Tumor pathology 5 MW + Flashcards
Disruption of normal regulatory genes
–Tumour-suppressor genes (anti-oncogenes)
•Normal growth-inhibiting genes
–Genes negatively regulating mitosis - Rb
–Genes regulating APOPTOSIS
–Genes regulating DNA repair
–PROTO-ONCOGENES
•Normal genes that promote normal cell growth and mitosis
What is the key event in tumour formation
Uncontrolled cell proliferation via cell cycle dysregulation through loss of tumour suppressor gene function
Retinoblastoma gene: an anti-oncogene
- Rb gene mutations favour cell proliferation
- Mutations in other genes controlling pRb phosphorylation mimic the effect of pRb loss:
–Mutational activation of cyclin D or CDK4
–Mutational inactivation of CDKIs also drive proliferation
Note: Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of cancer that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina, the light-detecting tissueof the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, and it is almost exclusively found in young children.[1]
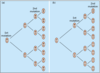
Sporadic vs inherited retinoblastomas
•“TWO-HIT HYPOTHESIS” of oncogenesis
–INHERITED FORM
- one defective inherited copy of pRb
- somatic point mutation of other copy
–SPORADIC FORM
•both hits occur in a single cell
loss/inactivation of both normal
allelic copies gives rise to cancer
Carcinogenesis
•Heredity
–accounts for 5-10% of all cancers
–Inherited cancer syndromes
–Familial cancers
–Autosomal recessive syndromes of defective DNA repair
Note: An autosomal recessive disorder means 2 copies of an abnormal gene must be present in order for the disease or trait to develop.
Inherited predisposition to cancer
Familial cancers
- family clustering of cancers but individual predisposition unclear
- multifactorial inheritance
- early age of onset
- multiple / bilateral tumours
- Some Breast cancers
- Some Ovarian cancers
- Non-FAP colon cancers
Proto-oncogenes
•Normal genes coding for normal proteins that regulate growth
–Growth factors
–Growth factor receptors
–Signal transduction
ONCOGENES
Cancer-causing genes
• Derived from proto-oncogenes
Activated by:
- Alteration of proto-oncogene structure
- point mutation
- chromosome rearrangements + translocations
- Dysregulation of proto-oncogene expression
- gene amplification
- overexpression
Oncogenes generate active ONCOPROTEIN products e.g?
–Growth Factors
–Growth Factor Receptors
–Proteins involved in Signal Transduction
–Nuclear Regulatory Proteins
–Cell Cycle Regulators
Viral carcinogenesis:
More than one mechanism
- virus genome inserts near a host proto-oncogene
- viral promoter or other transcription regulation elements cause proto-oncogene over-expression
- Retroviruses insert an oncogene into host DNA causing cell division
- DNA viruses known to cause cancer in humans
–HPV (cervical cancer)
–Hepatitis B (liver cancer)
–EBV (Burkitt lymphoma)
•
Chemical carcinogenesis
•Adduct formation at particular chromosome sites lead to activation of oncogenes and suppression of anti-oncogenes
Multistep caricnogenesis
- All sporadic cancers harbour multiple genetic aberrations (deviation from norm)
- Abnormalities accumulate with time
- Activation of several oncogenes and loss of 2 or more anti-oncogenes occurs in most cancers
Diagram