Thorax 2 Flashcards
(79 cards)
What is the thoracic skeleton composed of?
- 12 thoracic vertebrae
- 12 pair of ribs + costal cartilages
- Sternum
What does the costal cartilages articulate with?
- Articulate at the back with the vertebrae
- Articulate with sternum at the front
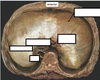
Describe the thoracic vertebrae
- 12 in number
- T1 to T12
- Heart shaped vertebral body
- Facets on the body for articulations with heads of ribs
- Facets on the transverse process for articulations with the tubercles of the ribs EXCEPT for ribs 11 & 12
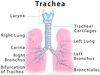
Label the diagram
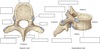

What is the vertebral foramen?
- The centre carries the spinal cord + the meningeal layers
Label this diagram

How many ribs are there?
-12 pairs of ribs
What are true ribs?
- The first seven ribs reach the sternum -> articulate with the sternum via their own costal cartilage

What are false ribs?
- Ribs 8,9 and 10 reach the sternum via the costal cartilage of the rib above
- These are false ribs

What are floating ribs?
- Ribs 11 and 12 lack an anterior attachment completely
- Ribs articulate at the posterior surface with a thoracic vertebrae

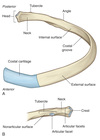
What do the different parts of the rib do?

- The head articulates with the body of the vertebral body
- The tubercle articulates with the facet on transverse process
- The costal cartilage which attaches rib to sternum

What is the outline of the costal margin?
Where the diaphagm attaches to the chest wall

Label the diagram


Where do the ribs attach to the sternum?
1st costal cartilages attach to manubrium
2nd to manubriosternal joint (joint between manubrium and sternum)
3-7th ribs attach directly to body of sternum
8th-10th ribs attach to sternum via costal cartilages of the rib above
11th and 12th have no anterior attachment to sternum -> floating ribs
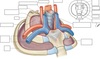
What is the thoracic inlet?
- Superior thoracic aperture
- Ring formed from the first thoracic vertebra posterior, the first ribs and the manubirum
- Conduit for structures passing from head + neck into thorax and abdominal cavity e.g oesophagus & trachea
- Conduit for vessels going to and from the heart

What vessels go to and from the heart inside the thoracic inlet?
- Internal jugular vein
- Subclavian veins
- Subclavian arteries (posterior to the above)
- Common carotid arteries (posterior to the above )
Label this diagram

Describe the appearance of the diaphragm
- Has a flat, central tendon with muscle radiating out to the costal margin + the vertebrae

Label the diagram


How does the diaphragm increase chest volume during breathing?
- Dome flattens to increase the vertical diameter of the chest
- Pulls the costal margin up to increase both the transverse + anteroposterior diameters
What do the intercostal muscles?
- They sit in between adjacent ribs
- Help to stiffen the chest wall and to improve the efficiency of breathing movements
What does elevation and depression of the diaphragm lead to?
They significantly alter the vertical dimensions of the thorax
Depression results when the muscle fibers of the diaphragm contract
Elevation occurs when the diaphragm relaxes
How do the sternum and the ribs move to increase the chest volume?
- Sternum moves anteriorly + superiorly increase anteroposterior dimension of the chest
- Ribs move in a bucket handle type movement where they elevate and increase the media-lateral dimensions of the chest

How are the intercostal muscles arranged?
- The intercostal muscles occupy the intercostal muscles
- Organised into 3 layers 90 degree to each other