Venous & Lymphatic Disease - Presentation, Investigation & Therapy Flashcards
What are varicose veins?
Swollen and enlarged veins that usually occur in the legs and feet
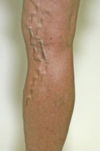
What are swollen and enlarged veins that usually occur in the legs and feet called?
Varicose veins

What percentage of the population is estimated to be affected by varicose veins?
33%
What is A?

Saphenofemoral junction
What is B?

Superficial iliac circumflex vein
What is C?

Anterior lateral tributary
What is D?

Femoral vein
What is E?

Deep femoral vein
What is F?

Anterior tributary vein
What is G?

Dorsal venous arch
What is H?

Posterior arch vein
What is I?

Greater saphenous vein
What is J?

Posterior medial tributary
What is K?

Pudendal vein
What is L?

Deep and superficial inferior epigastric vein
What is A?

Posteromedial superficial thigh vein
What is B?

Vein of Giacomini
What is C?

Saphenopopliteal junction
What is D?

Lesser saphenous vein
What is E?

Dorsal venous arch
What is F?

Posterolateral tributary vein
What is G?

Anterolateral superficial thigh vein
What is the course of the long saphenous vein?
Dorsal venous arch drains into the long saphenous vein which passes anterior to the medial malleolus, up the medial aspect of the leg
What does LSV stand for?
Long saphenous vein


