HNS 1 Flashcards
What structure is being pointed at here?

bregma
What is the biggest venous sinus?
Superior saggital sinus
Advantage of the anterior fontanelles?
Bones haven’t fused yet, gives skull a little flexibility in case the birth canal is too tight
Which suture does the sphenoid bone articulate with the squamous part of the temporal bone?
Sphenosquamous suture
Which 2 main artery systems form the Circle of Willis?
Internal carotid arteries
Vertebral arteries
Which bones articulate with the squamous part of the temporal bone?

Greater wing of sphenoid
Parietal bone at the squamous suture

Which bone does the temporal bone articulate posteriorly with?
Occipital bone
Which foramen does the facial nerve and vestibucochlear nerve + where is it on the diagram?

Internal acoustic meatus

What are the 8 branches of the external carotid artery?
Superior thyroid artery
Ascending pharyngeal artery
Lingual artery
Facial artery
Occipital artery
Posterior auricular artery
Maxillary artery
Superficial temporal artery
Describe characteristics of the pia mater
Innermost, thin + delicate layer
How does this artery enter the cranial fossa?

Foramen spinosum
Which foramen is associated with mandibular nerve + where is it on the diagram?

Foramen ovale

Which layer is closely adherent to the brain?
The pia mater
Which arteries supply the anterior cranial fossa + where is on the diagram?

Anterior meningeal arteries

Which structures of the brain are found within the posterior cranial fossa?
Cerebellum and brainstem

Which bones form the floor of the posterior cranial fossa?
Occipital bone
Temporal bone

How can you identify an extradural haematoma on a CT scan?
More focal
Does not extend beyond suture
Bi-convex (lens shaped)

What is the falx cerebri?
Falx cerebri is a crescent shaped downward projections of meningeal dura mater from the dura lining the calva that passes between the two cerebral hemispheres towards the corpus callosum.
Helps stabilise the brain within the cranial cavity
What structure is being pointed to?

Pterion
Name the different coloured structures

Green = frontal bone
Blue = sphenoid bone
Dark pink = nasal bone
Light pink = maxilla
Orange = zygomatic bone
Purple = mandible
Red = vomer
What is the highlighted bone?

Zygomatic process
Which foramen does the accessory nerve pass through?
Jugular foramen
Which part of the temporal bone has a flat plate appearance and forms the superior regions of the temporal bone?
Squamous part
What is a subdural bleed?
Deep to the dura
Role of the 2 posterior communicating arteries?
Connects internal carotid artery with posterior cerebral artery

What structures pass through the foramen ovale?
Mandibular nerve
Accessory meningeal artery
Lesser petrosal nerve (branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve)
Emissary vein connecting through cavernous sinus
Which bones do the body of the sphenoid bone articulate with?
Ethmoid, vomer and palatine bone
Label the parts of the maxilla:
- Zygomatic process
- Orbital surface
- Infra-orbital foramen
- Frontal process
- Alveolar process
- Anterior nasal space


What is the junction between the saggital and coronal suture?
Bregma
Upon CSF drainage which layer is collapsed onto surface of the brain?
Arachnoid layer
Identify structures on the diagram:
- optic canal
- superior orbital fissure
- foramen rotundum
- foramen spinosum
- foramen lacerum
- foramen ovale
- carotid canal

Which 2 branches arise from the middle meningeal artery + where do they go?
Anterior and posterior branch of meningeal artery
Anterior branch crosses sphenoid’s great wing reaching groove of parietal bone
Posterior branch curves back toward temporal bone before reaching back portions of parietal bone

Name of the 2 cranial foramina found on greater wing of sphenoid bone?
Foramen ovale
Foramen spinosum
What bone forms the forehead?
Frontal bone
What does the frontal bone form anteriorly?
Forehead, and the superior part of the rim of each orbit
Superior to the rim of the orbit on each side are the raised superciliary arches
Which foramen is circled in red + what nerve is associated with it?
What is its position to the superior orbital fissure?

Optic canal and optic nerve
Medial to the superior orbital fissure
Describe the 2 layers of the dura mater
Periosteal is very closely adherent to inner surface of the bone
Meningeal is close to the arachnoid
What is the tentorium cerebelli?
Horizontal projections of meningeal dura mater that covers and separates cerebellum in posterior cranial fossa from posterior parts of cerebral hemisphere
Provides structural support for brain in event head is shaken or hit
What meningeal layer lies beneath the dura?
The arachnoid mater
What structure is highlighted in the picture and what nerve passes through it?

Foramen lacerum + greater petrosal nerve (facial nerve)
What are the 5 layers that form the scalp + label them on the diagram

Skin
Connective layer
Aponeurotic layer
Loose connective tissue
Pericranium

Which nerve bundles is associated with the cribiform plate?
Olfactory nerve bundles
Which artery forms upon the union of the 2 vertebral arteries?
Basilar artery
Which carotid artery supplies the face?
External carotid artery
Role of anterior communicating artery
Connects the left and right anterior cerebral arteries

Which 4 cranial nerve pass through the superior orbital fissure + which structure is it?

Oculomotor nerve (CN3)
Trochlear nerve (CN4)
Abducens nerve (CN6)
Opthalmic nerve (first branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN5)

What structure is highlighted and what bones articulate with it?

Lamboid suture
Laterally, parietal bones and posteriorly, occipital bone
What is the glabella?
Depression within the raised supercilliary arches
(bony point present on the frontal bone between two superciliary arches)
What structure is being pointed to and what bone is it located on?

Mental foramen and mandible bone
Function of the CSF
Helps to protect the brain against movement
Nutrient role in terms of supplying nutrients to the brain
What structure is being pointed to and what bone is it located on?

Infraorbital foramen and maxillary bone
What projections are found in the subarachnoid space?
Spider-like projections of the arachnoid mater
When do venous sinuses form?
When the two layers of the dura mater open up, they form venous sinuses where venous blood circulates within the cranial cavity
Name the highlighted structure

Sphenoid bone
Which structures is formed from the fold and union of the two dura mater layers?
Falx Celebri
What are the 3 cranial fossa? Identify them on the diagram

Purple = anterior cranial fossa
Blue = middle cranial fossa
Green = posterior cranial fossa
What parts of the brain does the anterior cranial fossa contain?
- Frontal lobe of cerebral cortex
- Olfactory bulb
- Olfactory tract
- Orbital gyri

What is the large membranous and unossified structure between the bones of the skull found in infants?
Anterior fontanelles
How can you identify a subdural haematoma on a CT scan?
Usually large, crescentic + indirect (not a site of impact)

Describe the qualities of the arachnoid mater
Elastic and has spider-like projections
What structure is being pointed to?

Foramen magnum
Arteries within the circle of willis?
Left and right anterior cerebral artery
Anterior communicating artery
Left and right internal carotid artery
Posterior cerebral artery (left + right)
Posterior communicating artery (left + right)
Bones forming the anterior cranial fossa?

Frontal, ethmoid and sphenoid bones

Which bone does the zygomatic process anteriorly articulate with?
Zygomatic bone

Which artery resides deep to the pterion?
Anterior branch of middle meningeal artery
Which dura layer is adherent to the inner surface of the bone
Periosteum
Which suture does the unpaired frontal bone pair up with the parietal bones?
Coronal suture
Which foramen is characterised by its minute hole and where is it on the diagram?

Foramen spinosum

What are the different bones that form the pterion (colour)?

Red - frontal bone
Orange - parietal bone
Purple - temporal bone
Yellow - greater sphenoid wing
Which cranial nerves pass through the jugular foramen?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
Vagus nerve (X)
Accessory nerve (XI)
Which arteries arise from the internal carotid arteries?
Ophthalmic artery
Posterior communicating artery
Middle cerebral artery
Anterior cerebral artery
Which carotid artery supplies the cranial cavity?
Internal carotid artery
Which foramen does the hypoglossal nerve pass through?

Hypoglossal canal

Which foramen are located on the superior rim of the orbit?
Supraorbital foramen
Which foramen does the vagus nerve pass through?
Jugular foramen
Four main parts of the temporal bone and identify them on unlabelled diagram
Squamous part
Mastoid process
Zygomatic process
External acoustic meatus (timpanic part)

Which bones form the pterion?
Point where the greater sphenoid wing, temporal, parietal and frontal bones meet
What passes through the foramen spinosum?
Middle meningeal artery
Junction between the sagittal and lamboid suture?
Lambda
Which is the main foramen that can be seen on the inferior aspect of the skull?
Foramen magnum
What is the unlabelled structure called?

