Upper Limb 1 Flashcards
(148 cards)
What 2 major structures can the body be divided into?
Main body (head, neck + trunk)
The appendages (pair upper and lower limbs)
What 2 major parts is the skeleton divided into?
Axial skeleton (part of the main body of the head, neck and trunk)
Appendicular skeleton (upper and lower limbs including the bones forming the pectoral (shoulder) and pelvic girdle)
General function of the upper limbs?
Position the hand for manipulation and grip activities
General function of the lower limbs?
Support the body weight, locomotion + maintain balance
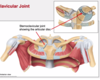
What are the upper limbs connected to the trunk by?
The left and right sternoclavicular joints

What type of joints are sternoclavicular joints?
True joints
Which joints connect the upper limb to the trunk and what type of joint is each one?
Left and right sterno-clavicular joints → True joints
Left and right scapulo-thoracic joints → Virtual or physiological joints
What is the true attachment of the upper limb with the trunk?
Manubrium
What are the scapulothoracic joint movements?
Movements of the scapula against the posterior and lateral thoracic wall

Which joints connect the lower limb to the trunk (axial skeleton)?
Sacroilliac joint
What type of joint is a sacro-iliac joint?
Synovial joint (relatively immobile joint)
What is the upper limb divided into?
- Pectoral (shoulder) girdle
- The arm
- The forearm
- The hand
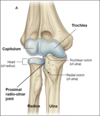
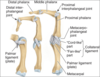
What is the clavicle?
Collar bone that connects the upper limb with the trunk

What does the clavicle articulate with at its medial end?
The manubrium (superior part of the sternum)
What does the lateral end of the clavicle articulate with?
Scapular acromion

Why does the clavicle have a number of small bony features?
Where muscles and ligaments can attach
Purpose of the clavicle?
Act as a movable strut supporting the scapula and the rest of the upper limb which are suspended from it.
Also a site of muscle attachment.
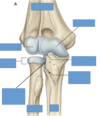
Label this diagram


Label this diagram of clavicle

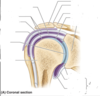
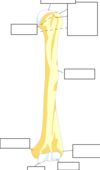
What is the scapula?
Flat triangular bone with a number of bony features that are sites of attachments for muscles and ligaments
What part of the scapula articulates with the clavicle?
The acromion
Important attachment point for muscles in the superior scapula?
Coracoid process which protrudes anteriorly

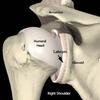
What is the glenoid fossa?
Shallow cut-like depression in a widened region of lateral scapula (socket for ball and socket shoulder joint)
What is the scapula spine?
Ridge of bone dividing the posterior scapula into infraspinatus and supraspinatus fossa -> lateral end =acromion