UE arthrology LOs Flashcards
1
Q
sternoclavicular joint
A
- sellar joint with articular disc
- superior –> inferior
- convex clavicle
- concave manubrium
- anterior –> posterior
- concave clavicle
- convex manubrium
- motions
- protraction: anterior glide of concave clavicle
- retraction: posterior glide
- elevation: superior roll and inferior glide of convex clavicle
- depression: inferior roll and superior glide

2
Q
acromioclavicular joint
A
- plane/gliding motion
- acromion and clavicle: flat?
- motions
- protraction and retraction: A-P glide
- abduction and adduction: acromion rotattion on clavicle

3
Q
glenohumeral joint
A
- like golf ball on tee, ball in socket
- convex humeral head
- concave glenoid fossa
- motions:
- convex on concave – roll and glide opposite (most off the time)
- ER: roll posterior, glide anterior
- IR: roll anterior, glide posterior
- flexion: roll superior, glide inferior

4
Q
scapulothoracic joint
A
- pseudo joint – muscular between scapula and joint
- no direct ligamentous attachments
- motions:
- abduction/protraction: lateral and anterior
- adduction/retraction: medial and posterior
- “rotations:” upward/downward, IR/ER, anterior/posterior tilt
- depression
- elevation

5
Q
labrum
A
- produces concavity of glenoid fossa
- deepens socket 50-75%
- glenoid is shallow socket: faces lateral/anterior/superior, changes with scapular position
- glenoid fossa is 1/4 side of humeral head, pear shaped
- deepens socket 50-75%

6
Q
joint capsule
A
- anterior and posterior capsula tissue continues on neck of humerus
- anterior and inferior cpasule thicker than posterior

7
Q
ligament complex
A
- anterior GH ligaments
- superior GHL, middle GHL
- inferior GHL: pliable redundant ligament complex

8
Q
muscles/dynamic stabilizes
A
- reotator cuff: pull head of humerus into glenoid fossa
- supraspinatus, subscapularis, infraspinatus, teres minor, long head of biceps
- RC <> capsule <> ligaments
- tendons intimate with capsule – interdigitate
- encapsulates humeral head
- tendon”itis”/inflammation rarely isolated to 1 tendon
- muscles/tendons do not function in isolation
- deltoid: largely stabilizing, regardless of humeral position

9
Q
sternoclavicular dislocation
A
- very rare: occurs with direct trauma or blow to clavicle or FOOSH/arm
- much more common to fracture clavicle
- can be anterior or posterior
- posterior type holds higher risk of injury to other structures
- auto/allograft
- posterior type holds higher risk of injury to other structures

10
Q
acromioclavicular sprain/separation
A
- fall on tip of shoulder/acromion
- progressive disruption of ligaments
- AC ligament
- trapezoid
- conoid
- then by displacement
- 1-3 generally managed non-surgically
11
Q
glenohumeral subacromial “impingement”
A
- RTC of LHB repeatedly compressed with bursa
- potential causes
- RTC dysfunction
- scapular position
- acromion shape
- GH mobility deficit or hypermobility

12
Q
elbow joint
A
- modified hinge joint
- humeroulnar and proximal radioulnar and humeroradial
13
Q
humeroulnar joint
A
- hinge: roll and glide same – ulnar on humerus
- concave ulnar (trochlear notch)
- convex humerus (trochlea)

14
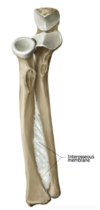
Q
proximal radioulnar joint
A
- ovoid joint: opposite roll and glide
- convex radial head
- concave ulna (radial notch)
- motions:
- pronation: radial head rolls anterior, glide posterior
- supination: radial head rolls posterior, glide anterior
15
Q
humeroradial joint
A
- hinge joint: roll and glide same directions for flexion and extension
- convex humerus capitulum
- concave head of radius

16
Q
distal radioulnar joint
A
- ovoid joint: roll and glide same
- convex head of ulnar
- concave radius (ulnar notch)
17
Q
radiocarpal/ulnocarpal joints
A
- ovoid: convex on concave, roll and glide opposite
- convex arm bone on concave

18
Q
midcarpal joint
A
- proximal surface of distal row
- convex ulnar compartment
- capitate and hamate
- radial compartment
- RD/UD: convex radial compartment
- trapezium and trapezoid
- flexion/extension: concave radial compartment
- dorsal/volar
- RD/UD: convex radial compartment

19
Q
first carpometacarpal joint
A
- sellar joint: R&G opposite palmar abd/add, R&G same radial abd/add
- distal trapezium
- convex radial/ulnar
- concave dorsal/volar
- proximal surface of 1st MC
- convex dorsal/volar – palmar abd/add
- concave radial/ulnar – radial abd/add

20
Q
thumb metacarpophalangeal
A
- condyloid
- capsule, volar plate, and collateral ligaments
- sesamoids

21
Q
interphalangeal joints (IP 1-5, thumb MP)
A
- true synovial hinge: roll and glide same for flexion and extension
- convex distal proximal phalanx
- concave proximal of distal phalanx
- PIP and DIP 2-5
- convex proximal, pull shaped
- bi-concave distal

22
Q
carpometacarpal joints 2&3 vs 4&5
A
- 2&3: interlocking articular surfaces prevent motion
- 4&5: opposite roll and glide
- slightly convex proximal MC surfaces
- slightly concave distsal surface hamate

23
Q
metacarpophalangeal 2-5
A
- ovoid: roll and glide same
- biconcave distal surface of metacarpals
- concave proximal surface of phalanges

24
Q
elbow capsule
A
- thin but strong
- does not respond well to injury or immobilization
- forms thick scar tissue resulting in flexion contractions

25
triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)
* components
* biconcave fibrocartilage disc
* palmar ulnocarpal ligament
* ulnar collateral ligament
* sometimes dorsal and volar radioulnar ligaments
* functionals
* major stabilizer DRUJ -- binds distal radius and ulna
* provides dual articular surface
* separates RU from RC joint
* cushion ulnar sided forces transmission

26
ulnar collateral ligament injury
* anterior band most commonly ruptured
* varied repair and reconstruction techniques

27
TFCC injury
* mechanism
* FOOSH
* extension with ulnar compression
* forced radial or ulnar deviation
* strong distraction force
* structures involved dictate symptoms
* disc injury from compression and sheer
* ligamentous attachment injury from distraction force or extreme radial deviation



