UL extra Flashcards
What are the joints that make up the pectoral girdle?
- clavicle and sternum (sterno-clavicular)
- clavicle and scapular (acromio-clavicular)
- scapula + humerus (gleno-humeral)
- scapula + thoracic wall (scapulo-thoracic)
Label the image


Label this image
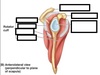

Label this image


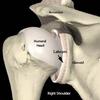
What does the glenoid labrum do?
Deepens the glenoid fossa to stabilise the shoulder
What are the different muscle compartments of the shoulder?
Anterior pectoral girdle
Posterior pectoral girdle
Intrinsic shoulder muscles
What muscles are contained in the anterior pectoral girdle?
pectoralis major
pectoralis minor
subclavius
serratus anterior
what muscles are contained in the posterior pectoral girdle?
trapezius
levator scapulae
latissimus dorsi
rhomboid major
rhomboid minor
what are the intrinsic shoulder muscles?
- deltoid
- teres major
- supraspinatus
- infraspinatus
- teres minor
- subscapularis
What are the two muscle groups that serve the shoulder region?
- pectoral girdle
- intrinsic shoulder muscles
What are the 4 surrounding ligaments that stabilise the glenohumeral joint?
glenohumeral ligaments
coracohumeral ligaments
transverse humeral ligaments
coracoacromial ligaments
What does the glenohumeral ligament do?
stabilises the anterior aspect of the joint and prevents it dislocating anteriorly

what does the coracohumeral ligament do?
attaches the coracoid process to the greater tubercle of humerus, supporting superior part of joint capsule

what does the transverse ligament do?
connects greater and lesser tubercles holding tendon of long head biceps brachia in place

what does the coracoacromial ligament do?
spans between acromion and coracoid prcoess forming coracoacromial arch
overlies shoulder joint and prevents superior displacement of humeral head

Label this image of ligaments


What is the pectoral region of the anterior chest wall?
contains 4 muscles that exert a force on the upper limb
pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior + subclavius
what is the pectoralis major muscle?
most superficial muscle in the pectoral region
large + fan shaped
has sternal head + clavicular head (sternal orginiates from anterior surface of the sternum, clavicle originates from the anterior surface of the medial clavicle)
distal attachment of both heads is into the intertubercular sulcus of humerus

Function of pectoralis major + innervation?
adducts + medially rotates the upper limb
draws scapula anteroinferiorly
clavicular head acts individually to flex upper limb
innervated by medial and lateral pectoral nerves
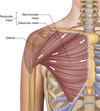
What is the pectoralis minor?
lies underneath the pectoralis major
both muscles form part of anterior wall of axilla region
originates from 3rd-5th ribs and inserts into coracoid process of scapula

function + innervation of pectoralis minor?
stabilises scapula by drawing it anteroinferiorly against thoracic wall
median pectoral nerve
what is the serratus anterior?
located more laterally in chest wall
consists of several strips -> originate from lateral aspects of ribs 1-8 and attach to costal surface of medial border of scapula

function + innervation of serratus anterior?
Rotates the scapula, allowing the arm to be raised over 90 degrees. It also holds the scapula against the ribcage.
long thoracic nerve

What is the subclavius muscle?
small muscle directly underneath the clavicle -> offers minor protection to underlying neurovascular structures
originates from junction of 1st rib and its costal cartilage -> inserts into inferior surface of middle third of the clavicle

function + innervation of subclavius?
anchors + depresses the clavicle
nerve to subclavius
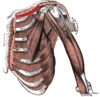
What can the muscles of the shoulder group be divided into?
extrinsic (from torso + attach to bones of the shoulder e.g. clavicle, scapula + humerus)
intrinsic (originate from scapula and/or clavicle + attach to humerus)
What can the extrinsic muscles of the shoulder be divided into?
- superficial (trapezius + latissimus dorsi)
- deep (levator scapulae + rhomboid minor and major)
what is the trapezius?
- broad, flat + triangular muscle
- most superficial of all back muscles
- originates from the skull, nuchal ligament and spinous processes of C7-T12
fibres attach to clavicle, acromion and scapula spine

function + innervation of trapezius?
Motor innervation is from the accessory nerve. It also receives proprioceptor fibres from C3 and C4 spinal nerve
upper fibres of the trapezius elevate the scapula + rotates it during abduction of the arm.
middle fibres retract the scapula
lower fibres pull the scapula inferiorly

what is the latissimus dorsi?
originates from lower part of the back
has a broad origin - spinous processes of T7-T12, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia and the inferior three ribs
fibres converge into a tendon that attaches to the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus

