2.1.2 Biological Molecules (Foundations in Biology) Flashcards
What’s the role of water in the body?
- provide a medium for reactions to occur
- transport medium e.g. blood
- maintain osmotic balance
- cooling mechanism i.e. sweating
- waste removal
- formation of urine
What are the roles of carbohydrates in the body?
Simple Sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides):
- use in respiration to provide energy for cells
- other roles e.g. attracting animals to eat fruit
Complex Carbohydrates (polysaccharides):
- starch and glycogen are energy stores
- cellulose: plant cell walls
What are the roles of lipids in the body?
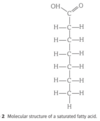
Fats and Oils (triglycerides):
- insulation
- protection of organs
- stored energy
Cholesterol:
- component of cell membranes
Steroid Hormones:
- testosterone, oestrogen, progesterone (sex hormones)
What are the roles of proteins in the body?
- enzymes
- some hormones
- antibodies
- blood clotting
- muscles
- structural roles e.g. keratin in hair and collagen in skin
- channel protein and protein pumps
- haemoglobin (transports oxygen)
What are the role of nucleic acids in the body?
DNA: - stores genetic info
- codes for proteins
RNA: - protein synthesis
Draw a water molecule

What are hydrogen bonds?
- a weak interaction which happens between slightly negatively charged atom (O, N, F) and slightly positively charged hydrogen
- they form between adjacent water molecules
- weaker than covalent bonds
Draw how water molecules are joined by hydrogen bonds

Name six properties of water, related to its importance for organisms
- liquid at room temperature
- ideal density
- ideal solvent
- cohesion and surface tension
- high specific heat capacity
- high latent heat of vaporisation
Describe and Explain why water being a liquid of room temperature is important to organisms
- as the water molecules move, they continually make and break hydrogen bonds
- the hydrogen bonds make it more difficult for them to escape to become a gas
- even with H bonds, water has quite a low viscosity so flows easily
water:
- provides habitats
- provides a reaction medium for chemical reactions
- forms a major component of tissues in organisms
- provides an effective transport medium (e.g. blood)
Describe and explain why the density of water is important to organisms
- water behaves differently from other liquids
- when most liquids get colder, they become more dense
- however, as water goes from 4 degrees Celsius to freezing point, due to its polar nature, the water molecules align themselves in a structure which is less dense than liquid water
due to this:
- aquatic animals live in a stable environment
- bodies of water are insulated against extreme cold, layers of ice reduce rate of heat loss
- organisms can live on ice
Describe and Explain why water being a solvent is important to organisms
- water is a good solvent for many substances found in living things (e.g. ionic solutions NaCl)
- since water is polar, positive and negative parts of water molecules are attracted to the negative and positive parts of the solute
- water molecules cluster around these parts of the solute molecules or ions and will help separate them and keep them apart
- so they dissolve and a solution is formed
- molecules and ions can move around and react together in water e.g. in the cytoplasm of the cell
- molecules and ions can be transported around living things whilst dissolved in water
Describe and Explain why cohesion and surface tension of water is important to organisms
- water molecules show cohesion, which is when H bonds between them pull them together
- this happens at the surface of the water as well:
- at the surface, water contracts as molecules are pulled inwards and gives the surface of the water the ability to resist force applied to it
- this is surface tension
because of cohesion and surface tension:
- transport in the xylem relies on cohesion between water molecules sticking together
- surface tension allows small insects to walk on water
Describe and Explain why high specific heat capacity of water is important to organisms
- water require a lot of energy to increase its temperature
- a lot of energy is needed to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules
- this means that water does not change temperature easily
- organisms need a stable temperature for enzyme-controlled reactions to happen properly
- aquatic organisms need a stable environment to live
Describe and Explain why high latent heat of vaporisation of water is important to organisms
- when water evaporates, heat energy, the latent heat of vaporisation, helps the molecules to break away from each other to become a gas
- because the molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds, a relatively large amount of energy to needed fro water molecules to evaporate
- water can help to cool living things and keep their temperature stable
- liquid water remains as liquid despite temperature changes e.g. oceans exist
What are carbohydrates?
- they are molecules made up of sugar units
- general formula: CnH2nOn
- include sugars, starch/glycogen and cellulose
What are monosaccharides?
- carbohydrates whose molecules contain just one sugar unit
- monosaccharides are the monomers of carbohydrates
How are larger carbohydrates made?
- by joining monomers, the monosaccharides, together
- a condensation reaction occurs to form a glycosidic bond
Why is it called a condensation reaction?
- a water molecule is formed as one of the products of the reaction
What are the properties and functions of monosaccharides?
- sweet-tasting
- soluble in water
- insoluble in non-polar solvents
- crystalline
- can exist as straight chains or in rings or cyclic forms
- they are a source of energy due to having a large number of carbon-hydrogen bonds
How are monosaccharides grouped?
- grouped according to the number of carbon atoms in the molecules
- e.g. triose sugars have 3 carbon atoms
- pentose 5
- hexose 6
What is the most common monosaccharide group?
- hexoses
- includes glucose, fructose and galactose
What is the role of alpha-glucose?
What is its displayed formula?
- energy source
- component of starch and glycogen, which act as energy stores

What is the function of beta-glucose?
What is its displayed formula?
- energy source
- component of cellulose, which provides structural support in plant cell walls