(11) EMBRYOLOGY SESSION 2 - WEEK 3 Flashcards
(43 cards)
Bilaminar Disk
The Epiblast and hypoblast. Derived from the embryoblast. This will later become the trilaminar disk with the formation of the primitive streak.
Germ Layer
A layer from which other developed tissues originated from
Ectoderm
The outermost layer of cells giving rise to the epidermis and nerve tissue
Endoderm
The innermost layer of cells giving rise to the gut lining
Doral Surface
The outermost surface during early development
Ventral Surface
The innermost surface during early development
Mesoderm
The middle germ layer giving rise to muscle, bone and more
Primitive Streak definition + role
A narrow groove that develops on the dorsal surface of the Epiblast. It has an important role in the orientation of the embryo, determining the front and the back.
Gastrulation
The reorganisation of the germ layers into the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm and hence establishing the origin of all tissues.
Trilaminar disc
The three germ layers. Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
Name 3 ectodermal derivatives
Skin, Skin derivatives (hair, nails, leans and cornea of eye, mouth annd anus lining), brain and spinal cord, peripheral nerves, Retina and iris of eye
(Outside and nervous system)
Name 3 mesodermal derivatives
Smooth, skeletal and cardiac muscle
Connective tissue
Bone
Cartilage
Blood and blood vessels
Urinary system
(Muscle, Skeletal and Urinirary system)
Name three endodermal derivatives
Lining of the digestive tract
Glands associates with digestion
(E.g. liver, pancreas)
Other gut derivates
(E.g. lungs)
(Gut and lungs)
What is B?

Amniotic Cavity
What is C?

Yolk sac
What is D?
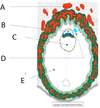
Connecting stalk
What is E?

Chorionic Cavity
What is A?

Embryo, made up of epiblast and hypoblast
Why are weeks 3-8 the most perilous for a developing child?
Period of greatest change, when all major structures and systems are formed
Why is week three called “the week of threes”?
Three cavities (at end of week 2), amniotic, yolk and chorionic.
Three “germ layers” - Mesoderm, ectoderm and endoderm
What are two ways via which cell rearrangement occurs?
Migration and invagination
What is A?

Primitive node, located at cranial end of streak
What is B?

Primitive pit, located at center of node
What is C?

Primitive streak








