Transtibial Gait Deviations Flashcards
Foot too inset:
Forces being applied:
1.
2.
Moment at knee:
1.

Forces being applied:
1. Medial proximal
2. Lateral distal
Moment at knee:
1. Varus

Foot too outset:
Forces being applied:
1.
2.
Moment at knee:
1.

Forces being applied:
1. Lateral proximal
2. Medial distal
Moment at knee:
1. Valgus
Foot too posterior:
Forces being applied:
1.
2.
Moment at knee:
1.

Forces being applied:
1. Anterior distal
2. Posterior proximal
Moment at knee:
1. Flexion

Foot too anterior:
Forces being applied:
1.
2.
Moment at knee:
1.

Forces being applied:
1. Anterior proximal
2. Posterior distal
Moment at knee:
1. Extension

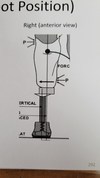
Standard bench alignment:
1.
2.
3.
4.
- 5-7 degrees flexion
- 5 degrees adduction
- Foot inset 1/2”
- Foot posterior 1-1 1/2” (inset foot to create varus moment at knee. Pre-flex socket to avoid knee hyperextension and create smooth rollover)
Why is varus moment desirable?
1.
2.
3.
- Energy efficient gait
- Minimize center of gravity
- Have a narrow base of support

Why is the socket pre-flexed?
1.
2.
3.
4.
- Prevent knee hyperextension
- Load anterior panel
- Match natural gait knee flexion during loading response
- Creates smooth rollover
Anterior distal pain:
1.
2.
3.
4.

- Foot too posterior
- Foot too dorsi-flexed (socket too flexed)
- Heel too firm
- Socket relief inadequate

Knee extension through midstance:
1.
2.
3.
4.

- Foot too anterior
- Foot too plantarflexed
- Heel too soft
- Insufficient socket flexion

Lateral trunk bending:
1.
2.
3.
4.

- Foot too outset
- Prosthesis too short or too long
- Pain in residual
- Habit

Heel whip:
1.
2.
- Hamstring relief inadequate
- Suspension issue
Lateral thrust, lateral gap:
1.
2.
- Foot too inset
- Socket M/L too big
Medial leaning pylon:
1.
2.
How do you adjust it to get to normal alignment?
Where are the pressures being applied in the socket?

- Foot too outset
- Socket adducted
You adjust the screws by loosening the lateral and tightening the medial.
Pressure areas are: proximal lateral and distal medial

Lateral leaning pylon:
1.
2.
How do you adjust it to get to normal alignment?
Where are the pressures being applied in the socket?

- Foot too inset
- Socket abducted
You adjust the screws by loosening the medial and tightening the lateral.
Pressure areas are: proximal medial and distal lateral

Drop off (stepping in a hole):
1.
2.
3.
- Foot too posterior
- Foot too dorsiflexed (excess socket flexion)
- Keel too short
Rapid knee flexion:
1.
2.
3.
4.
- Foot too posterior
- Foot too dorsiflexed (excess socket flexion)
- Heel too firm
- Weak quadriceps
Heel off too early:
1.
2.
3.
4.
- Foot too anterior
- Insufficient socket flexion
- Heel too soft
- Foot too plantarflexed



