3.2.2 Sleep Apnea Flashcards
What are the stages of sleep? What are some major characteristics of stage?
Stage 1 (N1): low V, mixed frequency (theta), <50% alpha (wake)
Stage 2 (N2): predominately theta w/ sleep spindles or K complexes
Stage 3/4 (N3): large delta waves (stage 3 is 20-50%, stage 4 is >50%)
REM: atonia or flat EMG, irregular breathing pattern and phasic eye movements
Deep sleep occurs during which stage?
N3
Which phase of sleep requires the loudest tone to wake up and most obnoxious stimuli to awake?
N3
During which phase of sleep do most parasomnias occur?
N3
What stage of sleep is shown in these graphs?
NREM

What stage of sleep is shown in the graphs below?

REM
What does the graph represent?
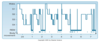
A typical progression through sleep
What acts as the central control of ventilation during sleep?
respiratory neurons of the medulla and pons
What type of breathing is present during REM sleep?
Irregular
How do the hypoxia/hypercarbia responses during sleep compare to responses during waking hours?
Less responsive, the least responsive during REM sleep
What is the NREM respiratory pattern?

What are some characteristics of the REM respiratory pattern?

How are cardiovascular physiology values are changed during NREM sleep?
HR, BP, CO, and SVR are all decreased, thus reducing myocardial workload. This a result of parasympathetic discharge combined with a reduce in central sympathetic discharge.
Describe the cardiovascular physiological state during REM sleep.
Unstable; Phasic REM results in flucuation in HR, BP, and SVR
Spontaneous arrousals have what effect on cardiovascular physiology?
Acute increases in HR, BP, CO, SVR much above the level of the awake state
What is apnea?
No airflow for 10 seconds or longer
What is central apnea?
No airflow and no respiratory effort for 10 seconds or longer
What is obstructive apnea?
No airflow with obstructed respiratory effort for 10 seconds or longer
What is hypopnea?
Reduction in airflow associated with at least 3-4% drop in O2 Sat
Describe how the airflow and respiratory effort graphs of both central and obstructive apnea would look on a time strip.

What are different levels of severity of OSA and their corresponding numbers of events in an hour?

What are some of the risk factors for OSA?
OBESITY and Age of >65

What are some of the daytime symptoms of sleep apnea?

What are some of the clinical features of OSA?

What are some of the physical correlations with OSA from the clinical examination?

What are some of the predisposing factors of OSA and their odds ratios?

Where does OSA commonly manifest in patients?
Narrowing in retro-palatal and and retro-glossal regions
Where are the retro-palatal and retro-glossal regions?

What are some of the cardio/cerebrovascular complications of OSA?

Describe the mechansims/pathways that sleep apnea can lead to CV complications.
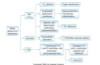
What is the label of the bracketed area?

Apnea
What two metabolic dysfunctions have been associated with sleep apnea?
Glucose intolerance and insulin resistance
What are some treatment options for OSA?

What is the gold standard of treatment for OSA?
CPAP
Who does Miles know that wears a CPAP at night?
His dad…. How could you not know that? He’s probably told you at least 20 times.


