The pituitary gland Flashcards
(35 cards)
What is a hormone?
A messenger carried from the organ where they are produced to the organ whcih they affect by means of the bloodstream
What is the difference between a peptide and a steroid (synthesis)
Peptide is synthesised as prohormones which required further processing (in inactive form)
Steroid is synthesised from cholestrol
What is the difference between a peptide and a steroid (storage)
Peptide it is stored in vesicles (regulatory secretion)
Steroid it is released immediately
What is the difference between a peptide and a steroid (receptors)
Peptide binds to receptors on cell membrane and transduce signal using 2nd messenger systems
Steroid bind to intracellular receptors to change gene expression regularly
Diagram of the pituitary

What are hypothalamic parvocellular neurons
Regulate anterior pituitary functions
Short, terminate on median eminence
Release hypothalamic factors into capillary plexus in median eminence
Hypothalamic regulatory factors carried by portal circulation to anterior pituitary

Diagram of anterior pituitary
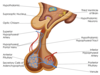
What are the steps of the hypothalamo-pituitary portal system
Axon terminals of hypothalamic neurosecretory cells release hormones
Travel through portal system through leaky blood vessels
Arrive in anterior pituitary hormones
Either release or inhibit from anterior pituitary
Hormones leave via blood
What are smatotrophns
Growth hormone (somatotrophin)
What are lactotophs
Prolactin
What are thyrotrophs
Thyroid stimulatin ghormone (TSH)/ thyrotrophin
What are gonadotrophs
Luteinising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
What are corticotrophs
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH or corticotrophin)
What hormone triggers the release of growth hormone
Growth hormone releasing hormone
(Inhibitory) somatostatin
What hormone triggers the inhibition of prolactin
Dopamine
What hormone triggers the release of thyroid stimulating hormone
Thyrotropin releasing hormone
What hormone triggers the release of LH and FSH
Gonadotrophin releasing hormone
What hormone triggers the release of ACTH
Corticotrophin releasing hormone
Main target cells of anterior pituitary hormones

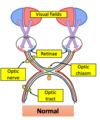
What is a bitemporal hemianopia
Peripheral vision is inhibited, cannot see outer view
Prevents sensory information from the lateral visual fields
How does the neuroendocrine reflex arc of mild production work
Mechanical stimulation of nipple and surrounding area affects afferent pathways
Inhibit dopmaine release in hypothalamus
Less dopamine in hypothalamic-pituitary portal means less inhibition of anterior pituitary lactotrophs
Increase plasma prolactin increase milk secretion
What are the mechanisms of growth hormone
Can travel to liver to stimulate liver to produce IGF-1 and IGF-2
Can travel straight towards body tissues
What is acromegaly
Excess growth hormone
Coarsening of facial features
Macroglossia
Prominent nose
Increase hand and feet
Sweatiness/headache
Why does acromegaly not affect height
Because the epiphyseal plates have already been fused which stops someone from growing




