Drug delivery system mw % + Flashcards
Drug Formulation
- Formulated to allow selective targeting of a tissue site.
- To avoid pre- or systemic metabolism,
- To allow a 24 hour action
- Different drug formulations allow a treatment regime to be tailored to a patients needs, pharmacological characteristics and disease state.
What determines the drug delivery system we use
- The dosage
- The frequency of administration
- The timing of administration
Oral Medication types
- Solutions
- Suspensions
- Capsules,
- Tablets
- Modified release tablets.
Absorption of drugs Via the GI tract:
◦Buccal- above the tongue
◦Sublingual- underneath the tongue
◦Oral
◦Rectal
Solutions
- Young, elderly and patients with swallowing difficulties.
- May be given via a naso-gastric or PEG tube
- Drugs given in this way are absorbed extremely rapidly
- Absorption depends on gastric emptying and is most rapid from the small intestine

Suspensions
- Young, elderly and patients with swallowing difficulties
- May be given via a naso-gastric or PEG tube
- Absorbed extremely rapidly
- Dispersions of course drug particles in a liquid phase
- The dose can be contained in a small volume
- Good for drugs which are insoluble, unpalatable as they are better tolerated
Tablets and Capsules
Note: Dissolution or tablet break down is the rate limiting step in absorption.
Distinct advantages:
- Convenience
- Accuracy of dose
- Reproducibility
- Drug stability
- Ease of mass production
Enteric Coated Tablets
- Delays disintegration of the tablet until it reaches the small intestine.
- Tablets are enteric coated to:
◦Protect the drug from stomach acid e.g Omeprazole
◦Protect the stomach from the drug e.g Aspirin

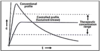
Prolonged or Delayed Release Formulations
- Most disorders required prolonged therapy
- Maintains drug levels within a therapeutic range
- Reduces the need for frequent dosing
- The time course for a drug in the body can be prolonged
- Ccontains more of the active drug but releases it more slowly over a prolonged period
Prodrugs
- Synthesised inactive derivatives of an active drug which requires to be metabolically activated after administration
- Prolongation of duration of action
- Avoids gut degradation of the drug
Buccal and Sublingual Administration
Ideal method for drugs which have extensive pre-systemic or first pass metabolism.
Forms of rectal Route
- Suppositories- solid dosage form that is inserted where it dissolves or melts
- Creams
- Liquids
Advantages of rectal route
- Useful in the young or old
- Patients unable to swallow
- Drugs may be administered rectally:
◦To treat local conditions such as proctitis
◦To achieve systemic absorption (indomethacin)
◦ Bypass pre-systemic metabolism
Vaginal Route
- Pessaries- a medical device
- Creams
- Useful in local disease

Injection based drug delivery system
- Provide fast systemic effects bypassing first-pass metabolism
- Drugs can be administered in unconscious or comatose patients
- Drugs having short half-life can be infused continuously

Intravenous Administration
Useful when:
- A rapid onset of action is required
- Careful control of plasma levels is required
- A drug has a short half-life

Intramuscular Injection
- The drug is given into the muscle mass
- May be insoluble or formulated in an oil base
- Allows a more sustained duration of action up to months
- Depot Injections contraceptive, neuroleptics
- May be painful

Subcutaneous Injection
- A common route of administration
- Easy to use and bypasses need for venous access
- Used for insulin, heparin and narcotic analgesics

Types of subcutaneous
- Dermojet- needleless injection used for mass inoculation (vaccination)
- Pellet implantation-drug as a solid pellet is implanted under the skin to provide uniform systemic effect .e.g.testosterone
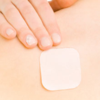
Transdermal Drug delivery system
- Adhesive patches containing the drug are applied on the skin
- The drug crosses the skin surface by diffusion by percutaneous absorption (through skin) and goes into systemic circulation
- Bypasses first-pass hepatic inactivation

Percutaneous
- Creams,ointments and skin patches
- Drugs can be administered to the skin to achieve a local effect i.e steroids or a systemic effect i.e HRT or nitroglycerin.
Skin Patches
- Allows the release of a drug from a reservoir into the skin and then into the systemic circulation.
- Possible to obtain controlled, sustained blood levels of the administered drug such as nicotine, nitroglycerin, opiates, HRT, contraception
Inhalation
- Used to deliver drugs directly to the lung for local effect or to achieve a systemic effect I.e anaesthetics
- Medication administered via a pressurised aerosol, breath actuated aerosol, nebuliser or dry powder device
Advantages and Disadvantages of inhalation?
Advantages
◦Drug delivered directly to site of action
◦Little systemic absorption (direct/specific)
◦Rapid effect
◦Small doses used
◦Reduced adverse effects
Disadvantages
◦Patient education is essential


