YM part 3 Flashcards
(15 cards)
How is the equipment set up?

Why should the test wire be as thin and as long as possible?
- longer and thinner the wire, the more it extends for the same force
- this reduces uncertainty in the measurement
How is cross sectional area of the wire determined?
- using a micrometer to measure the diameter
- measure in several places and take an average
- assume cross section is circular
- pi r squred
How is the test done?
- start with the smallest weight necessary to straighten the wire
- don’t include this in the equation
- measure distance between the fixed end of the wire and the marker on the wire, this is the unstretched length
- when weight is increased, the wire strethces
What marker should be used?
- to avoid random erros, you should use a thin marker on the wire and always look directly at the marker and ruler when measuring extension
What are the safety precaution in this experiment?
- place a suitable ‘crash pad’ on the floor under the weights to prevent them hitting the floor dirtectly when the wire breaks
- do not put feet under the weights
- wear goggles for eye protection when the wire breaks
What can be determined from a stress-strain graph?
- gradient gives young modulus
- area under the graph gives the strain energy (or energy stored) per unit volume
- the stress-strain graph is a straight line provided that Hooke’s law is objecyed
What are the parts of the the graph?
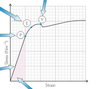
- area under the first part of the graph
- energy stored per unit volume
- before point p
- graph is a straight line through the orgin
- material is obeying Hooke’s law
- gradient constant, its the young modulus
- P
- limit of proportionality
- graph no longer straight line
- material stops obeying Hooke’s law
- would return to original shape if stress is removed
- E
- elastic limit
- material behaves pl;atically
- material would no longer return to its original shape once stress was removed
- Y
- yield point
- material sudennly starts to stretch without any extra load
- yield point (or stress) is the stress at which a large amount of plastic deformation takes place with a constant or reduced load
What are the characteristics of a stress-strain graph for a brittle material?
- doesn’t curve
- straight line through origin
- when stress reaches a certain point, the material fractures
- it doesn’t deform platically
What is the difference between force-extension graphs and stress-strain graphs?
- force-extension graphs look like stress-strain graphs
- force-extension graphs are specific for the tested object and depend on its dimensions
- stress-strain graphs describe the general behaviour of a material, because stress and strain are independant of the dimension
What is happening at 1 and 2? why?
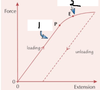
- elastic deformation
- plastic deformation
- stretched beyond its limit of proportionality so graph curve
Why is the unloiading curve parallel to the loading line?
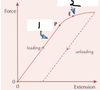
- the stiffness constant, k, is the still the same
- since the forces between the atoms were the same during the loading
Why does the unloading curve not go to the origin?
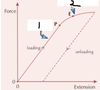
- wire stetched beyond elastic limit and deformed plastically
- it has been permanently stretched
What is the area between the two lines?
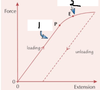
work done to permanently stretch the wire
Graph for force against extension
Outline how the student can use these results and other measurements to determine the Young modulus of the wire.
- convert to stress/strain graph and determine gradient
- or
- Measure original length and diameter
- Determine gradient of linear section to obtain F/extension
- E = F / e x length / area