function + innervation of latissimus dorsi?
extends, adducts + medially rotates the upper limb
thoracodorsal nerve

what is the levator scapulae?
small + strap like muscle
begins in the neck + attaches to scapula
originates from transverse process of C1-4 vertebrae and attaches to medial border of the scapula

function + innervation of levator scapulae?
elevates the scapula
dorsal scapular nerve
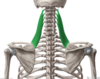
What is the rhomboid major?
originates from spinous process of T2-6 vertebrae
attaches to medial border of scapula, between scapula spine +inferior angle

function + innervation of rhomboid major
retracts + rotates the scapula
dorsal scapular nerve

what is the rhomboid minor muscle?
Originates from the spinous processes of C7-T1 vertebrae.
Attaches to the medial border of the scapula, at the level of the spine of scapula
superior to the rhomboid major

function + innervation of rhomboid minor?
dorsal scapular nerve
retracts + rotates the scapula

label the diagram


What are the 6 intrinsic muscles of the shoulder?
deltoid
teres major
4 rotator cuff group muscles (teres minor, supraspinatus, infraspinatus + subscapularis)
What is the deltoid muscle?
shaped like inverted triangle
can be divided into anterior, middle + posterior part
originates from lateral third of the clavicle, acromion + scapula spine
attaches to deltoid tuberosity on lateral aspect of humerus

What is the function + innervation of the deltoid muscle?
Anterior fibres – flexion and medial rotation.
Posterior fibres – extension and lateral rotation.
Middle fibres – the major abductor of the arm (takes over from the supraspinatus, which abducts the first 15 degrees).
axillary nerve

what is the teres major muscle?
Originates from the posterior surface of the inferior angle of the scapula
attaches to the medial lip of the intertubercular groove of the humerus

function + innervation of teres major muscle?
Adducts and extends at the shoulder, and medially rotates the arm
lower subscapular nerve

what are the highlighted structures?

deltoid (orange)
teres major (yellow)
what are the rotator cuff group muscles?
4 muscles that originate from the scapula and attach to the humeral head
the resting tone of these muscles is to ‘pull’ the humeral head into the glenoid fossa
gives glenohumeral joint additional stability

what is the supraspinatus muscle?
Originates from the supraspinous fossa of the scapula
attaches to the greater tubercle of the humerus

function + innervation of supraspinatus?
suprascapular nerve
abducts the arm 0-15 degrees + assists deltoid for 15-90 degrees
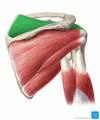
what is the infraspinatus muscle?
Originates from the infraspinous fossa of the scapula
attaches to the greater tubercle of the humerus

function + innervation of infraspinatus muscle?
laterally rotates the arm
suprascapular nerve

what is the subscapularis muscle?
originates from subscapular fossa on costal surface of scapula
attaches to lesser tubercle of humerus

function + innervation of subscapularis muscle?
medially rotates the arm
upper + lower subscapular nerve

what is the teres minor muscle?
originates from the posterior surface of the scapula adjacent to its lateral border
attaches to the greater tubercle of the humerus
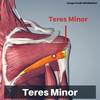
function + innervation of teres minor muscle?
laterally rotates the arm
axillary nerve

label the diagram

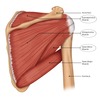
label the diagram


what can the muscles of the upper arm be divided into?
- anterior compartment -> BBC
- posterior compartment -> triceps brachii
what are the three muscles in the anterior upper arm?
arterial supply for anterior compartment of upper arm?
- Biceps, brachialis + coracobrachialis (bbc)
muscular branches of brachial artery

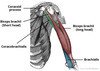
what is the biceps brachii?
- 2 headed muscle -> located majorly anteriorly to the humerus
- long head originates from supraglenoid tubercle of scapula
- short head originates from coracoid process of scapula
- both heads insert distally into radial tubersoity + fascia of forearm via bicipital aponeurosis

function + innervation of biceps brachii muscle?
supination in forearm + flexes arm at the elbow and at shoulder
musculocutaneous nerve

name the highlighted muscle

biceps brachii
what is the coracobrachialis muscle?
lies deep to biceps brachii in arm
originates from coracoid process of scapula -> muscle passes through axilla + attaches to medial side of humeral shaft at level of deltoid tubercle

function + innervation of coracobrachialis
flexion of arm at the shoulder + weak adduction
musculocutaneous nerve

what is the brachialis muscle?
lies deep to the biceps brachii
found more distally than the other arm muscles
forms floor of cubital fossa
Originates from the medial and lateral surfaces of the humeral shaft and inserts into the ulnar tuberosity, just distal to the elbow joint.

