Basic Bacteriology Flashcards
(177 cards)
Many guests, especially the elderly, have developed high fever and pneumonia after staying in a hotel with central AC. What medium is used to culture the causative organism?
Charcoal yeast extract agar buffered with cysteine and iron (the causative organism is Legionella)
What is typically found in the core of a bacterial spore?
Dipicolinic acid
What is the chemical composition of an endotoxin?
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
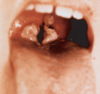
A painless black ulcer develops on the arm of a 56-year-old goat herder. What unique molecule does the capsule of the bacterium contain?
Poly-D-glutamate, which is only found in Bacillus anthracis (diagnosis: cutaneous anthrax)
In endotoxin-based complement activation, which complement(s) cause(s) hypotension/edema and histamine release?
C3a and C5a
What bacterial structural appendage, composed of protein, is known to help provide motility?
Flagellum
In the microbiology lab you find bacteria that produce yellow “sulfur” granules (sand). What are the granules made of?
Bacterial filaments; the bacteria are Actinomyces israelii (Israel has yellow sand)
Bacteria with thin peptidoglycan layers turn what color(s) with counterstain on Gram staining?
Red or pink, and are gram ⊖
After examining a patient suspected of having Clostridium difficile infection, you clean your hands with soap and water rather than the alcohol sanitizer. Why?
Spore-forming bacteria ( like Bacillus and Clostridium) are resistant to alcohol and can only be killed with soap and water
Which spirochete can be identified with Giemsa stain?
Borrelia
An elderly woman is vaccinated only against nonconjugated polysaccharide antigens. Why is this patient at greater risk for infection when compared to conjugated vaccines?
Polysaccharide antigens alone are not presented to T cells; this prompts a weaker immune response, in comparison to conjugated vaccines
On what part of the CNS does the Clostridium tetani toxin tetanospasmin act?
Renshaw cells in the spinal cord (toxin prevents release of inhibitory neurotransmitters, leading to spastic paralysis)
How does an indicator (differential) medium work? Give an example of such a medium.
A color change results in response to some organisms’ metabolites; Escherichia coli changes color on MacConkey agar (pH indicator) due to lactose conversion to acidic metabolites
What are the commonly encountered spore-forming bacteria, and what diseases do they cause?
Bacillus & Clostridium: B anthracis (anthrax), B cereus (food poisoning), C botulinum (botulism), C difficile (pseudomembranous colitis), C perfringens (gas gangrene), C tetani (tetanus)
A patient has a cough, and a culture grows a gram ⊖ rod that has a positive silver stain. What is the most likely pathogen?
Legionella
What color pigment does Pseudomonas aeruginosa produce?
Blue-green (aeruginosa: aerugula is green)
Shigella and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli share a mechanism for causing gastrointestinal mucosal damage and dysentery. What is it?
Both Shiga toxin and Shiga-like toxin cleave host cell rRNA, inactivating the 60S ribosomal subunit by removing adenine from rRNA
What are endotoxins composed of?
The lipid A component of lipopolysaccharide (a bacterium’s structural part); lysis releases it
What stain is useful to identify Tropheryma whipplei in a patient suspected to have Whipple disease?
Periodic acid-Schiff stain, that stains glycogen, and mucopolysaccharides (PaSs the sugar)
One type of conjugation process does not involve the transfer of chromosomes. How does it work?
In F+ to F- conjugation, plasmids are transferred from the F+ cell through a conjugal bridge; no chromosomal DNA is transferred
In which component of the cell envelope are oxidative and transport enzymes located?
Cytoplasmic membrane
A gram-positive bacterium produces offspring with a special keratin-like coat. How do these offspring survive?
By resisting dehydration, heat, and chemicals (the offspring are spores)
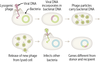
Cholera toxin is encoded in a phage. Describe how the phage helps the toxin gene undergo transduction.
A lysogenic phage infects bacteria, inserts viral DNA into chromosomes; viral (and bacterial) DNA are excised into the capsid and can infect other bacteria
A patient presents with contact lens-associated keratitis. What biofilm-producing bacteria are the cause?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa