1. DNA Structure and Properties Flashcards
(19 cards)
what is the difference between a primary and secondary structure of DNA?
primary - the backbone of nucleotides, it determines the genettic message (covalent bond)
secondary- double helix held together with hydrogen bonds (non polar)
what is the difference between purine and pyrimidine bases?which bases are purine and pyrimidine
purine - two rings.
adenine and guanine
pyrimidine - one ring
cytosine and thymine

what is a chemical property of the nitrogenous bases?
they accept an H+ proton in solution
what structure is this? explain why

adenine
it has 1 amino group (NH2)
adenine is the AA:
backbone for energy (AA insurance helps cars drive and ATP)
what structure is this? explain why

guanine
it has a ketone group
it has an amino group
guanine is AGO
amino guanine double bond oxygen

what structure is this? explain why

cytosine
has an amine and a ketone
cytosine is a CAK
cytosine, aminoe, ketone

what structure is this? explain why

uracil
RNA ONLY!!
two ketone groups
uracil is a KUK - ketone, uracil, ketone
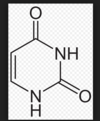
what struture is this? explain why

thymine
two ketones, two amines, one methyl!!
thymine is a tam-k
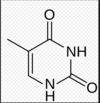
whats the difference between a base, nucleotide and nucleoside?
nucleoside:
a base + pentose sugar no phosphate! they are non reducing
base:
the purine or pyrimidine strucure
nucelotide:
phospate, base and pentose sugar

whats the difference between deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid?
DNA has one hydroxyl group on the 3rd carbon on the pentose sugar has polarity
RNA has two hydroxyl groups on the 2nd and 3rd carbon on the pentose structure
this means RNA is able to have a nucleophillic attack (base hydrolysis) and makes it more unstable

why does DNA have polarity?
it has ‘directionality’.
- 5’ end has acidic phosphate
- 3’ end has hydroxyl group where bases are linked with N-glycosidic bonds

what is a phosphodiester bond?
when two of the hydroxyl groups in the phosphoric acid react with the hydroxyl group of the DNA/RNA to make an ester bond

how is phosphate a pH buffer?
its at equilibrium with having OH- and O- attached to it.
- ability to release a proton or accept a proton
- always negativley charged

what is hydrolysis?
breaking down a reaction with water

how does acid hydrolysis of DNA and RNA occur?
- what do you need
what does it do (2 points)
what are the products
a strong acid and heat (6 M HCL, 110 degrees)
breaks phosphate ester bonds and N-glycosidic bond between bases in deoxyribose
products are free bases, phosphates and a polymer of deoxyribose
what occurs in base hydrolysis? why cant DNA be attacked?
DNA is stable because it only has the one OH- which is in a phosphodiester bond
RNA is degraded because of the 2’OH which can attack the phosphodiester bond in the presence of OH-
look at image carefully!

what is enzyme is DNA hydrolysed by? name the two types
cataltyic proteins called nucleases.
DNAases - hydrolyses phosphate ester bonds in RNA
RNAases - hydrolyse phosphate ester bonds in RNA
what is an exonucleases?
cut DNA or RNA from the ends of the strands
exo-DNAases cut DNA
exoRNAases cleave RNA
what is an endonuclease
can cut anywhere on the strand
some are very specific at their cutting sites - cut at specific sequences (restriction endonuclease)


