Virology Flashcards
What infection in a patient with a CD4+ count <100 cells/mm3 presents with non-specific systemic symptoms and lymphadenitis?
Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare or Mycobacterium avium complex infection
What is the most salient clinical difference between opportunistic infections of Candida albicans and Epstein-Barr virus?
White plaques are scrapable in oral thrush (Candida albicans) whereas white plaques of oral hair leukoplakia are unscrapable (Epstein-Barr virus)
Of the dengue and Chikungunya viruses, which is more likely to cause severe clinical symptoms that could lead to death?
Dengue (neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhage, shock)
What molecular characteristic allows the hepatitis C virus (HCV) to evade host antibodies?
HCV lacks 3′-5′ exonuclease activity → no proofreading → antigenic variation of HCV envelope proteins and new viral mutant strains
Which 2 RNA viruses do not replicate in the cytoplasm?
Retrovirus and influenza virus (retroflu is outta cyt [sight])
What stage of hepatitis B infection does positive hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis B e antibody (anti-HBe), and hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc IgG) indicate?
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) and low infectivity
Which 3 herpesviruses are transmitted via sexual contact?
Herpes simplex virus-2 (HSV-2), cytomegalovirus, and human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8)
In patients with HIV, what virus can cause progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)?
JC virus (polyomavirus, Junky Cerebrum)
Why can hepatitis D (HDV) infection only occur in conjunction with hepatitis B (HBV) infection?
HDV is a defective virus so it depends on the HBV HBsAg coat for entry into hepatocytes
If the intracellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1) receptor is blocked, what virus will have difficulty infecting the cells?
Rhinovirus (binds to ICAM-1); “I CAMe to see the rhino”
What cells are infected by the Epstein-Barr virus?
Infects B cells via CD21
What possible sequela can occur in mumps, especially after puberty?
Sterility
What are the symptoms associated with dengue hemorrhagic fever?
Dengue fever with bleeding and plasma leakage (thrombocytopenia) and extremes in hematocrit (high or low)
Describe how the genome of progeny virus is obtained from completed partial dsDNA.
Host RNA polymerase transcribes mRNA from viral DNA; DNA polymerase then reverse transcribes viral RNA to DNA
What do IgG antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg) signify?
Chronic infection or prior exposure to hepatitis B
What is the RNA structure of the rhabdovirus?
Enveloped, single-stranded, negative-sense, linear RNA with a helical capsid
What is the incubation period for Ebola?
Up to 21 days
What is the pathology that leads to dengue shock syndrome?
Plasma leakage leading to circulatory collapse
Compare the incubation periods of hepatitis A, B, C, and E.
Hepatitis A and E: short (weeks); B and C: long (months)
What is the purpose of neuraminidase antigen on the parainfluenza viral membrane?
Promotes progeny virion release (neuraminadaways sends virus away)
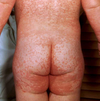
What is the pathophysiology of the “blueberry muffin” rash seen in congenital rubella?
Dermal extramedullary hematopoiesis
What endoscopic and biopsy findings are seen in Candida albicans esophagitis?
White plaques on endoscopy; biopsy shows yeast and pseudohyphae
Name 4 medically significant conditions caused by bunyaviruses.
Hantavirus infection (hemorrhagic fever, pneumonia), California encephalitis, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, Sandfly/Rift Valley fevers
What predisposing factor significantly increases the risk of developing dengue hemorrhagic fever?
Infection with a different dengue virus serotype after initial infection (due to antibody-dependent enhancement of disease)
What is the route of transmission for hepatitis A?
Fecal-oral via contaminated shellfish, exposure during travel, or in daycare centers
Describe the symptoms caused by Zika virus infection.
Conjunctivitis, low-grade pyrexia, and an itchy rash (20% of cases)
What virus can act like Epstein-Barr virus (HHV-4) but have a negative monospot test?
Cytomegalovirus (HHV-5)
What are the 2 most common renal manifestations of hepatitis B?
Membranous glomerulonephritis > membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
What virus causes croup?
Parainfluenza virus
Hepatitis D virus (HDV) infection needs coinfection with hepatitis B to supply the envelope protein for HDV. What is this mechanism called?