Anterior fontanelles
Which structure is highlighted and what does it contain?

Foramina of the cribiform plate (within the ethmoid bone)
Contains the olfactory nerve bundles
Which formamen does the hypoglossal nerve pass through?
Hypoglossal canal
Which two cranial nerves pass through the internal acoustic meatus?
Facial nerve (CN7)
Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN8)
Which types of bleed are associated with damage to the pterion?
Intracranial bleeds
What does a rupture of middle meningeal artery at the pterion typically lead to?
Epidural haematoma
Label the structures missing on the diagram
- Falx cerebelli
- Tentorium cerebelli


How far does the falx cerebri go?
Down to the corpus collosum
What nerve goes through optic canal and where does it go?
Optic nerve and goes through the back of the eye to supply the eye
Which foramen does the abducens nerve pass through?
Superior orbital fissure
Which artery supplies the posterior cranial fossa?
Posterior meningeal artery
What structure is highlighted in the diagram and what bone does it articulate with?

Saggital suture and the paired parietal bone
Which lobe of cerebrum resides within middle cranial fossa + what area of MCF?
Temporal lobe
Lateral part
How do the 2 posterior cerebral arteries form?
Bifurcation of basilar artery
Which part of the temporal bone forms part of the surface of the external acoustic opening?
Tympanic part

What is the largest artery supplying the dura mater?
Middle meningeal artery (branch of maxillary)
Which foramen does the maxillary nerve pass through + what structure is it on the diagram?

Foramen rotundum

What are the labeled structures?


Which meningeal artery passes through jugular foramen?
Posterior meningeal artery
Which foramen does the internal carotid artery pass through + where is it on the diagram?

Carotid canal

Which bone does the pituitary gland reside within?
Sella turcica of the sphenoid bone
Identify:
- Lesser wing
- Greater wing
- Foramen ovale
- Foramen rotundum
- Foramen spinosum
- Superior orbital fissure


Structures associated with optic canal?
Opthalmic artery + optic nerve
Which arteries supply the middle cranial fossa + what foramen does it come out of?

Middle meningeal artery and it enters through the foramen spinosum
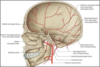
What is the highlighted structure?

Supraorbital foramen
Which foramen does the trochlear nerve pass through?
Superior orbital fissure
What does the subarachnoid space contain?
Spider-like projections of the arachnoid mater
Cerebral spinal fluid
What is the structure being pointed to?

Vomer bone
Which artery is deep to the pterion?
Middle meningeal artery
Describe the dura mater
Outermost layer
Thick + inelastic layer
Has 2 layers (periosteal and meningeal)
Which part of the skull is the weakest?
pterion

What bones form the middle cranial fossa?
Sphenoid and temporal bone

What is the extra-dural space?
Generated within vertebral columns
Spinal dura mater is adherent to the foramen magnum
Periosteal mater lines the vertebrae
This produces a separation which is the extra-dural space
Epidural anaesthesia is injected within this space
What is the structure highlighted?

Sphenosquamous suture
What cranial nerve is the maxillary nerve from?
One of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve (CN5)
Structures passing through superior orbital fissure?
Oculomotor nerve
Trochlear nerve
Opthalmic nerve
Abducens nerve
Opthalmic vein (superior divisions)
Structures forming the brainstem + label them on the diagram?

medulla
pons
cerebellum

What are the 6 main anterior bones of the skull?
Frontal
Nasal
Lacrimal
Maxilla
Zygomatic
Mandible
Which artery provides afferent information regarding vision?
Internal carotid artery
What are the 3 meningeal layers?
Dura mater
Arachnoid
Pia mater
Which are the six main bones on the lateral view of the skull and what colour do they correspond to?

Frontal bone - light yellow
Parietal bone - red
Occipital bone - orange
Temporal bone - pink
Zygomatic bone - blue
Sphenoid bone (greater wing) - purple
What is the effect of the haematoma on intracranial pressure?
Intracranial pressure increases
What structure is being pointed to and what bone is it located on?

Supraorbital foramen and frontal bone
Name of highlighted bone

Palatine bone
Which foramen does the glossopharyngeal nerve pass through?
Jugular foramen
Which artery provides impressions on the cranial cavity?
Middle meningeal artery
Which sinus is lateral to the sella turcica?

Cavernous sinus