function + innervation of brachialis muscle?
flexion at elbow
musculocutaneous nerve + contributions from radial nerve


what artery supples the posterior compartment of the arm?
profunda brachii artery
what is the triceps brachii?
long head -> originates from infraglenoid tubercle
lateral head -> originates from humerus, superior to radial groove
medial head originates from humerus, inferior to radial groove
the heads converge distally into one tendon + attach at olecranon of ulna

function + extension of the triceps brachii?
extension of arm at the elbow
radial nerve

label this diagram

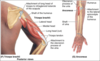


label the image


what happens when the biceps tendon enters the forearm?
connective tissue sheet is given off -> bicipital aponeurosis
forms the roof of cubital fossa + blends with deep fascia of anterior forearm
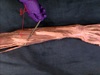
what runs through the highlighted struture?

long head of biceps brachii tendon
What is the anterior compartment of the forearm split into?
superficial
intermediate
deep
generally, what do the muscles in anterior compartment of forearm perform?
flexion at wrist + fingers and pronation
what are the superficial muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm?
- flexor carpi ulnaris
- flexor carpi radialis
- pronator teres
where do all the muscles in the superficial anterior compartment of the forearm arise from?
a common tendon -> arises from medial epicondyle of humerus

what is the flexor carpi ulnaris?
originates from the medial epicondyle with the other superficial flexors
has long origin from the ulna + passes into wrist and attaches to pisiform carpal bone

what is the highlighted structure?

function + innervation of flexor carpi ulnaris?
flexion + adduction at wrist
ulnar nerve



what is the palmaris longus?
originates from the medial epicondyle + attaches to flexor retinaculum at wrist

function + innervation of palmaris longus?
flexion at wrist
median nerve
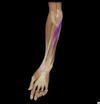
what can you see if you reflect back palmaris longus just distal to wrist?
median nerve immediately underneath
what is the flexor carpi radialis?
originates from medial epicondyle + attaches to base of metacarpals II and III

function + innervation of flexor carpi radialis?
flexion + abduction at wrist
median nerve
what is the pronator teres?
lateral border of the pronator teres forms the medial border of the cubital fossa, an anatomical triangle located over the elbow.
two origins -> one from the medial epicondyle
other from the coronoid process of the ulna
It attaches laterally to the mid-shaft of the radius.
function + innervation of pronator teres?
pronation of forearm
median nerve



what muscle is in the intermediate compartment of the anterior forearm?
flexor digitorum superficialis (in between deep and superficial muscle layers)
why is the flexor digitorum superficialis a good landmark in the forearm?
the median nerve and ulnar artery pass between its two heads, and then travel posteriorly

what is the flexor digitorum superficialis?
has two heads – one originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus, the other from the radius
muscle splits into four tendons at the wrist, which travel through the carpal tunnel, and attaches to the middle phalanges of the four fingers.

function + innervation of flexor digitorum superficialis?
flexes the metacarpophalangeal joints + proximal interphalangeal joints at the 4 fingers
flexes at the wrist
median nerve

flexor digitorum superficialis
what are the 3 muscles in the deep anterior forearm?
flexor digitorum profundus
flexor pollicis longus
pronator quadratus

what is the flexor digitorum profundus?
originates from the ulna + associated interosseous membrane
splits into 4 tendons at wrist + pass through carpal tunnel and attach to distal phalanges of 4 fingers

function + innervation of flexor digitorum profundus?
only muscle that can flex the distal interphalangeal joints of the fingers
also flexes at metacarpophalangeal joints and at the wrist
medial half (ring + little finger) = ulnar nerve
lateral half (middle + index finger) = innevrated by anterior interosseous branch of median nerve

what is the flexor pollicis longus?
lies laterally to flexor digitorum profundus
Originates from the anterior surface of the radius and surrounding interosseous membrane
Attaches to the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb.