Complementation
By what mechanism does rotavirus cause gastroenteritis?
Rotavirus causes destruction of the intestinal villi and atrophy → ↓ reabsorption of Na+ and loss of K+
What vaccine has made mumps uncommon?
MMR (measles, mumps, rubella)
During which phase of HIV infection does the CD8+ T-cell count decline the most rapidly?
Systemic immunodeficiency/AIDS-defining illnesses phase (associated with exhaustion)
Describe the progression of rabies infection.
Fever and malaise → agitation, photophobia, hydrophobia, hypersalivation → paralysis, coma → death
What is the RNA structure of the flavivirus?
Enveloped, single-stranded, positive-sense, linear RNA with an icosahedral capsid
Which 2 viruses in the picornavirus family are not enteroviruses?
Rhinovirus and hepatitis A virus (HAV)
What ⊕ markers are expected in a chronic hepatitis B virus infection with high infectivity?
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg), and hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) IgG
What test can be performed in the setting of an inconclusive HIV-1/2 differentiation assay?
HIV-1 nucleic acid test (NAT)
What condition in humans is caused by enteroviruses within the picornavirus family?
Aseptic meningitis
What RNA virus family does rabies belong to?
Rhabdoviruses
Why are the hepatitis B, C, and D viruses unable to spread via the fecal-oral route?
B, C, and D = enveloped viruses which are killed in the gut; A and E = naked viruses are not destroyed in the GI tract (vowels hit your bowels)
Infections with which organisms are possible when the CD4+ count is <200 cells/mm3?
JC virus reactivation, Pneumocystis jirovecii, HIV infection, Histoplasma capsulatum
Other than animal bites, how else can rabies virus be transmitted?
Aerosol transmission (eg, bat caves)
Name 2 viruses found in the reovirus family.
Rotavirus (fatal diarrhea in kids) and coltivirus (Colorado tick fever)
What are the 7 positive-stranded RNA viruses?
I went to a retro (Retrovirus) toga (togavirus) party, where I drank flavored (flavivirus) Corona (coronavirus) and ate hippie (hepevirus) California (calicivirus) pickles (picornavirus)
What hepatitis virus is associated with polyarteritis nodosa?
Hepatitis B
From what source do enveloped viruses generally obtain their envelopes?
From the plasma membrane as they exit the cell
What characteristic liver biopsy findings are seen in hepatitis C?
Lymphoid aggregates with focal macrovesicular steatosis
Which lobe of the brain is most commonly affected in herpes encephalitis?
Temporal lobe (implicated virus is herpes simplex virus)
What is the RNA structure of the hepatitis D virus (HDV)?
Single-stranded, negative-sense, circular RNA
What serologic markers would you expect in a patient immunized against Hepatitis B?
⊕ Anti-HBs (all other hepatitis B markers negative)
What is the RNA structure of the orthomyxovirus?
Enveloped, single-stranded, negative-sense, linear (in 8 segments) RNA with a helical capsid
How is infection with the Chikungunya virus diagnosed?
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or serology
What complications may occur to a fetus exposed to parvovirus B19?
Hydrops fetalis and fetal demise
Describe the DNA structure of hepadnavirus, including whether or not it is enveloped.
Partially double-stranded, circular DNA, enveloped
How does HIV integrate its genome into the host DNA?
Reverse transcriptase converts HIV viral RNA → double-stranded DNA → integrates into host DNA
What 2 groups act as reservoirs for the yellow fever virus?
Monkeys and humans
What occurs during the acute phase of infection by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)?
Widespread dissemination and seeding of the lymphoid organs
What rodent-borne bunyavirus causes a hemorrhagic pulmonary syndrome?
Hantavirus
What is the function of hemagglutinin antigen on the parainfluenza viral membrane?
Promotes viral entry by binding to sialic acid (hemagglutinin brings virus in)
What are the typical symptoms of infection by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2)?
Fever, dry cough, shortness of breath fatigue (however often patients are asymptomatic)
What is the incubation period before symptom onset in rabies?
Weeks to months
What is the viral structure of rotavirus?
