Week 3 Flashcards
(41 cards)
What is the vertebral formula for the dog? the cat? the horse?
* the dog: cervical- 7, thoracic- 13, lumbar- 7, sacral-3, caudal-20
* the cat: same as dog
* the horse: C7 T18 L6 S3 Cd~20
How can you recognize C6?

How do you recognize anticlincal vertebrae?
T11 (T10 pointing caudally)

How do we count lumbar vertebrae in a large dog in a radiograph?
Include T13 or the diaphragm attaches to the ventral border of L3 and L4 (they have a scalloped appearance)

What should the intervertebral disc space look like?
A hobby horse’s head (should be a nice dark grey)

What is important to remember about the size of the intervertebral disc space relative to each other in a radiograph?
They should be the same, however there will be distortion and they will look smaller than they are moving away from the central radiograph beam

What is radiograph used for with neurologic disease?
* Trauma, neoplasia of skull and vertebrae, intervertebral disc degeneration, +/- intervertebral disc herniation, discospondylitis, (hydrocephalus)
What is ultrasound used for with neurologic disease?
* high density of bone prevents ultrasound from penetrating through so can only image through a hole in the calvarium- natural hoels (fontanelle or foramen magnum) or surgical holes (craniotomy or pediculectomy)
* ultrasound allows you to see the internal structure of the brain or spinal cord
What is a myelogram?
Myleography- inject the positive contrast agent in the subarachnoid space to highlight the margins of the spinal cord
* using radiograph or CT
* allows you to identify spianl cord compression or enlargement
* indications:
- clinically: myleopathy (paresis, paralysis, neck pain, neurologic deficits of the limbs)
- find a lesion when radiographs are normal
- better define lesions suspected on radiographs (confirm or define extent)
- surgical planning and prognosis
Where is the cisternal puncture performed? The lumbar puncture?
* Cerebromedullary cistern
* Lumbar interarcurate space

What is the ideal method of imagine for neurological disease?
* MRI
*pictures are meningiomas (one in brain, on in the spinal cord in two different dogs)

What can happen with neoplasia in the brain with contrast?
BBB junctions are no longer as tight, so the contrast can leak out– normal neural tissue does not take up contrast due to the BBB
What is the constrast medium used in MRI?
Gadolinium
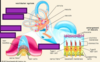
What anatomic structures make up the auditory system?
External ear, middle ear, cochlear part of inner ear
What is another name for the pinna?
Auricle




What is the tympanic cavity?
* Air-filled cavity in the temporal bone separated from external acoustic meatus by the tympanic membrane
* Changes air vibrations (sound waves) into mechanical movement through auditory ossicles



What moves the ossicles? What happens when they contract?

Stapedius muscle (attached to the stapes)
and
Tensor tympani muscle (attached to the malleus)
* When they contract, they dampen the vibrations of the auditory ossicles (protective mechanism)

What anatomically is the inner ear?
Membranous labyrinth sitting within a bony labyrinth within the temporal bone
*membranous labyrinth is surrounded by perilymph (the fluid, perilymph, suspends it inside the bony labyrinth)
*the membranous labyrinth contains endolymph
What does the vestibule contain?
It is one of three parts of the bony labyrinth
* utricle and saccule (part of the vestibular system)
What does the semicircular canals contain?
It is one of three parts of the bony labyrinth
* semicircular ducts (part of the vestibular system)- there are three semicircular canals.
What does the cochlea contain?
It is one of three parts of the bony labyrinth
* cochlear duct