Tumors of Bone and Cartilage - Gupta Flashcards
What are the tumors of bone?
1) Osteoma
2) Osteoid osteoma/osteoblastoma
3) Osteosarcoma
What is an osteoma?
Benign bone forming tumor composed of compact or mature trabecular bone –> usually involves facial bones
What is the clinical presentation of a pt with osteoma?
1) Pain
2) Headache
3) Vision changes
Associated with Gardner syndrome (familial colorectal polyposis)
What is the microscopic appearance of an osteoma?
Dense compact bone with paucicellular stroma (see very few cells)

What is Gardner syndrome?
Autosomal dominant (chromosome 5q21 - APC gene) disease leading to multiple colon polyps and tumors in thyroid, bone, epidermoid cysts, fibromas, and desmoid tumors
What are desmoid tumors?
Tumors that grow in b/t muscle fibers and can cause obstruction –> surgical resection causes more tumors to form
What is osteoid osteoma?
Benign tumor of osteoblasts
What population are osteoid osteomas seen in?
Males < 25 years old
What is the clinical presentation of osteoid osteoma?
Bone pain that resolves with aspirin
What is the microscopic appearance of osteoid osteoma?
Randomly interconnected trabeculae of woven bone, prominently rimmed by a single cell layer of osteoblasts

Where do osteoid osteomas occur and what do they look like on imaging?
Cortex of long bones
Bony mass (<2cm) with radiolucent center (osteoid, black arrow) with surrounding sclerosis (white arrow)

How does osteoblastoma differ from osteoid osteoma?
Osteoblastoma usually larger (>2cm)
Bone pain doesn’t respond to aspirin
Arise in the vertebrae
What does osteoblastoma look like microscopically?
Comprised of anastomosing trabeculae of osteoid and woven bone rimmed by osteoblasts

How is osteoblastoma treated?
Curettage (scooping) or excision en bloc
What is osteosarcoma?
Malignant prolferation of osteoblasts
What is the epidemiology of osteosarcoma?
Mostly in teenage males
Associated with Pagets disease and post-radiation in elderly
Rb gene = increased risk and poor prognosis
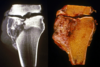
What characteristic feature does osteosarcoma show on imaging?
Codman’s triangle –> periosteol reaction to tumor destroying new bone before it ossifies
Indicates aggresive tumor

What does osteosarcoma look like microscopically?
Invades normal bone producing poorly formed bony spicules in a hypercellular matrix of osteoid and numerous pleomorphic malignant cells
Described as “lace-like” –> dainty little tumors

What is seen in chondroblastic osteosarcoma?
Malignant cartilage formation

What is the pathogenesis of osteosarcoma?
70% have acquired genetic mutation
Rb –> germline Rb 1000x increased risk
TP53 –> DNA repair and apoptosis
INK4a –> encodes tumor suppressor
MDM2 and CDK4 –> cell cycle regulators that inhibit p53 and Rb
What are the cartilage-forming tumors?
1) Chondroma
2) Osteochondroma
3) Chondrosarcoma
What is a chondroma?
What are the types of chondroma?
Benign cartilaginous tumor
1) Enchondroma –> arises from diaphyseal medullary cavity
2) Subperiosteal/juxtacortical
3) Soft tissue chondroma
What genetic mutations are associated with enchondromas?
IDH1 and IDH2 (isocitrate dehydrogenase)
What does a chondroma look like grossly?
Grey-white mass with color consistent with cartilage –> usually well circumscribed