Segmented double-stranded RNA virus (reovirus family)
Name the 2 major antigens of the influenza virus.
Hemagglutinin and neuraminidase
What is the most common cause of measles-associated death in children?
Pneumonia
Which 2 picornaviruses commonly cause aseptic meningitis?
Echovirus and coxsackievirus
What ⊕ markers would you expect during the acute stage of infection with hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg), and hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) IgM
What presentation might cytomegalovirus infection have in a patient with a CD4+ count < 100/mm3?
Colitis, Retinitis, Encephalitis, Esophagitis, Pneumonitis (CREEP)
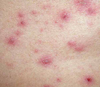
What is the name of the disease associated with “slapped cheeks” in children with parvovirus?
Erythema infectiosum or fifth disease
In addition to mononucleosis, name 3 diseases caused by Epstein-Barr virus infection.
Lymphomas (eg, Burkitt lymphoma), nasopharyngeal carcinoma (more common in Asian adults), and lymphoproliferative disease in transplant patients
What infection in patients with a CD4+ cell count < 500/mm3 presents with white patches on the lateral side of the tongue that cannot be scraped off?
Oral hairy leukoplakia (due to Epstein-Barr virus)
Which RNA virus family causes the often fatal diseases of Ebola and Marburg hemorrhagic fever?
Filoviruses
What is considered the normal range of CD4+ cell count?
500–1500 cells/mm3
Describe the DNA structure of poxvirus, including whether or not it is enveloped.
Double-stranded, linear DNA, enveloped (largest DNA viruses)
Which 3 herpesviruses are transmitted in respiratory secretions?
Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1), Epstein-Barr virus (HHV-4), and varicella-zoster virus (HHV-3)
In which type of cells do cytomegalovirus (CMV, HHV-5) establish latency?
Mononuclear cells
What is the RNA structure of the hepevirus?
Non-enveloped, single-stranded, positive-sense, linear RNA with an icosahedral capsid
What is the RNA structure of the picornavirus?
Non-enveloped, single-stranded, positive-sense, linear RNA with an icosahedral capsid
What test is performed for definitive diagnosis of skin and genital findings suggestive of herpes simplex virus?
Viral polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of skin lesions
What is the ploidy of the HIV genome?
Diploid RNA (2 molecules of RNA)
What are initial symptoms of Ebola?
Abrupt onset of flu-like symptoms, high fever, diarrhea/vomiting, and myalgia
Hepatitis C infection confers increased risk for which hematological cancer?
B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
Which DNA virus is single stranded?
Parvovirus (all other DNA viruses are double stranded)
The HIV RNA levels peak during which phases of infection?
Acute infection phase and systemic immunodeficiency/AIDS-defining illnesses phase
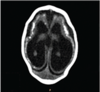
How does central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma differ from a Toxoplasma gondii infection on a brain MRI of a patient who has a CD4+ count <100/mm3?
A solitary ring-enhancing lesion is usually seen in CNS lymphoma; multiple lesions are usually found in a Toxoplasma gondii infection
Name 5 RNA viruses that are picornaviruses?
Poliovirus, Echovirus, Rhinovirus, Coxsackievirus, Hepatitis A virus (PERCH on a “peak” [picornavirus])
What kind of infections are HIV ⊕ patients generally at risk for as the CD4+ cell count drops?
Reactivation of past infections (eg, tuberculosis, shingles), non-Hodgkin lymphoma, dissemination of bacterial/fungal infections
What disease would be most likely in an unvaccinated young adult with personality changes, dementia, and autonomic dysfunction who had previously contracted rubeola as a child?
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE); occurs years after initial infection
In what parts of the world is hepatitis E infection most common?
Asia, Africa, and the Middle East
Which viral family includes the hepatitis D virus?
Delta viruses
Which human papillomavirus (HPV) serotypes are associated with warts?
Serotypes 1, 2, 6, and 11
What viral strains are found in the flu shot?
Viral strains that are most likely to appear during a flu season (reformulated vaccine)
What is a patient’s HIV status if the nucleic acid test (NAT) is negative following a positive HIV-1/2 Ag/Ab immunoassay?
