Benign Tumors of the skin- Fisher Flashcards
Describe the appearance of Milia
Clustered, small epidermoid cysts

Where are milia commonly located?
cheeks, eyelids, forehead, genitals (because, derm)
What age group does milia most commonly present in? What is the course of disease?
Infants, they resolve spontaneously
Describe the appearance of a dermatofibroma? How do you distinguish it from a malignancy?
Classically a 3-10 mm papule on the distal lower extremity with excess pigmentation (red/brown); exhibits no keratosis, scaling, or translucent appearance

What is the pathogenesis of a dermatofibroma?
A proliferation of fibroblasts, often following a localized trauma (such as a bug bite)
Describe the appearance of a seborrheic keratosis
Oval in shape with a waxy, hyper-keratotic surface. Feels very rough on the surface and is brown in color
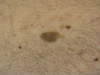
Which skin layer is a seborrheic keratosis located?
Epidermis
Seborrheic keratosis: benign or malignant?
Benign
What are seborrheic keratosis often confused with?
Melanomas; due to the deep brown pigmentation
Where on the body are seborrheic keratosis found? How do they organize there?
Commonly on the trunk (especially back); organize along skin tension lines in a “Christmas tree” formation
Patient presents with acute onset of multiple seborrheic keratosis. What do you do?
Immediately screen them for cancer; most commonly associated with colon cancer
What is the sign of Leser-Trelat
Sudden eruption of multiple seborrheic keratosis signifying underlying cancer; adenocarcinoma of colon, breast, stomach, and lung
Classic description of a seborrheic keratosis
round/oval, skin colored–> brown/black, slightly raised, “stuck on” papules; he said they look like you could “pick them right off the epidermis”

Someone presents with bright red papules on their trunk. What are they?
Cherry angiomas
Where are cherry angiomas commonly located? How old is the patient normally at presentation?
On the trunk; over 40 years

Difference between a hypertrophic scar and a keloid
Hypertrophic scar will not extend past the borders of the initial insult; keloids grow extensively outside of the borders
What is the risk of surgical excision of a keloid?
It will come back and most likely be worse
Who is at most risk for keloids?
African americans; equally affects men and women
Most common location for keloids?
Central chest
If you excise a keloid, what is done immediately post excision to reduce the chance of recurrence?
Corticosteroids are injected in the wound, inhibit fibroblasts
Describe an epidermal (epidermoid) cyst
A mobile dermal nodule with a central punctum

What is an epidermoid cyst filled with?
keratinaceous debris and sebum (cheesy appearing); smell awful when expressed
Where specifically do epidermoid cysts originate from?
The infundibulum of the hair follicle
What is a pilar cyst?
smooth, firm, dome-shaped, keratin-containing tumor



