Parasitology Flashcards
Name the helminth that causes perianal pruritus
Enterobius
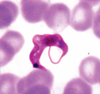
What findings on blood smear confirm a diagnosis of malaria?
Trophozoite ring forms within red blood cells and schizonts containing merozoites
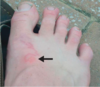
A patient has unilateral, nontender periorbital swelling after recent travel to Bolivia. What is the likely diagnosis?
Acute Chagas disease (Romaña sign)
How can Cryptosporidium infection be prevented?
With water filtration
What is the treatment for Loa loa infection?
Diethylcarbamazine
What lab finding might be expected on complete blood count in a patient with hookworm infection?
Microcytic anemia
In what region of the world is Babesia infection most common?
Northeastern United States
What organism causes scabies?
Sarcoptes scabiei
What is the treatment for leishmaniasis?
Amphotericin B, sodium stibogluconate
Which fluke (trematode) is transmitted in undercooked fish?
Clonorchis sinensis
All intestinal nematodes can be treated with which medication?
Bendazoles
What is the specific treatment for a dormant form of malaria?
Primaquine
What 2 methods are used to diagnose an Entomoeba histolytica infection in a blood sample?
Serology and serum antigen testing
How is Naegleria fowleri transmitted?
Acquired from warm freshwater lakes; enters the central nervous system through the cribriform plate
How are diarrhea-causing protozoans transmitted?
Via oocysts/cysts in contaminated water
What is the most appropriate diagnostic test for Naegleria fowleri?
Test for amoebas in the cerebrospinal fluid
Before using chloroquine to treat malaria, what should be verified about the patient’s particular strain of malaria?
Sensitivity to chloroquine; some have developed resistance to this drug
What are the commonly seen symptoms in patients infected withToxocara canis?
Myocarditis, hepatitis, visual impairment/blindness, seizures, and coma (patients also often asymptomatic)
On what continent is Chagas disease predominantly found?
South America
Why should pregnant women avoid cat litter boxes?
Cat feces may contain Toxoplasma oocysts, which can cross the placenta and cause birth defects
What are the common symptoms of Strongyloides stercoralis infection?
Duodenitis, dry cough, hemoptysis, and cutaneous symptoms
Where on the body are Pediculus humanus and Phthirus pubis commonly found?
Scalp/neck (head lice), waistline/axillae (body lice), or pubic/perianal regions (pubic lice)
How do you treat an infection with Strongyloides stercoralis?
Ivermectin or bendazoles
How does the fever pattern differ in malaria caused by Plasmodium vivax, P ovale, P falciparum, and P malariae?
P malariae: every 72 hours (quartan); P vivax/P ovale: every 48 hours (tertian); P falciparum: irregular
What is the common name for Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus?
Hookworms
What are 2 other classic findings associated with the infection causing river blindness?
Skin changes and loss of elastic fibers (Onchocerca volvulus infection)
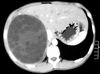
How is Cysticercosis transmitted?
By ingestion of food contaminated with human feces containing Taenia solium eggs
How is Entamoeba histolytica transmitted?
Via cysts in the water
How is Toxoplasma gondii acquired?
Either by ingesting meat infected with cysts or from exposure to oocysts in cat feces
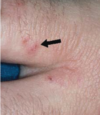
A man bitten by a female black fly experiences skin hyperpigmentation and blindness. What is the diagnosis?
Onchocerca volvulus infection (black flies, black skin nodules, “black sight”)
How does Cryptosporidium present in immunocompromised hosts with AIDS?
Severe diarrhea
How is Ascaris lumbricoides transmitted?
Fecal-oral route
How is Schistosoma transmitted to humans?
Through penetration of the skin by cercariae (larval form) in contaminated freshwater
What is the treatment for Diphyllobothrium latum?
Praziquantel, niclosamide
What is the common name for Ascaris lumbricoides?
Giant roundworm
What are the characteristics of a clinically significant infection with Trichuris trichiura?
Loose stools, rectal prolapse (usually in children), and anemia
How is babesiosis treated?
With atovaquone and azithromycin together
What are the 4 tissue nematodes?
Toxocara, Onchocerca, Loa loa, Wuchereria
What 2 treatments are used in life-threatening forms of malaria?
IV quinidine or artesunate
What is the mechanism of anemia in hookworm infestations?
The worms suck blood through the intestinal walls, leading to a microcytic anemia
How are acute infections of Trypanosoma cruzi treated?
Benznidazole or nifurtimox (cruzing in my Benz in my fur coat)
How are Necator americanus and Ancylostoma spp transmitted?
Larvae enter through the skin (usually from soil to soles of the feet)
How is Trypanosoma cruzi transmitted?
Fecal transmission from “kissing bug” that bites and defecates near the mouth or eyes
How can you diagnose babesiosis?
With a blood smear (look for “Maltese cross” or ring forms) or polymerase chain reaction test
What parasite causes brain cysts and seizures?
Taenia solium (neurocysticercosis)
What is the appropriate treatment for visceral larva migrans caused by Toxocara canis infection?
Bendazoles
How are infections with Clonorchis sinensis treated?
Praziquantel
What is visceral larva migrans?
A clinical syndrome where Toxocara canis nematodes migrate to the blood via the intestinal wall causing inflammation of heart, liver, eyes, and central nervous system
Name the parasite that is associated with the development of hematuria and squamous cell bladder cancer
Schistosoma haematobium
A woman from a rural area has new-onset skin swelling and conjunctival worms. What is the causative organism?
Loa loa nematode
How is Trichomonas vaginalis transmitted?
Sexually (Trichomonas vaginalis exists only in the human body due to inability to form cysts)
How can you distinguish Schistosoma mansoni from Schistosoma haematobium?
S mansoni = egg with a lateral spine; S haematobium = egg with a terminal spine
What is the typical treatment for infections from Ancylostoma spp and Necator americanus (hookworms)?
Bendazoles or pyrantel pamoate
What symptoms are associated with infection by Schistosoma mansoni?
Liver and spleen enlargement, fibrosis, inflammation, portal hypertension
What 3 infectious organisms can Pediculus humanus and Phthirus pubis transmit to humans?
Rickettsia prowazekii (typhus), Borrelia recurrentis (relapsing fever), and Bartonella quintana (trench fever)
How does hyperinfection syndrome occur with Strongyloides stercoralis?
Via autoinfection by larvae entering the bloodstream through the colonic wall
A patient with a past medical history of a trematode infection has painless hematuria. Why is this concerning?
Chronic Schistosoma haematobium infection is associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder
What is the treatment of choice for Wuchereria bancrofti infection?
Diethylcarbamazine
A man is bitten by a sandfly and develops spiking fevers, hepatosplenomegaly, and pancytopenia. What is the likely diagnosis?
Visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar)
What group of people are at risk for severe infections of babesiosis?
Patients with asplenia
What symptoms are typical of infection by Sarcoptes scabiei?
Pruritis that is worse at night and with serpiginous burrows between fingers and toes
Name the helminth that causes vitamin B12 deficiency.
Diphyllobothrium latum
How does an infection with Diphyllobothrium latum cause megaloblastic anemia?
The tapeworm competes for vitamin B12 in the intestines
Which 5 nematodes are transmitted by fecal-oral route?
Enterobius, Ascaris, Toxocara, Trichinella, Trichuris (don’t EATTT these!)
What form of the nematode is excreted in the stool of an individual infected with Strongyloides stercoralis?
Rhabditiform larvae