HIV ⊖ (HIV Ag/Ab immunoassay was likely a false positive)
What is the transmission vector of the Chikungunya virus?
Aedes mosquito
What CD4+ count is associated with Toxoplasma gondii infection?
< 100/mm3
How is Ebola diagnosed?
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) within 48 hours of symptom onset
Which types of hepatitis can have a carrier state?
Hepatitis B and C (very common in C)
Besides febrile pharyngitis, what other signs or symptoms could adenovirus be responsible for?
Acute hemorrhagic cystitis, pneumonia, conjunctivitis (“pink eye”), gastroenteritis, and myocarditis
What are the possible means of transmission for β-pleated prion proteins (PrPsc)?
Transmissible via infected CNS tissue (iatrogenic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease) or food contaminated by bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE; variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease)
What is the difference between IgM versus IgG hepatitis B core antibodies?
IgM is a marker for acute or recent disease; IgG is a marker for prior exposure or chronic infection
What type of infections might be seen with HIV when the CD4+ count is 200-400 cells/mm3?
Skin and mucous membrane infections (generally years post-infection)
Which disease caused by a DNA virus has been eradicated through the use of a live-attenuated vaccine?
Smallpox (poxvirus family)
What is the genomic structure of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)?
Enveloped ⊕ single-stranded RNA with a helical capsid
What is the time frame for the development of anti-envelope antibodies (gp120) following initial HIV infection?
Begins after the first month through the acute phase and remains elevated
What serological marker is best to detect acute hepatitis A?
IgM hepatitis A virus antibody (anti-HAV IgM)
What are 3 possible clinical conditions associated with infection by Dengue virus?
Dengue fever, dengue hemorrhagic fever, or dengue shock syndrome
Which well-known RNA virus family has reverse transcriptase?
Retrovirus
Name 4 segmented RNA viruses.
Bunyaviruses, Orthomyxoviruses (influenza), Arenaviruses, Reoviruses (BOAR)
What part of the nervous system does varicella-zoster virus lie latent?
In the dorsal root or trigeminal ganglia
Why are naked nucleic acids of negative-sense RNA viruses (both single- and double-stranded) not infectious?
They require polymerases found in the complete virion to become infectiou
What disease process should you consider in a patient with a CD4+ count <200/mm3, progressive memory loss, and an otherwise negative infectious work-up?
HIV dementia
What 5 diseases are caused by paramyxoviruses?
Parainfluenza (croup), measles, mumps, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and human metapneumovirus
What stage of hepatitis B infection does positive hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs), hepatitis B e antibody (anti-HBe), and hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) IgG indicate?
Recovery stage
Name 5 medically significant members of the picornavirus family.
Poliovirus, Echovirus, Rhinovirus, Coxsackievirus, HAV (hepatitis A virus) (PERCH)
What is the mechanism of action of palivizumab?
Monoclonal antibody against the surface F protein preventing pneumonia caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
What is the RNA structure of the calicivirus?
Non-enveloped, single-stranded, positive-sense, linear RNA with an icosahedral capsid
What are 4 common clinical findings of measles?
Cough, Coryza, Conjunctivitis, and “C”oplik (Koplik) spots (4 C’s of Measles)
According to the CDC guidelines, all infants should be vaccinated against rotavirus with the exception of which medical conditions?
History of intussusception or severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)
All segmented viruses have what type of viral genome (DNA or RNA)?
RNA
Which herpesvirus is the most common cause of mononucleosis?
Epstein-Barr virus (HHV-4)
What is the function of the hepatitis B DNA polymerase?
Has both DNA- and RNA-dependent activities Enters nucleus → completes partial double-stranded DNA; also reverse transcribes viral RNA → DNA for progeny genome synthesis
Which virus is the most important global cause of infantile gastroenteritis?
Rotavirus (ROTAvirus = “right out the anus”)
What type of viral genomic structure is necessary for viral genome reassortment?
A segmented genome
What are the functions of the influenza viral antigens hemagglutinin and neuraminidase?
Hemagglutinin binds sialic acid to promote viral entry (hemagglutinin lets virus in); neuraminidase promotes progeny virion release (neuraminidaways sends virus away)
What are the 4 stages of untreated HIV infection?
