W4 diagnostic tests, radiographs, risk factors Flashcards
What are diagnostic tests?
- Radiographs
- Saliva tests
- Sensibility tests
- Study models
- Dietary analysis
- Other
What do you measure in a salivia test?
Resting saliva.
- Visual examination
- Viscosity
- Hydration
- Resting pH
Stimulated saliva
- Flow
- quantity
- Buffering capacity
What are sensibility tests?
TTP: tender to percussion testing, indicates whether inflammation of PDL. Pulp sensibility testing: CO2 test (endo frost).
- No response
- moderate, transient response
- a painful response but subsides after stimulus is removed
- painful response that lingers after removal
What is a diet analysis?
Diet record/dietary which determines sources of diet sugars and frequency of exposure. ↑ caries risk, we work to council pat about dietary changes.
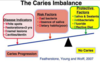
What is the caries imbalance?
Disease indicators
- white spot lesions
- restoration <3yrs
- enamel lesions
- cavities/ dentin
Risk factors
- bad bacteria
- absence of saliva
- poor dietary factors
Protective factors
- saliva and sealants
- antibacterials
- fluoride
- effective diet
What is caries?
Caries is a transmissible bacteria infection and a multi factorial disease that reflects the change in one or more significant factors in the total oral environment. Diagnosis involves recognition of those changes rather than simply noting cavities.
How do you identify risk factors for caries?
Caries is the refection of adverse changes occuring in the oral environment over time. Effected tx planning will be achieved by long term sustainable changes to the oral cavity.
OHT role: - diagnosis and manage disease process - manage and repair caries defects
Primary factors: which are the biological factors that act directly on the biofilm.
Modifying factors: which are indirect influence on the biofilm. SES, lifestyle, dental rx, compliance history, ortho appliance, pits and f/s
What factors are to be assessed for an individual assessment?
Saliva Diet Fluoride Biofilm Modifying factors
What is CAMBRA?
Caries Management by Risk Assessment Tool. Risk status is determined by the balance or imbalance between pathological and protective factors. MID. - History taking - Clinical exam, detection of carious lesions. Use caries risk assessment form and finding above to determine overall risk.
What is the Caries risk assessment for patients under the age of 6?
Low, moderate, high
What is the caries risk assessment or patient ages 0-5 years old?
Discuss with caregiver regarding risk factors and protective factors. Clinical exam including plaque and caries evaluation, x-rays if required.
Periodontal risk factors
Risk factors can effect the host response or the bacterial biofilm. Based on individual risk factors, systemic factors associated with periodontal disease. 1. Plaque accumulation Life style factors: gender, smoking, alcohol 3. Diabetes 4. Obesity and metabolic syndromes 5. Osteoporosis 6. Stress 7. Genetic factors
What are systemic risk factors for periodontal disease?
These may modify the host response and me predispose people to specific forms and patterns of periodontal disease: Haemalogical disorders Leukocytes disorders Horomones Immunosuppresion
What are other risk factors?
Attrition and abfraction - Grinding/bruxism, clenching - uneven occ loading Erosion - Acidic food and beverages - GERD/Reflux - Social factors Abrasion - Tooth brushing technique/type, piksta, toothpaste grit.
Define Normal Occlusion
Molar relationship: Mesiobuccal cusp pf maxillary first mola occludes with the medionuccal groove of the mandibular first molar.
Canine/premolar relationship: Maxillary canine occuldes with the distal half of the mandibular canine and mesial half of the mandibular first molar.
Incisor relationship: Lower incisor occlude below or at the cingulum of upper incisors