28 Microbiology: Viral CNS infections Flashcards
(44 cards)
1
Q
Agents
- What are the 5 common viral causes of aseptic meningitis?
A

2
Q
Non-viral aseptic meningitis causes
- What are the common organisms for this?
A

3
Q
Clinical Manifestations of Viral Meningitis
- What do symptoms do patients present with?
A

4
Q
Clinical Manifestations of Viral Meningitis
- CSF
- What is notable about:
- Lymphocytes
- Leukocytes
- Protein
- Glucose
- What is notable about:
A

5
Q
Enteroviruses
- How common are they the pathogenic agent in viral meningitis?
- What time of year are these viruses most abundant?
- What type of enteroviruses is particularly fatal for infants?
- What is notable about Enteroviruses 70 and 71?
A

6
Q
Other viral causes of meningitis
- Of the HSV family, which herpes virus is the most common cause of this?
- What other 5 viruses are known to cause meningitis?
A

7
Q
Encephalitis
- What is the main difference between this and meningitis in terms of how patients present with viral CNS infections?
A

8
Q
Viral Encephalitis
- Assign one of the follow to each A, B, or C
- Arbovirsues
- HSV
- Rabies Virus

A

9
Q
Viral Encephalitis
- Name the 3 primary endemic viruses
- Name the 2 notable Arboviruses
- Others
- NAme the 4 other viruses to remember for this prof… (lol)
A

10
Q
Viral Encephalitis
- For all types of encephalitis
- Name the 9 basic tests to analyze the CSF and brain in suspected encephalities
A

11
Q
Treatment for Meningitis
- How do patients present?
- Initial treatment
- 1st line treatment for non-acute?
- If acute presentation
- What are the 3 drugs you would give?
A

12
Q
Viral Encephalitis: Endemic - Herpes
- Which 2 HSV viruses can cause this?
- Which one is genital herpes?
- Which one causes cold sores?
- What is notable about the presence of this virus during the year?
A

13
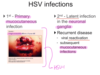
Q
Viral Encephalitis: Endemic - Herpes
- When a patient becomes infected with an HSV virus, what is the first thing to occur?
- Where does latent infection take place?
- Recurrent disease
- What 2 things can cause this type of viral encephalitis to reoccur?
A
14
Q
Herpes Simplex Virus Encephalitis
- What is notable about the incidence of this type of encephalitis?
- What percentage of cases are from primary exposure?
- What is notable about this condition’s fatality rate?
- Which virus predominates: HSV1 or HSV2?
A

15
Q
HSV Encephalitis
- What is notable about the age distribution of these infections?
- Besides a primary infection, what can cause this condition to occur?
- At the start of symptom manifestation:
- What can you note about the presentation of symptoms on the body?
A

16
Q
HSV Encephalitis
- Clinically
- How long can the initial headache and fever last before more serious symptoms start?
- What are these serious symptoms? (4)
- What genetic defect can this be linked to?
- How long can the initial headache and fever last before more serious symptoms start?
A

17
Q
HSV Encephalitis
- What lobes does is this infection usually localized to?
- What happens to the lobes?

A

18
Q
Tx for HSV Encephalitis
- What drug is used for this?
- What percentage does it decrease mortality?
- If patients survive, what conditions do they usually have?
A

19
Q
Tx for HSV Infections
- What drug is a purine nucleoside analog?
- What drug is a prodrug of the answer to the above question?
- What drug is a prodrug of penciclovir?
A

20
Q
Viral encephalitis: Varicella Zoster Virus
- How common is this in viral encephalitis?
- Children
- About how long after a child has a chickenpox rash does this occur
- What condition arises from this type of encephalitis?
- Adults
- What causes this to happen in most adults?
- How do adults present with this condition?
A

21
Q
Viral encephalitis: Varicella Zoster Virus
- What is the tx for this?
- What can prevent it?
- How deadly is it?
A

22
Q
Viral encephalitis: Other Viruses
- EBV
- What kind of neurological features does this have?
- Is this severe or mostly benign?
- HHV-6
- What age group is this most common in?
- What kind of signs and symptoms do these patients have?
A

23
Q
Viral encephalitis: Rabies
- What cell does this virus initially have replication in?
- How does this virus get into the CNS?
- In what way does infection spread to the peripheral nerves?
A

24
Q
Viral encephalitis: Rabies virus
- Associate each decade with a rabid animal
- 1980’s
- 1990’s
- 2010’s
A

25
Viral encephalitis: Rabies Virus
* This shows the animals with highest number of rabid members in the US
* What animal is
* A
* B
* C
* D

26
Viral encephalitis: Rabies Virus
* What contents have the highest risk for rabies contact?

27
Viral encephalitis: Rabies Virus
* How does rabies patients initially present?
* 1 to 2 weeks after an infection
* What does furious rabies present with?
* What does paralytic rabies present with?

28
Viral encephalitis: Rabies Virus
* What is the tx for people who have rabies?

29
Arboviral Encephalitis
* What are the viruses that mosquitos can give to humans under this group (that we talked about)?
* What virus can be transmitted by ticks?

30
Arboviral Encephalitis
* When do neurologic symptoms usually emerge?
* Besides encephalitis, what else can this cause in the CNS?

31
Arboviral Encephalitis
* What kind of symptoms do patients present with, BEFORE getting encephalitis?
* How can you treat this?
* Sequalae
* What virus do about 30% of patients have neurological sequelae? How does this percentage relate to that viruses' fatality rate?
* What virus do about 10% of patients have neurological sequelae? How does this percentage relate to that viruses' fatality rate?

32
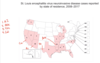
Arboviral Encephalitis: St. Louis Encephalitis
* What states have the highest rate of infection?
33
Arboviral Encephalitis: La Crosse Encephalitis
* What states have the highest rate of infection?

34
Arboviral Encephalitis: West Nile Virus
* How common is this virus in the US?
* Is encephalitis from this virus common?

35
Arboviral Encephalitis: West Nile Virus
* What states have the highest rate of neuroinvasive disease from this virus?
* Hint: Think ICOM rotation sites for 4 out of the 7 top infection rate states.

36
Arboviral Encephalitis: Equine Encephalitis
* What animals transmit this virus?
* What kind of fatality rate does it have?
* What do people who survive this disease usually have?
* What population is at a higher risk for this condition?

37
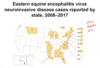
Arboviral Encephalitis: Equine Encephalitis
* What states have high infection rate for this virus?
38
Just be aware of these random arboviral infections

39
Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus
* What animal acts a reservoir for this?
* How can people get it?
* What is the clinical hallmark for this?
* What symptoms can be present?
* Do patients improve?

40
List the 5 childhood infections that may cause encephalitis

41
What non-polio enteroviruses have neurological manifestations that cause mild encephalitis?

42
Mumps and Measles
* How common is encephalitis in these diseases?
* What about measles?
* Measles
* What is the mortality rate for this, and what is present in 25% of survivors?

43
Measles
* What chronic progressive neurological condition is associated with this?
* When can it manifest?
* Is it deadly?

44
Be aware of these viruses that can cause CNS pathology long after primary infection