Flu-like (acute); Feeling fine (latency); Falling count; Final crisis (Four stages)
Name the 4 families of RNA viruses that have no envelope.
Reoviruses, picornaviruses, hepeviruses, and caliciviruses
What are the characteristics of the vaccine against dengue virus?
Live, recombinant vaccine that uses yellow fever virus genes into which dengue virus envelope and premembrane proteins are inserted
Chronic hepatitis B is associated with what hematologic abnormality?
Aplastic anemia
What is the source of the hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) found in the serum of a patient infected with hepatitis B?
Secretion by infected hepatocytes into the circulation; it is not part of the mature HBV virion
What 3 organs are affected by Kaposi sarcoma?
Skin, gastrointestinal tract, and lungs
What is expected on a biopsy of bacillary angiomatosis in a patient who is HIV ⊕?
Neutrophilic inflammation caused by Bartonella spp
How do the Epstein-Barr virus (HHV-4) and strep throat differ in the location of cervical lymphadenopathy?
HHV-4 is more strongly associated with posterior cervical lymphadenopathy; strep throat involves anterior cervical lymphadenopathy
Which herpes simplex virus is more likely to cause viral meningitis?
Herpes simplex virus-2 (HSV-2)
Why are contact sports avoided in patients with mononucleosis?
Risk of splenic rupture
What 2 vaccines can be used for poliovirus infections?
Salk = inactivated polio vaccine (IPV); Sabin = oral polio vaccine (OPV)
To what viral family does hepatitis B virus belong?
Hepadnaviridae
All DNA virus are linear with the exception of which DNA virus families?
Papillomaviruses, polyomaviruses, and hepadnaviruses (circular genomes)
What is the prognosis for most patients who do not receive treatment for HIV infection?
Most eventually die due to complications of HIV infection
What is the RNA structure of the arenavirus?
Enveloped, single-stranded, positive- and negative-sense, circular (in 2 segments) RNA with a helical capsid
What are the most common endocrine manifestations of hepatitis C?
↑ risk of diabetes mellitus and autoimmune hypothyroidism
At what levels of CD4+ cell count do infections with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare and M avium complex most commonly occur in immunocompromised patients?
CD4+ cell count < 50/mm3
How does the monospot test work, and what is it used to detect?
Detects heterophile antibodies via agglutination of sheep or horse red blood cells as a method to detect Epstein-Barr virus
What population is vulnerable to infection by paramyxoviruses?
Children and infants
What are the characteristics of the Reovirus family?
Naked, multisegmented, double-stranded RNA viruses with double icosahedral capsids
What is the viral receptor for rabies?
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR)
What are possible central nervous system sequelae of measles?
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) and encephalitis
What rare sequela of measles can arise in the lungs, particularly in the immunosuppressed?
Giant cell pneumonia
Which DNA virus contains the reverse transcriptase enzyme in order to replicate its genome?
Hepadnavirus (eg, hepatitis B)
What is the most common complication of shingles?
Post-herpetic neuralgia
What infection is associated with a CD4+ < 200/mm3 and fever, fatigue, weight loss, cough, nausea, vomiting, dyspnea, and diarrhea?
Histoplasma capsulatum infection
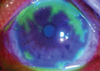
What are the possible presentations in a patient with herpes simplex virus-1?
Cold sores, herpetic whitlow, keratoconjunctivitis, erythema multiforme, esophagitis, temporal encephalitis, and gingivostomatitis
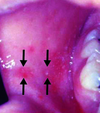
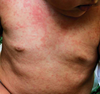
What is the typical presentation of rubella (German measles) infection?
Fever, postauricular and other lymphadenopathy, arthralgia, and maculopapular rash
Coltivirus is the causative agent for which illness?
Coltivirus causes Colorado tick fever
Purified nucleic acids from which 2 double-stranded DNA viruses are not considered infectious?
Poxvirus and hepatitis B virus (HBV)
What is the RNA structure of the paramyxovirus?
Enveloped, single-stranded, negative-sense, linear (nonsegmented) RNA with a helical capsid