Mycology Flashcards
How do Mucor and Rhizopus enter the body?
Via inhalation of spores
What is the clinical name for dermatophyte (cutaneous fungal) infections?
Tinea (dermatophytes)
How does Pneumocystis pneumonia appear on methanamine-stained samples?
Disc-shaped yeasts
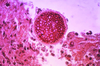
What 2 stains are used to diagnose Cryptococcus neoformans?
India ink (shows clear halo) and mucicarmine (shows inner red capsule)
What disease is caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii?
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP), which is a diffuse interstitial pneumonia
What structure must Mucor and Rhizopus penetrate to invade the brain?
Cribriform plate
A man with diabetes mellitus has a headache, facial pain, a black necrotic facial eschar, and cranial nerve palsies. What is the likely diagnosis?
Cavernous sinus thromboses leading to cranial nerve involvement, a complication of Mucor and Rhizopus infections
An athlete has hypopigmented and hyperpigmented macules on her back after intensive summer training. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Tinea (pityriasis) versicolor (Malassezia spp, Pityrosporum spp)
An immunocompromised patient presents with “soap bubble” lesions in his brain on imaging. How does an infection with Cryptococcus neoformans lead to this?
Through hematogenous dissemination after inhalation
What are the 3 different manifestations of tinea pedis?
Moccasin distribution, vesicular type, and interdigital (most common)
A male patient, positive for HIV, has an infection with a heavily encapsulated, nondimorphic yeast. What is the likely diagnosis?
Cryptococcus infection
What are the various prophylaxis options for Pneumocystis pneumonia?
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX), dapsone, pentamidine, or atovaquone
How can tinea corporis be acquired?
From contact with infected pets or farm animals
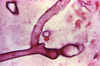
How does Sporothrix schenckii exist in the human body and in the soil?
Cigar-shaped yeast in the human body at 37°C; hyphae with spores in soil (conidia); S schenckii is dimorphic
Where are the abscesses in Mucor and Rhizopus infections most commonly found?
Rhinocerebral and frontal lobes
You culture Cryptococcus neoformans at 25°C and then at 37°C. What morphology do you note?
C neoformans grows as a yeast at both temperatures (it is not dimorphic)
What is observed when Candida albicans is grown at 20°C and then at 37°C?
Forms pseudohyphae and budding yeast at 20°C; germ tube formation at 37°C
How do you treat disseminated candidiasis?
Amphotericin B, fluconazole, or echinocandins
How is Pneumocystis pneumonia diagnosed?
From a bronchoalveolar lavage or lung biopsy; sample stained with methenamine silver or identified with a fluorescent antibody
At what CD4+ count should patients who are HIV+ begin to receive prophylaxis against Pneumocystis pneumonia?
< 200 cells/mm3
What populations are more likely to develop invasive aspergillosis?
Patients who are immunocompromised and those with disorders of neutrophil dysfunction (ie, chronic granulomatous disease)
What is the first-line treatment for oral thrush alone?
Treatment for superficial Candida infections is nystatin, fluconazole, or echinocandins
What class of organisms causes tinea pedis, cruris, corporis, capitis, and unguium?
Dermatophytes (representative geni include Microsporum, Trichophyton, Epidermophyton)
Which population is at an increased risk of developing vulvovaginitis due to Candida albicans?
Patients with diabetes and those using antibiotics
What treatment options are available for Aspergillus infections?
Voriconazole, echinocandins (2nd line)
How does tinea versicolor cause hypopigmentation on skin?
Lipid degradation by Malassezia spp (Pityrosporum spp) produces acids → inhibit tyrosinase (melanin synthesis) → hypopigmentation
What opportunistic fungus is a cause of endocarditis in IV drug users?
Candida albicans
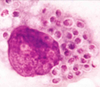
Name 3 infections caused by Cryptococcus neoformans typically found in immunocompromised patients.
Cryptococcosis, cryptococcal encephalitis (“soap bubble” lesions in the brain), and cryptococcal meningitis
A gardener presents with a pustule on her forearm and multiple nodules tracing upward toward her axilla. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Sporotrichosis (rose gardener’s disease)
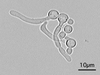
How does Aspergillus fumigatus appear on culture media at 37°C?
45° branching septate hyphae (broom-like appearance)
Which group of hosts would be symptomatic if infected with Pneumocystis?
Immunocompromised patients (eg, those with AIDS); otherwise, most are asymptomatic
What part of the body is affected in a tinea unguium infection?
Nails (fungal nail infection is also termed onychomycosis)
What is the appearance of Pneumocystis pneumonia on chest imaging?
Diffuse, bilateral ground-glass opacities with pneumatoceles
What is the treatment of tinea (pityriasis) versicolor?
Selenium sulfide, topical and/or oral antifungal medications
A man has multiple erythematous scaling rings with central clearing. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Tinea corporis infection (ringworm)
What populations are at high risk for oral/esophageal thrush?
Immunocompromised: neonates, patients with diabetes and AIDS, chronic steroid users
How is sporotrichosis transmitted?
Introduction of fungal spores into the skin after an injury, often caused by thorns (hence, rose gardener’s disease)
What is the treatment for vaginal candidiasis?
Oral fluconazole/topical azoles