function + innervation of flexor pollicis longus?
Flexes the interphalangeal joint and metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb
median nerve (anterior interosseous branch)

what is the pronator quadratus?
square shaped muscle found deep to tendons of flexor digitorum profundus + flexor pollicis longus
originates from anterior surface of ulna + attaches to anterior surface of radius

function + innervation of pronator quadratus?
pronates forearm
median nerve (anterior interosseous branch)



label


label

label


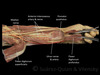
what are the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm commonly known as and what is their general function?
extensor muscles
produce extension at wrist + fingers
what are all the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm innervated by?
radial nerve
what are the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm divided into?
deep
superficial
separated by layer of fascia
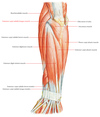
how many muscles are there in the superficial layer of the posterior forearm + what are they?
there are 7 muscles:
extensor carpi radialis brevis
extensor digitorum
extensor carpi ulnaris
extensor digiti minimi
(all share a common tendinous origin at the lateral epicondyle)
brachioradialis
extensor carpi longus
anconeus
what is the brachioradialis muscle?
origin and innervation are characteristic of an extensor muscle, but it is actually a flexor at the elbow
muscle is most visible when the forearm is half pronated
distal forearm, the radial artery and nerve are sandwiched between the brachioradialis and the deep flexor muscles
originates from proximal aspect of lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus + attaches to distal end of radius (before radial styloid process)

function + innervation of brachioradialis?
flexion at elbow
radial nerve

where are the extensor carpi radialis muscles situated?
lateral aspect of wrist
produce abduction as well as extension at wrist

where does the extensor carpi radialis longus originate from?
supracondylar ridge
tendons attach to metacarpal bones II and III
where does the extensor carpi radialis brevis originate from?
the lateral epicondyle
tendons attach to metacarpal bones II and III
function + innervation of the extensor carpi radialis muscles?
extends + abducts wrist
radial nerve
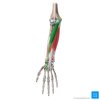
what is the extensor digitorum communis?
main extensor of the fingers
originates from lateral epicondyle
tendon continues into distal part of the forearm where it splits into 4 + inserts into extensor hood of each finger

function + innervation of extensor digitorum communis?
extends medial four fingers at MCP and IP joints
radial nerve (Deep branch)

what is the extensor digiti minimi?
medially to extensor digitorum
originates from lateral epicondyle of humerus
attaches with extensor digitorum tendon into extensor hood of little finger
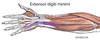
function + innervation of extensor digiti minimi?
extends the little finger + contributes to extension at wrist

what is the extensor carpi ulnaris?
located on medial aspect of posterior forearm
originates from lateral epicondyle of humerus + attaches to base of metacarpal V

function + innervation of extensor carpi ulnaris?
extension + adduction of wrist
radial nerve (deep branch)

what is the anconeus?
situated medially + superiorly in extensor compartment of forearm
blends with fibres of triceps brachiii (2 muscles hard to distinguish)
originates from lateral epicondyle -> attaches to the posterior + lateral part of olecranon

function + innervation of anconeus?
extends + stabilises elbow joint
abducts ulna during pronation of forearm
radial nerve

what are the 5 deep muscles of the posterior forearm?
supinator
abductor pollicis longus
extensor pollicis brevis
extensor pollicis longus
extensor indicis
what is the supinator muscle?
lies in the floor of the cubital fossa
has two heads, which the deep branch of the radial nerve passes between
has two heads of origin -> one originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus
other from the posterior surface of the ulna -> they insert together into the posterior surface of the radius.

function + innervation of supinator muscle?
supinates forearm
radial nerve (deep branch)
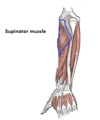
what is the abductor pollicis longus?
situated immediately distal to supinator muscle
tendon contributes to lateral border of anatomical snuffbox
originates from interosseous membrane + adjacent posterior surfaces of radius and ulna
attaches to lateral side of metacarpal I

function + innervation of abductor pollicis longus?
abducts the thumb
radial nerve (posterior interosseous branch)

what is the extensor pollicis brevis?
found medially + deep to abductor pollicis longus
in the hand, its tendon contributes to the lateral border of the anatomical snuffbox
originates from posterior surface of radius + interosseous membrane
attaches to base of proximal phalanx of thumb

function + innervation of extensor pollicis brevis?
Extends at the metacarpophalangeal and carpometacarpal joints of the thumb.
Radial nerve (posterior interosseous branch).

what is the extensor pollicis longus?
larger muscle belly than the EPB
its tendon travels medially to the dorsal tubercle at the wrist, using the tubercle as a ‘pulley’ to increase the force exerted
tendon of EPL forms medial border of snuffbox in hand
originates from posterior surface of the ulna + interosseous membrane
attaches to distal phalanx of thumb

function + innervation of extensor pollicis longus?
Extends all joints of the thumb: carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal.
Radial nerve (posterior interosseous branch).

what is the extensor indicis proprius?
muscle allows the index finger to be independent of the other fingers during extension.
originates from the posterior surface of the ulna and interosseous membrane, distal to the extensor pollicis longus.
attaches to the extensor hood of the index finger.

function + innervation of extensor indicis proprius?
extends index finger
radial nerve (posterior interosseous branch)





