24 Anticoagulants Flashcards
In what form are coagulation factors present in blood?
- Inactive zygomens
- Serine proteases
- Cofactors
- Calcium- important cofactor
Where are heparins produced naturally in the body?
- Mast cells
- Vascular endothelium
How do we acquire heparins for pharmaceutical use?
- Porcine intestinal mucosa
- Bovine lung
How do heparins work? (general terms?
Enhance antithrombin III activity
Unfractionated heparin has an unpredictable elimination. What is its half life like at high doses? What is its elimination like at low doses?
Low doses: half-life= 30 mins
High doses: half life= 2hrs
What is the mechanism of action for unfractionated heparin?
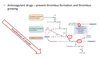
Binds to antithrombin III (ATIII)
Conformational change and increased activity of ATIII
- Heparin binds ATIII and thrombin (IIa)
- Catalyses inhibition of IIa
- ATIII binds to Xa and inhibits it

Give 2 examples of low molecular weight heparins.
- Dalteparin
- Enoxaparin
How are low molecular weight heparins normally administered?
Sub cutaneous
(Enoxaparin i.v. in ACS)
What is the bioavailabilty of LMWHs like? What are their half-lives like?
- Bioavailability= 90%
- Half life= 2+hrs
Why do low molecular weight heparins have a more predictable dose response than Unfractionated heparin?
- Absorbed more uniformly
- Do not bind to endothelial cells, plasma proteins, macrophages
Outline the mechanism of action for low molecular weight heparins.
Enhance ATIII activity - inhibit factor Xa specifically

Fondaparinux is a synthetic pentasaccharide.
- How does it work?
- How is it administered?
- What is it’s half life?
- How does it work?
- Like LMWH
- Binds to ATIII
- Selectively inhibits Xa
- How is it administered?
- S.C
- What is it’s half life?
- 18hrs
How do we monitor Unfractionated Heparin?
aPTT (activated partial thromboplastin time)
Dose titrated against this value
When might UFH be used instead of LMWH?
UFH=
- severe renal impairment
- fine control

What are the indications for heparins? (3)
- Venous thromboembolism
- Prevention
- Perioperative prophylaxis
- DVT and PE
- Initally and long term in some patients
- Cancer related VTE
- Prevention
- Pregnancy (doesn’t cross placenta)
- Monitored with caution
- ACS
- Reduce recurrence/extension of coronary artery thrombosis
- STEMI
- NSTEMI
- Reduce recurrence/extension of coronary artery thrombosis
State some of the adverse reactions for heparins.
- Bruising/bleeding
- Site of injection, GI, epistaxis
- Hepatic/renal impairment
- Elderly/those with carcinoma
- HIT (Heparin induced thrombocytopenia)
- 1/100- UFH 1/1000- LMWH
- Autoimmune response 2-14 days after initiation
- Antibodies to heparin platelet factor 4 complex
- Hyperkalaemia
- Inhibition of aldosterone secretion
- Osteoporosis
- Rare long-term use
- More prevalent in pregnancy
What drug can we use as heparin reversal? How does it work?
Protamine sulphate

Outline the mechanism of action of warfarin.
Vitamin K antagonist
- Inhibit activation of vitamin k dependent clotting factors
- Inhibits conversion of vitamin K epoxide to vitamin K (active reduced form)
- Competitive inhibitor of VKOR
- Inhibits conversion of vitamin K epoxide to vitamin K (active reduced form)
Clotting factors (hepatic synthesis) requiring active vitamin K as co-factor:
- II
- VII
- IX
- X

What is the half life like for warfarin?
36-48hrs
State some of the indications for the use of warfarin: (3)
- Venous thromboembolism
- PE
- DVT and secondary prevention
- Superficial vein thrombosis
- AF
- w./ high risk of stroke
- Heart valve replacement
(Longer term anticoagulation compared with heparins)
(May require heparin cover if required immediately)
What is the bioavailability like for warfarin if taken orally? Why is there inter individual variability?
95%
Interindividual variability due to:
- CYP2C9 polymorphs
- [Plasma] does not correlate directly with clinical effect
- Warfarin- racemic mixture
- Enantiomers- different potency and metabolised differently
- Response varies by vitamin K intake
–> MONITORING REQUIRED due to variation in patient response
INR used to monitor
State the adverse drug reactions to warfarin that can occur.
- Bleeding
- Epistaxis
- Spontaneous retroperitoneal bleeding
When initiating or temprarily stopping warfarin, what bridging therapy may be required?
LMWH
What can we use as warfarin reversal? (2)
- Vitamin K1
- Prothrombin complex concentrate (i.v.) (PCC)
STOP warfarin
Warfarin has a huge number of drug interactions. State the important interactions to be aware of. (most enhance anticoagulation)
- Inhibition of hepatic metabolism (esp CYP2C9)
- Amiodarone
- Clopidogrel
- Intoxicating dose of alcohol
- Quinolone
- Metronidazole
-
Reduce vitamin K- eliminate gut bacteria involved in production
- Cephalosporins
- Displacement of warfarin from plasma albumin
- NSAIDs
- Drugs decreasing GI absorption of vitamin K
- Acceleration of warfarin metabolism (decrease INR)
- barbiturates
- phenytoin
- rifampicin
- St Johns Wort
DOAC stands for direct acting oral anticoagulant. Name the 3 DOACs that inhibit free Xa and that bound to ATIII.
- Apixaban
- Edoxaban
- Rivaroxaban

What is the half life like for DOACs?
Xa inhibitor- Half-life= 10hrs
IIa inhibitors- Half-life= 9hrs
Name the DOAC that is a direct competitive thrombin inhibitor (IIa) (both circulating and thrombus bound).
Dabigatran
Can warfarin cross the placenta?
Yes- don’t use - esp 1st and 3rd trimestres
What are the advantages and disadvantages of DOACs compared to other anticoagulants?
Advantages:
- Less frequent interactions than warfarin
- Lower intracranial bleed risk
- Require less monitoring
- Oral administration
- Standard dosing
- Little info on pregancy effect- avoid
Disadvantages
- Still need caution- GI bleeding
- Dabigatran contraindicated in low creatinine clearance
- Affected by CYP inhibitors and inducers
- [plasma] reduced by carbamazepine, phenytoin and barbiturates
- [plasma] increased by macrolides
(Antidotes are now available)


