16. Riboswitches In The Control of Gene Expression Flashcards
define what a riboswitch is?
a regulatroy segment that is located within mRNA and is able to regulate gene expression independently by binding a small molecule (a ligand)
what percentage of gene expression is subject to having a riboswitch?
3-4%
why are riboswitches important? 2 points
important roles in regulating metabolic genes in response to environmental changes.
its the regulation of gene expression by an alternative mRNA 2D structure

what are the two parts that make up a riboswitch?
the aptamer and the expression platform

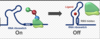
see image
what is the aptamer?
the region of mRNA that binds to the ligand
they are like the lock where the ligand (a key) fits in
what is the expression platform? (3 examples)
it can be a terminator hair pin
ribosome binding site
another RNA element that affects gene expression

what is the structure and function of essentially how a riboswitch works?
its structurally changes the secondary strucutre of mRNA (think hairpins) which therefore act as a function to turn on/off gene expression

how can a riboswitch work at the transcription level?
the ligan binding allows a termination loop to form which causes transcription to stop. this is because of a change in the secondary structure
look at image closeley

how does a riboswitch work at the translational level?
ligand binding results in the shine dalgarno sequence being hidden - the ribsome cant bind and translation is prevented.
(shine dalgarno sequence is the binding site in prokaryotes)

why is attenuation not an example of a riboswitch? also what is the similarity?
because there is no ligand (small molecule) that binds. its similar because it changes the 2D secondary structure of mRNA affecting transcription

what is a small non-coding RNA (ncRNA) in post-transcriptional control of gene expression?
function as regulators by base pairing with trans-encoded mRNAs. They repress or activate gene expression at post transcriptional levels

what are two examples of riboswitches?
RibD for riboflavin
ThiM for thiamine


