neurone in the CNS
- impulse is then passed from the relay neurone to motor neurones
- motor neurones send impulses to the effectors, the orbicularis oculi muscles that move your eyelids
- these muscles contract causing your eyelids to close quickly and prevent your eye from being damaged
Describe the knee jerk reflex
- stretch receptors in the quadriceps muscle detect that the muscle is being stretched
- a nerve impulse is passed along a sensory neurone, which communicates directly with a motor neurone in the spinal cord
- no relay neurone involved
- motor neurone carries the nerve impulse to the effector (quadriceps muscle), causing it to contract so the lower leg moves forward quickly
Describe what happens during fight or flight response?
- nerve impulses from sensory neurones arrive at the hypothalamus, activating both the hormonal system and the sympathetic nervous system
- the pituitary gland is stimulated to release the hormone ACTH
- this causes the cortex of the adrenal gland to release steroidal hormones
- the sympathetic nervous system is activated, triggering the release of adrenaline from the medulla region of the adrenal gland which then has these effects: (see other flashcard)
What effects do adrenaline and sympathetic nervous system have during fight or flight response?
- heart rate is increased, so blood is pumped around faster in the body
- muscles around the bronchioles relax, so breathing is deeper
- glycogen is converted to glucose, so more glucose is available for muscles to respire
- muscles in the arterioles supplying the skin and gut constrict and muscles in the arterioles supplying the heart, lungs and skeletal muscles dilate, so blood is diverted from the skin in the gut to the heart, lungs, and skeletal muscles
- erector pili muscles in the skin contract, making hairs stand on end so the animal looks bigger
How do the nervous and hormonal systems control heart rate?
Nervous system:
- the sinoatrial node (SAN) generated electrical impulses that cause the cardiac muscles to contract
- the rate at which the SAN fires are unconsciously controlled by a part of the brain called the medulla
- animals need to alter their heart rate to respond to internal stimuli
- stimuli are detected by pressure receptors and chemical receptors:
- baroreceptors in the aorta and vena cava are stimulated by high and low pressure
- chemoreceptors in the aorta, the carotid artery and in the medulla monitor the oxygen level in the blood and also CO2 and pH
- electrical impulses from receptors are sent to the medulla along sensory neurones
- the medulla process information and sends impulses to the SAN along motor neurones (look at the table)
Hormonal:
- helps to control heart rate by releasing adrenaline
- adrenaline bonds to specific receptors in the heart
- this causes the cardiac muscle to contract more frequently and with more force, so heart rate increases and heart pumps more blood
What is important about the circulatory system?

How can heart action be modified to adapt to the needs of tissues?

Why is cardiac muscle in the heart myogenic?
- it can initiate its own beat at regular intervals
Why is a coordination mechanism necessary for heart beat?
- the atrial muscle has a higher myogenic rate than the ventricular muscle
- the two pairs of chambers must contract in a coordinated fashion or the heart action will be ineffective
Describe the heart’s own pacemaker
- the sinoatrial node (SAN) initiates waves of excitation that usually override the myogenic action of the cardiac muscle
- the SAN is a region of tissue that cna initiate an action potential, which travels as a wave of excitation over the atrial walls, through the AVN and down the Purkyne fibres to the walls of the ventricles, causing them to contract
- adrenaline also directly causes the heart to increase its rate of contraction
How can the frequency of excitation waves be altered, changing the heartrate?
- by the output from the cardiovascular centre in the medulla oblongata
- nerves from the cardiovascular centre supply the SAN
- they are part of the autonomic nervous system
- they do no initiate a contraction but can affect the frequency of contractions
Which nerve causes the heart rate to increase?
- action potentials sent down a sympathetic nerve (the accelerans nerve)
- causes the release of noradrenaline at the SAN
- increasing the heartrate
Which nerve causes the heart rate to decrease?
- action potentials sent down the vagus nerve
- release neurotransmitter acetylcholine
- reduce heart rate
What kind of sensory input to the cardiovascular centre changes heart rate
- stretch receptors in the muscles detect movement of the limbs
- sends impulses too cardiovascular centre informing that extra oxygen is needed
- increase in heart rate
- more see pic

What is used to artificially control heart rate?

What are the two protein filaments in muscle?
- actin
- myosin
What are the three types of muscle?
- involuntary (smooth)
- cardiac
- voluntary (skeletal, striated)
Describe the structure involuntary (smooth muscle) and where it is found
- consists of individual cells
- they are tapered at both ends
- at rest each cell is about 500µm long and 5µm wide
- each cell contains a nucleus and bundles of actin and myosin

Describe the contraction of involuntary muscle
- contract slowly and regularly
- it does not tire quickly
- controlled by the autonomic nervous system
Describe the structure and location of cardiac muscle
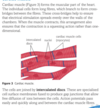
Describe the contraction of cardiac muscle

What does cardiac muscle look like?

Describe the structure of voluntary (skeletal or striated) muscle
- the muscles are arranged in pairs called antagonistic pairs
- muscle cells form fibres of about 100µm in diameter
- each fibre is multinucleate and surrounded by a membrane called the sarcolemma
- muscle cell cytoplasm is known as sarcoplasm
- it is specialised to contain many mitochondria and an extensive sarcoplasmic reticulum
- contents of fibres are arranged into a number of myofibrils, which are contractile elements
- these myofibrils are divided into a chain of subunits called sarcomeres
- sarcomeres contain the protein filaments actin and myosin
- actin and myosin are arranged into a banded pattern,
- dark bands are A bands and lighter are I bands

What muscle is this?

- voluntary muscle
What is a neuromuscular junction?
- skeletal muscles’ contractions are stimulated by the somatic nervous system
- the junction between the nervous system and the muscle is a neuromuscular junction
- it has similarities to synapses
How is muscle contraction stimulated?
- action potentials arriving at the end of the axon open calcium ion channels in the membrane
- calcium ions flood into the end of the axon
- vesicles of acetylcholine move towards and fuse with the end membrane
- acetylcholine molecules diffuse across the fap and fuse with receptors in the sarcolemma
- this opens sodium ion channels, which allow sodium ions to enter the muscle fibre, causing depolarization of the sarcolemma
- a wave of depolarization spreads along the sarcolemma and down transverse tubules into the muscle fibre
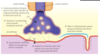
What is a motor unit?
- some motor neurones stimulate single muscle fibres
- however, many motor neurones divide and connect to several muscle fibres
- all these muscle fibres contract together, providing a stronger contraction
- this is a motor unit


