Thorax 1 Flashcards
What does the base of the heart consist of?
- the left atrium
- a small portion of the right atrium
- the proximal parts of the great veins (superior and inferior venae cavae and the pulmonary veins)

Where is the base of the heart directed?
It is quadrilateral and directed posteriorly + fixed posteriorly to the pericardial wall
Oesophagus lies immediately posterior to the base
What is the apex of the heart formed by and where is it positioned?

Positioned deep to the left fifth intercostal space, 8-9 cam from midsternal line
Formed by the inferolateral part of the left ventricle
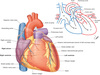
What does the anterior surface face and consist of?

- Faces anteriorly
- Consists mostly of right ventricle
- Has some of right atrium on right
Has some of left ventricle on the left

In the anatomical position, what does the heart rest on?
- The diphragmatic surface
What does the diphragmatic surface consist of?
- Consists of left ventricle + small portion of right ventricle
- Rests on the diaphragm
What does the left pulmonary surface face + what does it consist of?
- Faces the left lung
- Broad + convex
- Consists of left ventricle + portion of left atrium
What does the right pulmonary surface face + consist of?
- Faces the righ lung
- Is broad + convex
- Consists of right atrium
What are the right and left margins the same as?
- The right and left pulmonary surfaces of the heart
What is the interior margin defined as?
- The sharp edge between the anterior and diaphragmatic surface of the heart
- formed mostly by right ventricle + small portion of left ventricle near apex
What is the obtuse margin?
- Separates anterior and left pulmonary surfaces
- It’s round + extends from left auricle to cardiac apex
- Formed mostly by left ventricle + superiorly by small portion of left auricle
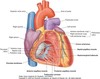
What does the right border in a standard posteroanterior view consist of?
- The superior vena
- Right atrium
- Inferior vena cava

What does the left border consist of?
- arch of aorta
- pulmonary trunk
- left auricle
- left ventricle
What does the inferior border consist of?
= Right ventricle and left ventricle at the apex

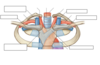
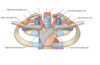
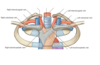
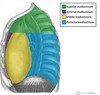
Label the image


What is the coronary sulcus and what does it contain?
- Circles the heart, separating the atria from the ventricles
- Contans the right coronary artery, the small cardiac vein, the coronary sinus + circumflex branch of left coronary artery
Label the image of coronary sulcus


What sulci separates the 2 ventricles + what does it contain?
- Anterior and posterior interventricular sulci
- The anterior interventricular sulcus is on anterior surface of the heart -> contains the anterior interventricular artery and great cardiac vein
- Posterior interventricular sulcus is on diaphragmatic surface of heart -> contains posterior interventricular artery + middle cardiac vein
Why does the left ventricule have a thicker muscular wall than the right?
More force is required to pump blood through the bdy than through the lungs
How does the blood return to the right atrium?
Enters through 1 of 3 vessels:
- Superior + inferior venae cavae -> together deliver blood to heart from body =
- coronary sinus -> returns blood from heart walls
Where does the superior and inferior vena cava enter the right atrium?

- Superior vena cava -> enters upper posterior portion of right atrium
- Inferior vena cava + coronary sinus enter lower posterior portion of right atrium
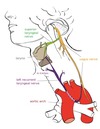
What is the heart housed inside of?
- Located within the mediastinum (the middle mediastinum)
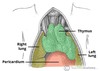
Label this image of the mediastinum and what type of image is it

- Cross section through the mediastinum

Label this image

- Saggital view of mediastinum
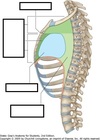
Inside the mediastinum, what is the heart contained in?
- Contained in the pericardial sac
What is the pericardial sac?
- Fibroserous sac surrounding heart and great vessels
- Consists of 2 layers: fibrous and serous
Describe the fibrous layer of the pericardium
- Strong connective tissue
Describe the serous layer of the pericardium
- Inner layer
- Encloses pericardial cavity which encloses pericardial fluid
- Divided into 2 layers:
1) Parietal (lines fibrous pericardium) -> most superficial layer of pericardium
Made up of dense + loose connective tissue, protects the heart + anchors it to surrounding walls
2) Visceral part -> adheres to heart
What are the 2 separate pumps of the heart?
- Pulmonary pump -> delivers poorly oxygenated blood to the lungs where it is oxygenated and returned to the heart
- Systemic pump -> delivers highly oxygenated blood to rest of body
Describe the pathway at which blood moves through the heart
- Blood leaves the left ventricle via aorta (head, neck to rest of body)
- Returns to right atrium through the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava (deoxygenated)
- Goes to right ventricle where it exits the heart into the pulmonary trunk and into either right or left pulmonary artery.
- Dexoygenated blood travels to lungs
- Blood returns from the lungs via pulmonary veins into left atrium
What do the different surfaces consist of?
- Anterior or sternocostal surface, formed mainly by the right ventricle
- Inferior or diaphragmatic surface, formed mainly by the left ventricle
- Posterior surface, formed mainly by left atrium
- apex formed entirely by left ventricle
What is the line of demarcation between the right atrium and right ventricle?
- The atrioventricular groove
- The right coronary artery lies in this groove