(15) - Bladder I Flashcards



no evidence of structural obstruction

what do you need to know to solve this dog’s problem?
anatomy, need to know innervation

and now on to the hellish
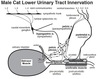
Anatomically, the Lower urinary tract consists of the urinary bladder and urethra, plus the caudal portion of each ureter, which tunnels through the bladder wall and is connected to the bladder neck and urethra
(Functionally, the lower urinary tract consists of three components arranged in series (functional components are determined by their innervation)
- the smooth muscle coat of the bladder apex and body
it expels urine, when activated by what kind of innervation?
- Smooth muscle of the bladder neck and, in the case of females and male cat, the cranial urethra.
It provides tonic resistance, when contracted by what kind of innervation?
- ? = urethralis muscle
It opposes sudden increases in abdominal/bladder pressure, and is used for what?
activated via what?
- detrusor muscle
parasympathetic innervation (via the pelvic nerve)
- smooth muscle sphincter
sympathetic innervation (via the hypogastric nerve)
- striated urethral sphincter
voluntary continence
the pudendal nerve
(The central nervous system ultimately controls the three functional components so they work synergistiaclly to store and void urine)
- forebrain decides what?
- pons - does what?
- spinal reflexes do what?
- when it is appropriate to urinate
- inhibits sphincters and sustains detrusor during micturition
- generate sphincter resistance during urine storage
(THIS IS BID TYPE)
normal micturition entails coordinated actions of detrusor and sphincter musculature to enable complete emptying of the urinary bladder at appropriate times
- Can voluntary urination be emotionally motivated?
- in neonatal kittens, micturition reflex can be triggered by doing what?
- yes (marking)
- licking the perineum

read pages 2-3 of notes
(III. Filling and Storage)
(Bladder filling)
- urine drains continuously from what?
- Urine is collected by what?
- Accumulated urine stretches pacemaker myocytes in the wall of the renal pelvis, triggering them to fire AP that result in what?
- The end result is a peristaltic wave of smooth muscle contraction that does what?
- the medullary surface of the kidney
- the renal pelvis
- increased intracellular [Ca] (which spreads amoung smooth muscle cells of the renal pelvis and ureter gap junctions)
- propels a urine bolus along the ureter
(III. Filling and Storage)
- By passing obliquely through the bladder wall, the terminal segment of the ureter is normally closed or open? by what? to do what?
- Each peristaltic wave must convey a bolus or urine into the bladder with sufficient force to do what?
- closed by intravescial pressure to preclude urine reflux
- to open the terminal intramural ureter
(Note: urinary continence, the ability to store urine without leakage, requires outlet resistance to exceeed intravesical pressure)
(III. Filling and Storage)
(Bladder Storage - First Step)
- initially, when bladder pressure is low, what of the urethral wall maintains outlet closure?
(Note: in quadrupeds, passive resistance is augmented when urine weight pulls the bladder cranially into the abdomen away from the urethra (Squatting to urinate shifts urine weight caudally against the urethral opening)
- passive viscoelastic resistance (passive resistance is the result of mucosal enfolding, submucosal elastic fibers, and stratum spongiosum, particularly when the latter is filled with blood)
(III. Filling and Storage)
(Bladder Storage - step 2)
1-2. As bladder volume approaches half-full, continued continence requires spinal sympathetic reflexes to do what two things?
- contract the smooth muscle sphincter
- inhibit spontaneous contraction of the detrusor
(These sympathetic reflexes involve afferent axons that run through the pelvic nerve to sacral spinal roots and efferent axons that come from lumbar spinal segments and travel through the hypogastric nerve)
(III. Filling and Storage)
(Bladder stoarge: step 3)
- To halt urine leakage during abrupt increases in intravescial pressure (when the tonic smooth muscle sphincter in breached), what contracts?
This involves a spinal reflex triggered by what?
- the striated urethralis muscle
urine flow into the urethra
Both afferent and efferent axons run through the pudendal nerve and sacral spinal cord
(also the levator ani muscle reflexly contracts to support pelvic viescera when muscles of the abdominal wall contract to increase intra-abdominal pressure during running, jumping, etc.)
(III. Filling and Storage)
- the urethralis muscle is used for what kind of continence?
- this is also the muscle that contracts during what?
- voluntary continence (including abrupt cessation of urine flow)
- male ejaculation
(IV. Micturition)
- As bladder volume expands (particularly during spontaneous waves of detrusor contraction and when compliance reaches its limit) mechanoreceptors sensitive to wall tension generate what?
- Afferent axons travel through the pelvic nerve to what?
- they synapse on interneurons to generate what?
- they also synapse on projection neurons that do what?
- increased afferent activity
- the sacral spinal cord
- continence related spinal reflexes
- relay wall tension to the brain
(IV. Micturition)
- What senses bladder awareness/fullnes/urgency along with cognitive interpretations of surroundings and emotional status?
- These perceptions are factored into a decision either to do what or what?
- the forebrain
- inhibit or initiate micturition
(the latter involves the onset of behavior to facilitate micturtion (movement, posture, abdominal press) and neural instructions to the pons)
(IV. Micturition)
- What switches from continence to micturition?
- the pons
(Descending tracts from the pontine micturition center inhibit neurons to smooth and straited sphinceter and excite parasympathetic preganglionic neurons to the detrusor)
and then
Detrustion contraction boosts bladder wall tension and intravesical pressure within the closed bladder. The detrusor pulls open the bladder neck and intravesical pressure forces urine into the relaxed bladder neck and urethra. Eventually, wall tension and mechanoreceptor activity delcine along with bladder volume, but brain facilitation sustains detrusor contraction until the bladder is virtually empty.)
Clinical Note
1-2. Spinal lesions that damage descending tracts from the pons impair normal micturition by doing what two things?
- reducing sustained detrusor contraction
- producing detrusor-sphincter dyssnergy
(as a result, smooth and striated sphincter reflexes are not adequately inhibited during attempted micturition)
the chronic result is detrusor hypertrophy and frequent cystitis due to bacterial contamination fo retained urine. The same dyssynergy impedes attempts to macually empty the baldder in paraplegic patients)

it’s not always…
he didn’t say which one for dogs
like to save urine for marking

the answer is B


